![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
148 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Define synovial joint |
joint found between bones that move against each other, with a sepcialised cell layer that secretes synovial fluid into a cavity (synovial membrane) . Other features include a fibrocartilage meniscus/ articular disk or bursa |
|
|
|
Types of synovial joints and examples ? |
Pivot : C1 and C2 HInge : elbow Saddle : trapezoid and 1st metacarpal Condyloid :radius and carpal |
|
|
|
What is arthritis ? |
Inflammation of synovial joints , causing some swelling , pain and reduced mobility. |
|
|
|
Risk factors for arthritis ? |
Female family Hx Obesity previous fracture of the joint Congenital joint dysplasia pre-existing joint damage occupation : labourer or excessive use |
|
|
|
Investigations and what they indicate ? |
Bloods : FBC : ACD microcytic picture ESR and CPR (raised in inflammatory RA) Anti-CCP (raised in RA) ANCA Rheumatoid factor : can be positive RA Order X-rays Can do urine tests for suspected viral cause , Gout synovial stain/ histology can show gout |
|
|
|
Symtpoms of OA ? |
painful , stiff joints , might have swelling affects larger, weight bearing joint like the hip and knee and smaller hand joints like DIP not usually symetrical older age onset might make grating or crackling sound not inflammatory morning stiffness not significant |
|
|
|
What does X-ray show in OA ? |
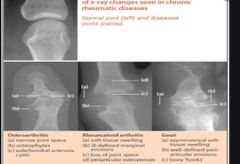
L- loss of joint space O - osteophyte formation S- subchondral sclerosis S - sunchondral cysts
|
LOSS |
|
|
Interventions for OA? |
Non- pharma : education ,lifestyle advice eg weight loss , knee stregthening exercises, heat/ice , supportive footwear, walking aids Pharma: analgesic ladder, intra-articular injections , dihydrocodeine increases risk of falls and constipation . do not use in renal failure final option is arthroplasty |
|
|
|
Conditions for arthroplasty ? |
Any age (60-80) for whom steroid injections and analgesia failed pain severly impacts QOL and sleep depressed , no sociallife / job cannot carry out basic tasks such as shopping |
|
|
|
Contraindications for arthroplasty ? |
Active joint infection Systemic infection Osteomyelitis severe paralysis of muscle neuropathic joint BMI>45 risks : infection, clots, malfunction of prosthesis, nerve injury . |
|
|
|
X-ray changes in RA ? |
L- loss of joint space I- ill defined margins P - peri articular osteoporosis S- soft tissue swelling S- sublaxation |
LIPSS |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of RA ? |
morning stiffness that lasts over an hour inflammation : red , warm , swelling polyarthritic fever ,fatigie , loss of appetite can have extra-articular effects such as dry eyes and breathing difficulties |
|
|
|
American college of rheumatology criteria for RA ? |
morning stffness lasting over an hour 3+ joints for more than 6 weeks Affects hand joints , DIP sparing symmetrical presence rheumatoid nodules ( rubbery , on elbows) serum rheumatoid factor positive Radiographic changes need 4 out 7 |
|
|
|
immunopathology of RA ? |
Aggregates of T-cells, plasma cells and macrophages in the synovial membrane. Neutrophils in the synovial fluid with pro and anti-inflammatories (IL-10 is Anti) interaction between anti-inflammatories and immune cells cells generate joint damage. |
|
|
|
genetic components of RA? |
HLA-DR4 and DR1 increased risk . some parts of Africa not impacted . |
|
|
|
what does histology of RA show ? |
biopsy of synovial membrane shows villous folds with compact nodular clusters of lymphocytes |
|
|
|
hand signs in RA ? |
swan neck deformity ( sublaxtion of tendon so form a dip at the PIP) Buttoniere deformity Z-thumb feature Ulnar deviation |
|
|
|
list some extra-articular changes of RA ? |
rheumatoid nodules ( elbow , sacrum) rubbery(thought to be small vessel vasculitis) nail fold infarcts / splinter haemorhhages venous ulcers lung pleural thickiening and effusions pulmonary nodules pulmonary fibrosing alveolitis ( methotrexate also causes this ) thenar wasting - median nerve carpal tunnel syndrome pericarditis , IHD (endothelial dysfuncytion) renal : glomerulonephritis (NSAIDs) ocular : secondary SJorens , scleritis
