![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
109 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Impasto Ware; 10th- 8th Century BCE; brown- black in color, handmade, not decorated, dull |
|

|
Bucchero Ware; 8th- 4th Century BCE; pure black in color, made on a wheel, very polished: shiny and reflective |
|

|
Campanian Ware; 4th-1st Century BCE; essentially lower quality Bucchero Ware e.g. shiny, but not as shiny as BW. |
|

|
Arretine Ware; 30BCE- 30CE; red in color, raised designs, stamp on bottom (terra sigillata) |
|
|
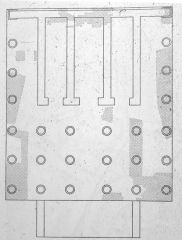
Plan of Temple of Jupiter Capitolinus; Rome; 509 BCE |
|

|
Sculpture of Apollo; Veii; ca. 500 BCE |
|

|
Temple of Portunus; Rome; ca. 75 BCE |
|

|
Capitolium; Ostia; ca. 120-130 CE |
|

|
San Ildefonso group from Gardens of Sallust, Rome (ca. 50-25 BCE) |
|

|
Head of Pompey the Great from Via Salaria, Rome (ca. 55-50 BCE) |
|

|
Bust of Julius Caesar; Egypt; ca. 44 BCE |
|

|
Census-taking relief, Altar of Domitius Ahenobarbus; Rome; late 2nd or early 1st century BCE |
|

|
Head of an old man; Osimo, Italy; mid 1st Century BCE |
|

|
Man with portrait busts of ancestors; Rome; Late 1st Century BCE |
|

|
Pseudo-Athlete; Delos, Greece; early 1st century BCE |
|

|
Denarius of Caesar; find spot unknown; 44 BCE |
|

|
sestertius with portraits of Octavian and Caesar; find spot unknown; ca. 37-31BCE |
|

|
Temple to Mars Ultor, Forum of Augustus; Rome; Dedicated 2 BCE |
|

|
Relief with Venus and Cupid, Mars, and Divus Julius; find spot unknown, now in Algiers; early 1st century CE |
|

|
Theater of Marcellus; Rome; 13 or 11 BCE |
|

|
Panel with Tellus, Altar of Augustan Peace; Campus Martius, Rome; dedicated 13-9 BCE |
|

|
panel with procession of imperial family, Altar of Augustan Peace; Campus Martius, Rome; 13-9 BCE |
|

|
Bust of Augustus wearing corona civica; find spot unknown; early 1st century CE |
|

|
Prima Porta statue; Villa of Livia at Primaporta; early 1st century CE |
|

|
Gemma Augustea; find spot unknown; ca.15 CE |
|

|
Head of Caligula; Marino, Italy; 37-41 CE |
|

|
Claudius as Jupiter; Lanuvium; 42-43 CE |
|

|
Head of Nero; Palatine Hill, Rome; ca. 59-64 CE |
|

|
Octagonal Hall; Domus Aurea, Rome; 64-68 CE |
|

|
Porta Maggiore; Rome; 50 CE |
|

|
Pyramid Tomb of Caius Cestius; Rome; 15 BCE |
|
|
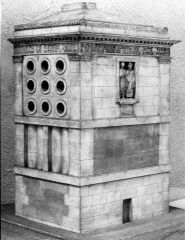
Tomb of Marcus Vergilius Eurysaces; Rome; late 1st century BCE |
|

|
Funerary relief of a midwife from tomb 100, Isola Sacra necropolis; Ostia; mid 2nd century CE |
|

|
Head of Vespasian; find spot unknown; (ca. 75-79) |
|

|
Arch of Titus; Rome (ca. 81 CE), |
|

|
Frieze from the Palazzo delle Cancelleria;, Rome (93-95 CE) |
|

|
Bust of a Flavian woman; Rome; ca. 90 CE |
|

|
Earthquake relief; House of L. Caecilius Iucundus, Pompeii; 62-70 CE |
|

|
basilica; Pompeii; 2nd century BCE |
|

|
caldarium of Forum Baths; Pompeii; 80-70 BCE |
|

|
riot fresco; House I,3,23, Pompeii; 60-79 CE |
|

|
atrium from House of Silver Wedding; Pompeii; mid 2nd cent. BCE |
|

|
peristyle in House of Vetii; Pompeii; rebuilt ca. 50-79 CE |
|

|
Neptune and Amphitrite mosaic from House of Neptune and Amphitrite; Herculaneum; ca. 62-79 |
|

|
Alexander Mosaic from the House of the Faun; Pompeii; late 2nd or early 1st cent. BCE |
|

|
fresco from Samnite House; Herculaneum; late 2nd cent. BCE |
|

|
fresco from cubiculum M; villa at Boscoreale; ca. 50-40 BCE |
|

|
fresco from the Black Room; the villa at Boscotrecase; ca. 10 BCE |
|

|
fresco from Pentheus Room in the House of the Vettii; Pompeii; ca. 62-79 CE |
|

