![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
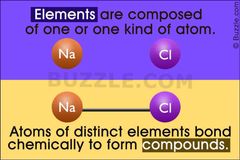
What is a difference between an element and an atom? |
Element is material made of only one kind of atom. Atom is a unit of an element. |
|
|
|
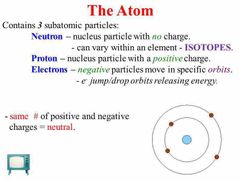
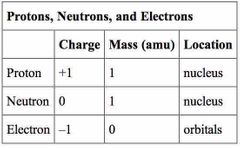
What are the three subatomic particles of an atom? |
Protons, neutrons, and electrons. |
|
|
|
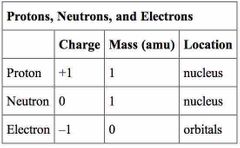
Where are protons, neutrons, and electrons located in the atom? |
Protons- nucleus Neutrons- shells Electrons- outside nucleus |
|
|
|
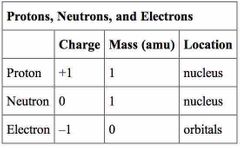
What is the relative charge of protons, neutrons, and electrons? |
Protons- +1 Electrons- -1 Neutrons- 0 |
|
|
|
What is the mass of protons, neutrons, and electrons? |
Protons- 1 Electrons- 0 Neutrons- 1 |
|
|
|
What is the difference between the atomic number and the atomic mass? |
Atomic number is the number of protons. The atomic mass is how much mass is in the atom. |
|
|
|
How can you determine the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons? |
Protons- atomic number Electrons- atomic number Neutrons- mass number |
|
|
|
Define isotope |
Atoms of the same element that contain the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. |
|
|
|
Identify the main characteristic differences between solids, liquids, and gases. |
Solid is rigid, has a fixed volume, and a fixed shape. Liquid is not rigid, has no fixed shape, has a fixed volume. Gas is not rigid, has no fixed volume, and no fixed shape. |

|
|
|
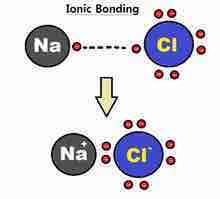
Determine the type of bond that holds a metal and a nonmetal together. |
Ionic |
|
|
|
Determine the type of bond that holds two nonmetals together. How do you name them? |
Covalent. 1-mono 2-di 3-tri 4-tetra |
|
|
|
Define ion |
An atom that has lost or gained electrons |
|
|
|
Identify a molecule as polar, nonpolar, or ionic. |
Polar is unequal sharing. Nonpolar is equal sharing. Ionic is metal and nonmetal. |