|
|
|
|
pulmonary fibrosis : identify and diagnose ? Tx? |
breathlessness , fine crackles. HRCT shows honeycombing . Give steroids |
|
|
|
manage of RA ? |
education analgesia (paracetamol) anti-inflammatories (NSAIDS - naproxen) steroids DMARDs ( methotrexate , gold) biological therapies - anti-TNF (infliximab) which works by monoclonal antibodies to target cytokines or cells |
|
|
|
pathogenesis and risk factors for gout ? |
too much uric acid which forms Sodium Urate crystals lots of cell breakdown eg in the TX of lymphoma, polycythemia vera ( and other myeloproliferative disease) or under-excretion : CKD, thiazide diuretics (Indapamide), alcohol, family Hx , diet high purines (alcohol, meat) |
|
|
|
Tx for gout ? |
diet, weight loss, less alcohol NSAIDs (naproxen) colchicine (2nd line) intra-articular injections (steroids) or oral prednisalone (3rd line) Allopurinol ( in recurrent and frequent) as prophylaxis vit C may be preventative |
|
|
|
pseudogout ? |
CCPD ( calcium pyrophosphate crystals - knees and wrists) precipitaed by illness , or hereditary skin is red/purple, swollen , very acute, tender risks : elderly , thyroid issues , kidney failures, calcium/ iron metabolism disorders. need to analyse synovial fluid under microscope. Tx: NSAIDS , coritcosteroids, ) |
|
|
|
Fibromyalgia ? |
several joints impacted ( tender points , pain when nail-blanching pressure is apllied ) . More tha n 11 tender points , middle aged , painful joints , severe fatigue , poor memory, poor sleep polymyalgia is inflammatory , dont confuse ! |
|
|
|
typical rheumatoid presentation |
female 2:1 ration , prevalence 30-50 , insidious onset , impacts both hands . Morning stiffness. outcomes better if treated earlier . |
|
|
|
haematological maifestations of RA ? |
lymphadenopathy Felty's syndrome anaemia thrombocytosis |
|
|
|
CV changes in RA |
pericarditis , pericardial effusion , Rynauds syndrome , accelerated ischameic heart diseased |
|
|
|
Bone manifestations of RA ? |
osteoporosis |
|
|
|
eye manifestations of RA ? |
dry eyes , scleritis , scleromalacia preforans |
|
|
|
anaemia of chronic disease ? |
normocytic |
|
|
|
Non-pharmacological approaches to RA tx ? |
regular exercise, hand exercises , OT , physio healthy diet and weight loss smoking cessation sulfalazine safe forpregnant women if they take folic acid. |
|
|
|
Side effects of Methotrexate and monitoring required ? |
nausea , Mouth ulcers, diarrhoea, liver fibrosis, pulmonary fibrosis, renal impairment . Check FBC, U+E , LFT every 2 weeks for 6 weeks, then monthly for 3 months. not safe for pregnancy |
|
|
|
How is gout diagnosed ? |
clinical picture usually diagnostic hyperuricaemia - UA levels may drop during attack Joint aspiration and microscopy - gram stain culture to rule out septic arthritis . long thin needle crystals X-ray : soft tissue swelling |
|
|
|
How does allopurinol work ? |
Xanthine oxidase inhibited to decrease serum urate levels Dont start it 1 month within acute attack |
enzyme |
|
|
some differences between gout and pseudogout ? |
gout = males pseudogout = more females gout = sodium urate pseudogout= Calcium pyrophosphate gout= MTP psuedogout = wrist and knee gout = needle-shape -ive befringment pseudo = rhomboid, +ive X- ray punched out lesion vs chondrocalcinosis (deposits on articular cartilage) |
|
|
|
What is a spondyloarthropathy |
chronic related arthropathies defined by three features : inflammatory back pain <50 , worse with rest sacroiliitis : erosion of joint margins , fusion of SI joints Enthesitis |
|
|
|
what is inflammatory back pain |
patients under 50 should raise suspicion chronic worse after rest morning stiffness buttock pain |
|
|
|
what is sacroiliitis? |
X-rays show erosion of joint margins fusion of SI joints (4= total joint ankylosis) |
|
|
|
What is Enthesitis/ Enthesopathy? |
inflammation of site of insertion of tendon or ligament of bone eg Achilles tendon ASIS |
|
|
|
what is a seronegative condition ? |
rheumatoid factor negative butwith familial clustering due to HLA B27 association |
|
|
|
features of spondyloarthropathies : |
