![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
DMARDs |
Azathioprine Methotrexate Infliximab |
|
|
SLE treatment |
Moderate: NSAIDs, CS (topic for rash) +- hydroxychloroquine Severe:Immunosuppressants: mycophenolate, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, methotrexate Steroids |
|
|
Secondary vasculitis |

|
|
|
Diseases that mimic vasculitis |
DIC Beurger's disease GoodPasture Cholesterol emboli syndrome Bacterial endocarditis Amyloidosis Paraneoplasic syndrome |
|
|
Polymyalgia rheumatica |
High association with giant cell temporal arteritis in elderly Muscle pain and stiffness in proximal mm of the shoulder girdle and C and L spine No muscle weakness or wasting Symmetric and systemic symptoms
Temporal biopsy shows GCA |
|
|
Kawasaki disease clinical features |
CRASH and burn
Conjunctivitis Rash Adenopathy (cervical) Strawberry tongue Hand (palmar erythema + finger desquamation)
Burn = fever Atypical disease : coronary arteries aneurysms |
|
|
Complication of kawasaki |
Coronary artery aneurysm and rupture or Myocardial infarction |
|
|
Systemic vasculitis |
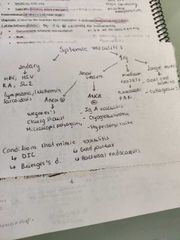
|
|
|
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies associated with |
HLA-b27 |
|
|
Why are they called seronegative? |
Rheumatoid factor negative |
|
|
Reactive arthritis - post GUT infection triad |
Conjunctivitis Oligoarthritis Urethritis |
|
|
Specific for genittourinary reactive arthritis |
Keratoderma blenorrhagica Circinate balanitis |
|
|
Treatment of gout |
Acute: pain control - self-limited NSAIDS (indomethacin), ice ,rest Colchicine CS
Chronic: Allopurinol - decreases uric acid production Probenecid - increases uric acid excretion |
|
|
Pseudogout |
Calcium pyrophosphate dehydrate |
|
|
Etiology of pseudogout |
1ry: idiopathic -elderly 2ry: hyperparathyroidism, hemochromatosis - suspect in young patient (<40 y.o.) |
|
|
Pseudogout |
Elderly patients Or younger patients if secondary (hemochromatosis, hyperparathyroidism) Affects large joints- knee, wrist, polyarticular (may resemble RA) 50%= chondrocalcinosis - calcification of the cartilage |
|
|
ESR |

Males: 0-22 mm/hr Females: 0-29 mm/hr |
|
|
Importance of ESR |
There has been some question about ESR usefulness but this is very important in ruling out giant giant cell arteritis Can also be used to monitor treatment of GCA, PRM and systemic vasculitis Isolated or very high ESR indicates possible rheumatic diseases (SLE, RA) and flares in pts with underlying rheumatic disease |
|
|
Glucocorticoids |
Short acting: hydrocortisone, cortisone Medium acting : prednisolone, Prednisone Long acting: betamethasone, dexamethasone |
|
|
Which glucocorticoid is used in pulse therapy? |
Methylprednisolone
|
|
|
Corticosteroids |
- glucocorticoids - mineralocorticoids |
|
|
Mineralocorticoids |
Synthetic: fludrocortisone Used in aldosterone deficiency |
|
|
Methylprednisolone uses |
RPGN Graft rejection Anaphylaxis |
|
|
NSAIDS |
Aspirin Ibuprofen Diclofenac Indomethacin |
|
|
Osteoporosis vs osteomalacia |
Decrease in bone mineral density (de a scan with T score >> - 2.5 (between - 1 and - 1.5 = osteomalacia) Osteoporosis = decrease in bone density Osteomalacia/rickets = problem in bone mineralization |
|
|
Osteoporosis |

|
|
|
2ndary osteoporosis |

|
|
|
Treatment of osteoporosis |
Non-pharmacological: supplements or diet rich in calcium and vitamin D Stop smoking and drinking alcohol Pharmacological: -biphosphonates (alendronate) (1st line) - calcitonin SERM: raloxifene (selective estrogen receptor modulators) acts as HRT HRT |
|
|
Labs in Paget disease |

|
|
|
Management of Paget disease |
Supportive with NSAiDs Treat if ALP very elevated: biphosphonates 2nd line calcitonin |