|
|
|
What does a “mole” refer to? |
6.02x10^23 used to measure numbers of atoms or molecules. |
|
|
|
What is the formula for molarity? |
Molarity=moles of solute/liter of solution |
|
|
|
Distinguish between solute and solvent. |
Solvent is the major component of a solution. Solute is the minor component of a solution. |
|
|
|
Contrast exothermic and endothermic reactions. |
Endothermic is the net release of energy. Endothermic is the net absorption of energy- more upon exit. |
|
|
|
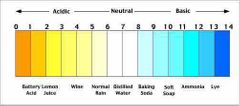
Contrast acids and bases. |
An acid donates hydrogen. A base accepts hydrogen. |
|
|
|
Where do strong/bases fall on the pH scale. |
More acidic is to the left. More basic is to the right. |
|
|
|
Identify and briefly describe the characteristics of living things. |
Use energy, develop and grow, maintain themselves, have he capacity to reproduce, parts of populations that evolve. |
|
|
|
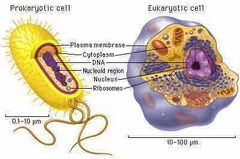
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells |
Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus and eukaryotic cells don’t. |
|
|
|
What does the cell theory refer to? |
All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells |
|
|
|
Describe the main characteristics of the cell membrane |
Defines a cells boundary. Controls what moves into and out of the cell. |
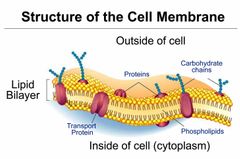
|
|
|
Explain diffusion. |
The tendency of molecules to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. |
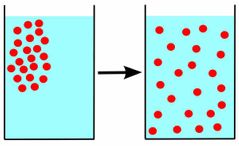
|
|
|
How do cells reproduce? |
Mitosis- one parent cell divides int two daughter cells that have the same genetic information as the parent cell. |
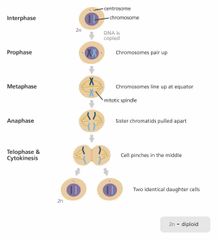
|
|
|
Describe prophase. |
Chromosomes condense and nuclear membranes break down. |
|
|
|
Describe metaphase. |
Chromosomes line up along the equatorial plane. |
|
|
|
Describe anaphase. |
Sister chromatids are pulled apart and move to opposite poles of the cell |
|
|
|
Describe telophase. |
New nuclear membranes form around each set of chromosomes |
|
|
|
How many daughter cells are made from the mother cell durning mitosis? |
Two daughter cells. They are identical. |
|
|
|
What is ATP? |
Provides energy for chemical reactions in cells. |
|
|
|
What are enzymes? How do they work? What factors influence their activity? |
Large complex proteins. Bonds the reactants at its active site and releases the products. PH, temp, and other features of the environment affect it. |
|
|
|
What organisms are capable of undergoing photosynthesis? |
Plants, algae, and bacteria. |
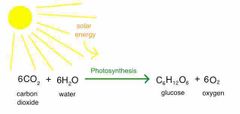
|
|
|
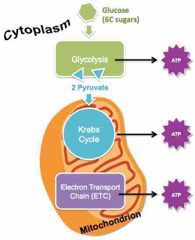
What organisms are capable of undergoing aerobic cellular respiration? |
All eukaryotic organisms. |
|
|
|
Define a gene. |
A section of DNA that controls the instructions for building a protein. |

|
|
|
Contrast genotype and phenotype. |
An organisms genes make up its genotype. The traits of an organism make up its phenotype. |
|
|
|
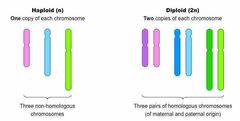
Define haploid and diploid. |
Haploid- only one of each kind of chromosome- sperm and egg Diploid- two of each kind of chromosome |
|
|
|
What is the typical human haploid chromosome number? |
46 |
|
|
|
What is the typical human diploid chromosome number? |
23 |
|
|
|
How many sex chromosomes are there typically in humans? |
2 X and Y |
|
|
|
How many autosomes are there typically in humans? |
44. All but sex chromosomes |
|
|
|
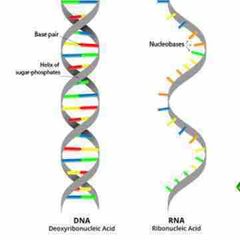
Provide a description of the composition and structure of DNA. How is RNA different? |
DNA is a double helix. RNA is single stranded. |
|
|
|
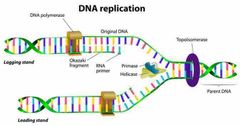
What happens during DNA replication? |
1. DNA strands are separated. 2. Each strand serves as a template. 3. Each new strand contains one new and one old. 4. Each new DNA is identical to the original. |
|
|
|
Be able to produce the complementary strand for a provided strand of DNA. |
A-T G-C |

|
|
|
Be able to transcribe a strand of DNA to build RNA. |
T-U G-C |
|
|
|
What is a codon? |
Set of three nucleotides are “read” from the mRNA occurs at ribosomes in the cytoplasm. |
|
|
|
What is a permanent change to the DNA sequence called? Are the always harmful? Wha kinda of things can cause such changes in the DNA? |
Mutation Not always harmful Errors during DNA replication or exposure to things that damage DNA. |
|
|
|
Describe the basic events of meiosis. |
One diploid cell divides into four haploid cells. They are all unique. |

|
|
|
Name two sources of genetic diversity during meiosis. |
1. Crossing over 2. Independent separation |
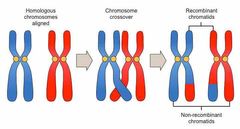
|
|
|
Do populations or individuals evolve? |
Populations |
|
|
|
What are the 8 evidences of evolution presented? |
Evolution of the whale blowhole Evolution and loss of whale hind legs Peppered moth Antibiotic resistant bacteria |
|