inflammatory back pain stiffness asymmetrical involvement of large peripheral joints oligoarthritis = <5 joints dactylitis = inflammation of entire digit extra-articular manifestations |
|
|
|
examples of extraarticular manifestations: |
ocular : uveitis, episcleritis skin lesions - psoriasis oral ulcers |
|
|
|
what is ankylosing spondylitis ? |
chronic inflammatory disease of the spine and sacroiliac joints , young adults <30 progressive loss of spinal movement , gradual onset better after exercise and end of day morning stiffness pain radiates to sacroiliac joints pain at night , wakes them up in morning thoracic expansion fatigue , weight loss, peripheral synovitis later presentation : loss of lumbar lordosis ,increased kyphosis
|
|
|
|
Diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis requires : |
> 3 months Hx of inflammatory spine pain with : buttock pain or sacroiliitis on XR, enthesitis , family Hx, psoriasis , IBD, urethritis 1 month before onset |
|
|
|
extra articular features of ankylosing spondylitis ? |
iritis achilles tendonitis plantar fasciitis ( enthesitis) microscopic colitis aortitis , aortic regurg apical pulmonary fibrosis secondary amyloidosis (amyloid builds up on organs ) |
|
|
|
What are vertebral syndesmophytes ? |
typically T11-L1 bony proliferations due to enthitis between ligaments and vertebrae fuse with vertebral body above calicification of ligaments results in bamboo spine |
|
|
|
exam findings for ankylosing spondylitis ? |
loss of lumbar spine movement loss of lumbar lordosis exacerbated thoracic kyphosis schober test +ive decreased chest expansion |
|
|
|
what is schober test ? |
make a mark 5 cm below PSIS and 10 cm above , at midline ask patient to touch toes the line should increase length (>20cm) reduced range indicates ankylosing spondylitis |
|
|
|
Investigations to do? |
bloods : raised : ESR, CRP IgA ALP HLA B27+ normocytic anaemai (ACD) images : MRI , X-ray of SI joints isotope bone scans show enhancement USS shows enthesitis |
|
|
|
X-rays in AS show : |
sacroiliitis squaring of vertebraes ligament calcification bamboo spine appearance joint ossification syndesmophyte formation |
|
|
|
non-pharma management of ankylosing spondylitis: |
exercise not rest ! physio hydrotherapy occupational therapy |
|
|
|
pharma management of Ankylosing spondylitis ? |
NSAIDs DMARDS (disease modifying anti-rhuematic drugs) e. g methotrexate , sulfasazine - peripheral arthritis , not spine Anti-TNF (infliximab) - biological agents Bisphosphonates (risk of osteoporotic spinal fractures secukinumab bind IL-17A
|
|
|
|
what is enteropathic arthritis ? |
arthritis with UC or Crohns 2 main presentations Often improves with Tx of bowel symptoms Tx is DMARDs and anti-TNF |
|
|
|
what are the 2 main presentations of eneteropathic arthritis? |
correlating with activity of bowel disease = acute peripheral arthritis of large joints not correlating with activity of bowel disease =sacroiliitis and spondylitis (clinically identical to AS ) must have US or Crohns |
|
|
|
5 types of psoriatic arthritis |
more association with palmo-plantar pustular psoriasis 1) oligoarticular assymetrical large joint 2) polyarticular symmetric arthtiris (affects DIPS, unlike RA) 3) spondyloarthritis / sacroiliitis 4) distal interphalangealpredominant 5) arthritis mutilans - extensive erosion , telescopic digits - small bones hands feet |
|
|
|
reactive arthritis ? |
immunological phenomenon in which sterile inflammatory arthritis occurs following infection in another site ( gut , genitourinary) lasts 2-6 weeks infections include : salmonella , shigella , chlamydia |
|
|
|
presentation of reactive arthritis ? |
lower limb oligoarthritis inflammatory lower back pain and buttock pain fever and blennorrhagica common classid triad = conjunctivitis , urethritis/cervicitis and arthritis ( cant see , cant pee cant climb a tree) |
|
|
|
investigations for reactive arthritis ? |
stool culture for HX of GUT infection full GUM sti screen routine bloods (ESR, CRP, RhF/ ANA) joint aspiration to rule out septic arthritis X-ray of SI joint |
|
|
|
Tx of reactive arthritis ? |
