![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What happens to the 5' and 3' ends of mRNA after transcription?
|
1) The 5' end is capped very soon after the start of transcription.
2) The 3' end is poly-adenylated at the end of transcription. |
|
|
|
What are the 3 modifications made to mRNA when the 5' end is capped? Describe them and draw it.
|
1) 7-methylguanosine is added to the 5' end of the mRNA.
2) The first two bases are methylated at the 2' position (to make ethers). 3) There is three phosphates between the 7-methylguanosine and the first base. |
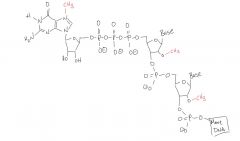
|
|
|
1) Where is the mRNA polyadenylated?
2) Where do the "As" come from? |
1) An endonuclease cleaves about 10-25 nucleotides after the recognition site, then the poly-A tail is added.
2) The adenines come from ATP. |
|
|
|
What are snRNPs? What do they do?
|
Small Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein Particles.
They are RNA-protein complexes that catalyze splicing. |
|
|
|
What are the 5 snRNPs involved in splicing?
What does each one do? |
U1: Binds 5' splice junction (its snRNA is complemetary to the 5' splice site).
U2: Binds branch point U4/U6: binds the 5' splice junction U5: Aligns the 2 exons working with U4 and U6 |
|
|
|
Regarding snRNPs, which 3 steps require ATP?
|
U2 binding the branch point
U4/U6 binding the 5' splice junction U1/U4 disassociation, allowing U6 to move closer to U2 and create the lariat. |
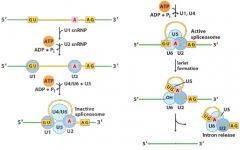
|
|
|
What is rRNA? What does it do?
|
Ribosomal RNA. Components of ribosomal complexes, some of which catalyze translation.
|
|
|
|
What are the two important bacterial ribosomes to remember?
|
30S & 50S
|
|
|
|
In bacteria, which rRNAs make up each of the two ribosomes?
|
16S rRNA becomes part of the 30S ribosome.
23S & 5S become part of the 50S ribosome. |
|
|
|
What are the two important eukaryotic ribosomes to remember?
|
40S and 60S
|
|
|
|
In eukaryotes, which rRNAs make up each of the two ribosomes?
|
18S rRNA becomes part of the 40S ribosome
28S, 5.8S and 5S rRNA become part of the 60S ribosome. |
|
|
|
Describe tRNA? What does it do?
|
Transfer RNA. It's small (~80nt). It's secondary structure is a cloverleaf.
It brings amino acids to the ribosome for translation. |
|
|
|
What are the two non-standard tRNA bases?
|
Pseudouridine & dihydrouridine. They are both pyrimidines.
|
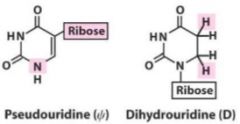
|
|
|
In E. coli, what does RNase P endonuclease do?
|
Cleaves the 5'end of tRNA and adds CCA at the 3'end.
|
|
|
|
In E. coli, what does tRNA nucleotidyl transferase do?
|
If the 3'end of tRNA is damaged, RNase P endonuclease can't add the CCA on the 3' end. tRNA nucleotidyl transferase does this instead.
|
|

