![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
list the steps of the scientific method
|
1) state the problem
2) form a testable hypothesis 3) design an experiment 4) collect and analyze data 5) draw conclusions 6) share information |
|
|
define scientific method
|
the diverse ways in which scientists study the natural world and propose explanations based in the evidence they gather
|
|
|
define hypothesis
|
a prediction that can be tested
|
|
|
define law
|
a rule describing a consistent pattern in nature. It happens every time, all the time
|
|
|
define theory
|
a well tested explanation of something that occurs
|
|
|
liquid;liter as rock;
|
gram
|
|
|
what are the characteristics of a living organism?
|
1) cellular organization
2) reproduction 3) response to environment 4) growth and development 5) energy use 6) chemicals of life |
|
|
what are the five levels of organization?
|
cells
tissues organs organ systems organism |
|
|
what did Hooke do?
|
discovered "tiny rooms" in cork he called cells
|
|
|
Schleiden
|
determined all plants are made of cells
|
|
|
Schwann
|
determined all animals are made of cells thus all living things are made of cells
|
|
|
Virchow
|
determined that all cells come from other celss
|
|
|
what are the three parts of the cell theory
|
1) all living things are composed of cells
2) cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all living things 3) all cells are produced from other cells |
|
|
define homeostasis
|
the maintenance of stable internal conditions
|
|
|
what three things do animals rely on photosynthesis for
|
1) food
2) oxygen 3) removal of carbon dioxide |
|
|
photosynthesis equation
|
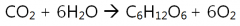
carbon dioxide + water > sugar + oxygen
^raw materials^ ^products^ |
|
|
define active transport
|
the movement of dissolved materials through a cell membrane using cellular energy
|
|
|
define passive transport
|
the movement of dissolved materials through a cell membrane without the use of cellular energy
|
|
|
list and describe the three stages of the cell cycle
|
1) Interphase- the cell grows and makes a copy of DNA
2) Mitosis- the stage during which the cell's nucleus divides into two new nuclei 3) Cytokinesis- the cell divides into two new daughter cells |
|
|
what is the function of the Endoplasmic Reticulum?
|
carries materials from one part of the cell to another
|
|
|
what is the function of the Nucleus?
|
directs all of the cell's activities
|
|
|
what is the function of the Mitochondria?
|
where most of the cell's energy is produced
|
|
|
what is the function of the Ribosome?
|
used to transport proteins throughout the cell
|
|
|
what is the function of the Cell Membrane?
|
protects the cell and regulates what substances enter and leave the cell
|
|
|
what is the function of the Cytoplasm?
|
gel-like fluid in which many organelles are found
|
|
|
what is the function of the vacuole?
|
stores water, food, waste products and other materials
|
|
|
what is the function of the Golgi Body?
|
receive materials from the ER and send them to other parts of the cell. can release materials outside of the cell
|
|
|
what is the function of the cell wall?
|
gives a plant cell its boxlike shape and provides protection
|
|
|
what is the function of Chloroplast?
|
capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell
|
|
|
list the four phases of mitosis in order
|
1) Prophase
2) Metaphase 3) Anaphase 4) Telophase |
|
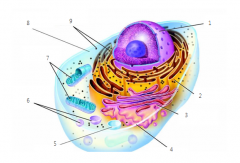
Label the parts of the animal cell
|
1) Nucleus
2) Endoplasmic Reticulum 3) Golgi Body 4) Cell Membrane 5) Vacuole 6) Lysosomes 7) Mitochondria 8) Cytoplasm |
|
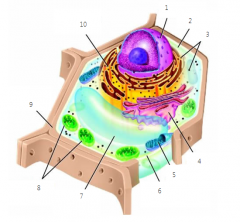
Label the parts of the plant cell
|
1) Nucleus
2) Cytoplasm 3) Ribosome 4) Golgi Body] 5) Mitochondria 6) Cell Membrane 7) Vacuole 8) Chloroplast 9) Cell Wall 10) Endoplasmic Reticulum |
|
|
define diffusion
|
the main method by which molecules move across the cell membrane and the the process by which molecules tend to move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
|
|
|
define osmosis
|
the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane
|
|
|
define phenotype
|
an organism's physical appearance
|
|
|
define genotyope
|
an organism's genetic makeup
|
|
|
define probability
|
a number that describes how likely it is that an event will occurr
|
|
|
define mutation
|
a change in gene or a chromosome
|
|
|
define allele
|
different forms of a gene
|
|
|
define dominant allele
|
the allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present
|
|
|
define recessive allele
|
the allele that is hidden whenever a dominant allele is present
|
|
|
what is a punnett square
|
a chart that shows all the possible outcomes of a genetic cross
|
|
|
what are the base pairs
|
Adenine & Thymine
Cytosine & Guanine |
|
|
BB , bb , and Bb refer to what vocabulary
|
BB- homozygous dominant (2 dominant alleles)
bb- homozygous recessive (2 recessive alleles) Bb- heterozygous (1 dominant & 1 recessive allele) |
|
|
define meiosis
|
the process where the chromosome pairs separate and are distributed to two new cells- the resulting cells have as many chromosomes as the original cell
|
|
|
amount of cells at the beginning and end of
1) Mitosis 2) Meiosis |
1) 46-46
2) 46-23 |