usually self limiting Tx of underlying infection NSAIDs and intra-articular steroids chronic course requires DMARDs |
|
|
|
what are some connective tissue diseases? |
group of autoimmune, syetmic, rheumatic diseases which present with symptoms involving many systems SLE Scleroderma myositis/ dermatomyosisits Sjogrens syndrome mixed connective tissue disease |
|
|
|
what is SLE ? |
commonest autoimmune inflammatory multi-sytem disease pathogenic auto antibodies resulting in immune complex formation and compliment mediated tissue damage charecterised by remissions and relapses variable course and prognosis more common in women and Afro-carribeans |
|
|
|
general features of sle ? |
fatigue fever lymphadenopathy weight loss myalgia - rarely myositis arthritis - arthraligia , symmetrical, non-erosive nodules possible (same as RA joints) Jacoubs arthropathy - reducible defomrities skin rashes - photosensitivity butterfly rash , discoid rashes |
|
|
|
rashes in SLE? |
photosensitive butterfly discoid vasculitic rashes - feet and fingers - erythema under the nail bed |
|
|
|
more SLE signs ? |
RAynauds phenomenon livedo reticularis alopecia diffuse or patchy |
|
|
|
what is livedo reticularis ? |
'fishnet' rash , purple/ brown antibodies to phospholipid - higher risk of blood clots can occur in vasculitis |
|
|
|
SLE mucous membrane signs ? |
ulcers - mouth nose , genital genitsl ulcers more common in Bechets |
|
|
|
what are sicca symptoms ? |
dryness of mouth ! with lupus / RA= secondary sjogrens syndrome , dry eyes and mouth |
|
|
|
pulmonary symptoms of lupus ? |
pleurisy is commonest (pleuritic chest pain due to inflamed pleura) consider PE (especially in those with phospholipid antibodies) consider infection also : pulmonary hypertension pneumonitis and fibrosis with diffuse involvement |
|
|
|
cardiac manifestations of SLE? |
pericarditis , myocarditis Libman-Sacks endocarditis - release of vegitations - stroke coronary artery disease (premature) |
|
|
|
abdominal symtpoms of SLE? |
if vasculitis affects intra-abdo organs , can present with anorexia, nasusea , malabsorption kidney - check urine for proteinuria as this is asymptomatic , eGFr may be reduced or raised serum creatinine (after 50% glomeruli damaged) |
|
|
|
neuro syndromes in SLE? |
cerebrovascular disease (stroke secondary to vascultis or premature atheresclerosis) seizure disorder / psychosis (rare) chorea - movement disorder cognitive dysfunction mononeuropathy ( glove/stocking) , carpal tunnel secondary to vasculitis polyneurotpathy |
|
|
|
reproductive features of SLE? |
recurrent miscarriages feta growth restrcitions - baby may develop neonatal lupus syndrome neonatal lups syndrome congenital heart block premature menopause |
|
|
|
what is antiphospholipid antibody syndrome? |
recurrent venous/arterial thrombosis or recurrent miscarrigaes ( thrombosis in placental vessels) and associated with anti-phospoholipid antibodies |
|
|
|
lupus laboratory findings: |
anaemia : chronic disease or blood loss ( blood loss from NSAIDs) or haemolytoc anaemia is typical- positive coombes test leucopenia - less lymphocytes thrombocytopenia ESR high/ low CRP always check urine for protein (protein:creatinine ratios) monitor renal functions : GFR - can cause a lot of glomeruli - cant just rely on creatinine as it rises slowly autoantibodies! ANA test is most common but not specific - can occur in other in other connective diseases and also glandular fever |
|
|
|
auto antibodies in lupus ? |
autoantibodies! ANA test is most common but not specific - can occur in other in other connective diseases and also glandular fever anti-dsDNA Abs - more specific , not occurong in 40% of pts , increased risk of kidney disease Anti Extractable NAs - Antiphospholipid antibodies - APTT prolonged ( due to presence of antibody to phospholipid) , lupus anti-coagulant most strongly associated anticardiolipin antibodies- associated with blood clots and miscarriages Anti- ENA (ro and la) - skin rashes , neonatal heart anti-RNP : 10-30% - also associated with mixed connective tissue disease anti - SM - sjorgrens syndrome |
|
|
|
management of SLE? |