|
Copy of Doryphoros (Spear-Bearer) head made by Apollonios of Athens based on original by Polykleitos in the Villa of the Papyri; Herculaneum; 1st cent. CE
|
|
|
surface survey |
used to gather facts before an excavation, two forms: Systematic and Unsystematic. |
|
|
aerial photography |
pictures taken from airplanes before excavation that can help identify sites through earthworks, soil marks, and crop marks |
|
|
magnetometry |
measuring and mapping patterns of magnetism in the soil; some ancient activities esp. burnt things leave magnetic traces. |
|
|
experimental archaeology |
the study of past cultures through experimental reconstructions under carefully controlled scientific conditions |
|
|
context |
the way in which an artifact is found focusing on the immediate matrix, provenience, and association with other artifacts |
|
|
stratigraphy |
the concept that an undisturbed site will have different sedimentary layers in which the highest are the most recent and the deepest are the oldest |
|
|
stratum/strata |
A stratigraphic layers which contain material culture from the same time period |
|
|
Law of Superposition |
Relative dates; higher strata are more recent while deeper strata are older. |
|
|
Law of Association |
Absolute dates; if an artifact can be dated then that date can be applied to the entire strata |
|
|
Radio- Carbon (C14) dating |
A method of dating organic material through the half-life of carbon. Generates a very broad date range. |
|
|
Tarquinius Superbus |
The last king to rule Rome, Etruscan, built the Temple of Jupiter Capitolinus (509 BCE) |
|
|
Jupiter |
King of the gods, god of the sky and heavens; Greek equivalent: Zeus |
|
|
Juno |
Queen of the Goddesses, goddess of marriage, married to Zeus, Greek equivalent: Hera |
|
|
Minerva |
Daughter of Zeus, goddess of wit, craft, and battle strategy, Greek equivalent: Athena |
|
|
aes signatum |
ca. 300 BCE; lit. trans. "stamped bronze"; large, brick-like; break off pieces as currency |
|
|
aes grave |
ca. 3rd cent. BCE; lit. trans. "heavy bronze"; cast; used as small change |
|
|
denarius |
begin 289 BCE; struck; silver, size of a dime, faces of gods (republic) |
|
|
patricians |
wealthy Roman citizens |
|
|
plebians |
working middle/lower class Roman citizens |
|
|
castrum |
Roman military camp |
|
|
patrician art |
heavy Greek influence to demonstrate knowledge |
|
|
plebeian art |
tells a story; verism (true nature i.e. wrinkles); unnatural proportions to show significance |
|
|
patron-client system |
a mutually beneficial business relationship between Patricians and Plebeians |
|
|
Julius Caesar |
voted dictator for life; killed by the senate |
|
|
ideology |
the knowledge or beliefs used by human societies to understand and cope with their existence; evolves over time |
|
|
Octavian/ Augustus Caesar |
first Roman emperor; nephew of Julius Caesar; before 27 referred to as Octavian, after referred to as Augustus |
|
|
princeps |
title given to Augustus; "first emperor" |
|
|
Battle of Actium |
31 BCE; final battle between Octavian and Mark Antony |
|
|
Pax Augusta |
the time of peace under Augustus' rule |
|
|
pyroclastic flow |
lava, rock, etc. from volcanic eruption; travels 50-100 mph |
|
|
frigidarium |
cold water area of bath house |
|
|
tepidarium |
luke-warm water section of bath house |
|
|
caldarium |
hot water section of bath house |
|
|
Vesuvius |
Volcano in Italy; destroyed Pompeii and Herculaneum |
|
|
Pliny the younger |
wrote about the eruption |
|
|
thermopolium |
essentially a fast-food restraunt in antiquity |
|
|
impluvium |
a pool that captured rainwater from an opening in the roof |
|
|
triclinium |
formal dining room |
|
|
peristyle |
an open courtyard enclosed by a colonnade |
|
|
Romulus and Remus |
753 BCE; founding myth of Rome; twin brothers; descendants of Aeneas, sons of Rhea Silvia; suckled by she-wolf (lupa); fight over which hill to build the city on; Remus dies; Romulus builds Rome on the Palatine Hill |
|
|
Cardo |
Main street in a Castrum (Roman military camp); oriented north-south |
|
|
Decumanus |
West-east oriented road in a Castrum (Roman military camp) |
|
|
Contrapposto |
art style in which a figure is depicted with most of their weight on one leg (the engaged leg) creating an asymmetrical balance and curve to the figure. |
|
|
Pompey the Great |
d. 48 BCE; military leader and politician during the fall of the Roman Republic; lost the civil war to Julius Caesar |
|
|
Principate |
the rule of the early Roman emperors, under which some of the outward forms of the Republic were maintained |
|
|
Cleopatra |
d. 30 BCE; ally and lover to Julius Caesar; Allied with and became a lover to Antony in the war following Caesar's death |
|
|
Mark Antony |
d. 30 BCE; supporter and loyal friend of Julius Caesar; after Caesar's death allied with Cleopatra against Octavian for control of Rome; Last major battle was the battle of Actium; committed suicide in 30 BCE when Octavian invaded Egypt |
|
|
tria nomina |
"three names" way a Roman could indicate he had citizenship |
|
|
Tiberius |
14-37 CE; Augustus' adopted son; toward the end of his reign he was a tyrannical recluse; had the Gemma Augustea carved |
|
|
Caligula |
37- 41 CE; restored treason trials and put many people to death |
|
|
Claudius |
41-54 CE; conquered the British; killed by wife; named Nero heir |
|
|
Nero |
54-68 CE; fire in Rome 64 CE burned 6 days; insane; murderous and paranoid; committed suicide after the senate declared him a public enemy |
|
|
insula |
Roman apartments |
|
|
columbarium |
underground chamber, used for preserving the ashes of the dead |
|
|
Southern Gaulish Terra Sigilatta |
1st 3rd of 1st cent. to end 1st cent. CE; vivid red; mirror-like shine; |
|
|
vomitorium |
the passage that led out of a theater or amphitheater to the street |
|
|
Civil War (69 CE) |
With Nero dead and no successors left the throne was up for grabs; Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian claimed the empire; Vespasian won |
|
|
Vespasian |
69-79 CE; brought stability to the empire and military after the war
|
|
|
Titus |
79-81 CE; |