NSAID - take care (peptic ulcers, hypertension , atheresclerosis) corticosteroids antimalarial immunosupressants= cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, Cyclosporin A , methotraxate |
|
|
|
diagnostic requirements of SLE : |
serositis oral ulcers arthritis photosensitivity blood ( haematological) disorders renal disorders ANA+ Immunological disorder neurological disorder MAlar rash Discoid rash |
soap brain MD |
|
|
How is SLE monitored ? |
Anti-dsDNA , C3, C4, ESR |
|
|
|
management of SLE? |
prevent symptoms and limit severity use sunblock analgesia and immunosupression corticosteroids only used to treat acute phases NSAIDs useful for pain management |
|
|
|
Mild SLE disease management? |
skin rash and arthritis = NSAIDs and Hydroxychloroquine (anti-malarial) |
|
|
|
moderate SLE disease management? |
azathioprine, prednisolone, methotrexate |
|
|
|
severe SLE disease management ? |
Cyclophosphamide (increases bladder cancer risk) cyclosproin for leukopenia MMF 3rd line Rituximab in resistant cases
|
|
|
|
when is cyclosporin A used in SLE? |
where thereis leucopaenia |
|
|
|
what is anti-phospholipid antibody syndrome ? |
charecterised by recurrent thrombosis not specific to SLE causes CLOT : coagulation defect, Livedo reticularis, Obstetric ( recurrent miscarrigae) and Thrombocytopenia |
|
|
|
what is lovedo reticularis |
various conditions in whoch there is mottled discolouration of the skin , being reticular ( net-like) - cyanotic discolour that surrounds pale skin |
|
|
|
how are apas patients identified ? |
thrombocytopenia on FBCor prolonged APTT further tests may show anti-cardiolipin antibodies B2 glycoprotein and lupus anticoagulant |
|
|
|
Tx for apas ? |
Aspirin,warfarin and immunosupression |
|
|
|
what is mixed connective tissue disease? |
features of SLE, systemic sclerosis and dermatomyositis? charecterised by anti- RNP (ribonuclear protein) antibodies |
|
|
|
what is sarcoidosis? |
multi-system granulomatous disorder affects 20-40y/o , more females results in pulmonary diseases, lympahdenopathies, CNS impacts andmany more |
|
|
|
6 clinical features of sarcoidosis ? |
pulmonary disease = bihilar lympahdenopathy, pulmonary fibrosis lymphadenopathy hepatomegaly and splenomegaly CNS effects erythema nodosum = red boggy and tender swellings in lower limbs and forearms (also caused by IBD, post-strp infection and as a medication reaction) Lower limb arthritis - ankle and bigger joints) |
|
|
|
investigations for sarcoidosis ? |
CRP and ESR raised , serum ACE can be raised CXR tissue biopsy - reveals non-ceseating granulomas |
|
|
|
what is sysetmic sclerosis ? |
diffuse = generalised disorder of the connective tissue affecting skin (scleroderma) and internal organs charecterised by fibrotic atheresclerosis of peripheral and visceral vasculature alongside acumulation of collagen in skin and viscera Limited= below elbows and face |
|
|
|
presentation of systemic sclerosis ? |
peripheral skin changes which migrate centrally skin feels thickened and waxy, atrophic thinned and tight skin changes deform joints by pulling them abnormal positions and leading to a loss of function will also have raynauds phenomenon and later develop calcinosis as a complication of Raynauds |
|
|
|
facial appearance of systemic sclerosis ? |
small mouth , tightened skin , less forehead wrinkles and vitiligo , cant talk or eat as easily |
|
|
|
why might systemic sclerosis patients struggle with eating ? |
microstomia - limited mouth opening tongue stiff - hypomobile and board like fibrosis of oesophagus generalised gingival recession fibrosis of salivary glands |
|
|
|
musculoskeletal effects of systemic sclerosis : |
arthralgia myalgia |
|
|
|
GI effects of systemic sclerosis : |
ororpharynx to large bowel dysmotility dysphagia hiatus hernia diverticulae |
|
|
|
Pulmonary effects of SS ? |
interstitial fibrosis Pulmonary hypertension ( cause of death) |
|
|
|
Cardiac effects of systemic sclerosis : |
CCF Arrythmia |
|
|
|
renal effects of SS ? |
accelerated hypertension due top abnormal renal vessels , may lead to renal crisis |
|
|
|
Investigations for systemic sclerosis ? |
renal function ! ANA, Anti-ENA and anti_SCL&) ( diffuse disease with gut involvement) and anti- centromere antibodies normal complement and no anti-dsDNA antibodies pulminary function testing ECG BP monitoring imaging : CXR, HR-CT chest if lung function is abnormal barium swallow non-rputine = nail capillaroscopy , showing dilated and tottuous and missing capillaries renalangiography |
|
|
|
management of RAynauds ? |
vasodilators topical nitrates, prenteral prostacyclin . severe cases need oral nifidipine |
|
|
|
skin disease in sclerosis management: |
mobility, moisturise , massage , methotrexate |
4 Ms |
|
|
systemic involvement managed by: |
cyclophosphamide for lungs ACEi for renal |
|
|
|
what is CREST syndrome ? |
limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis only face, forearms and legs involved . this is 70% of cases . milder form , slower progression . STarts with Raynauds many years before skin , limited to face and distal limbs cahrecteristic microstomia and breaking of nose calcinosis (deposits on the skin) raynauds esophageal dysmobiltiy sclerodactyly Telangectasia related to anti-centromere antibodies |
|
|
|
what is Sjogrens ? |
slowly progressive inflammatory disease , affects exocrine glands- especially salivary and lacrimal lymphocytic infiltration of glands if seen with other diseases , counts as secondary (RA,SLE, SS, POlymyositis ) |
|
|
|
presentation of sjogrens ? |
mucosal dryness : eyes, mouth (Xerostomia) , genital tract (dry vagina) polyarthritis, parotid gland swelling, lethargy , polyarthritis females much more common . middle aged. lung , kidney (renal tubular acidosis) , liver and blood vessel involvement |
|
|
|
examination of sjogrens ? |
swelling of salivary glands, most recognisable in parotids less production of tears - do aSchirmner tear resr , <mm on filter paper in 5 mins is abnormal |
|
|
|
investigations for Sjogrens ? |
ANA positive + in 90% , Anti-Ro and Anti-La antibodies are charecterisitc of Sjogrens exocrine gland biopsy - definitive destruction
|
|
|
|
management of Sjogrens ? |
avoid anticholinergics artificial tears , artificial saliva , Pilocarpine can be used to alleviate |
|
|
|
MSK signs for SLE? |
small joint arthritis, Myalgia (muscle aches), myositis aseptic necrosis of knee or hip |
|
|
|
general sytemic signs of SLE? |
fatigue, fever, depression, weight loss, malaise |
|
|
|
Mucocutaneous effects of SLE |
butterfly rash, photosensitivyt, alopecia, mouth ulcers, Raynauds |
|
|
|
Blood signs of SLE? |
Anaemia (NORMOCYTIC) , leucopenia, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia |
|
|
|
lung sings of SLE? |
pleurisy /pleural effusions, fibrosing alveolitis |
|
|
|
cardiovascular signs of SLE? |
pericarditis/pericardial effusions, myocarditis,aortic valve lesion , thrombosis, Raynauds phenomenon |
|
|
|
REnal impacts of SLE? |
Glomerulonephritis |
|
|
|
CNS signs of SLE? |
seizures, migraines, cerebella ataxia, cranial nerve lesions , polyneurotpathy |
|
|
|
Blood tests in SLE? |
normocytic anaemia neutropenia/ lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia ESR raised CRP raised U&Es |
|
|
|
what is vasculitis ? |
condition involving vessel inflammation . relapse and remitting multisystemic, symtpoms vary based on site and size of vessel inflammatory infiltrate and necrosis of blood vessel wall - impaired blood flow wall destruction = aneurysm or rupture stenosis = tissue ischaemia and necrosis |
|
|
|
causes of vasculitis : |
Infection e.g. HIV, meningococcal septicaemia, streptococci, TB, Hep B/C, parvovirus- Malignancy e.g. Leukaemia, Lymphoma- Medications e.g. Propylthiouracil, Allopurinol, Aspirin- Endocarditis- Connective tissue disease e.g. RA, SLE, Sjogren’s- Primary idiopathic vasculitis |
|
|
|
artery size affected dependson : |
disease! ANCA associated affected mulitple sizes large artery= GCA, Takayasu's medium = polyarteritis nodosa, kawasaki syndrome medium/ small = microscopic polyangitis, wegners, allergic GPA small vessel = henlock-schonlein purpura, leucocytoclastic vasculitis , goodpastures variable vessel vasculitis = bechets, Cogan's syndrome |
|
|
|
presentation of vasculitic diseases : |
elderly males acute/ chronic variable presentations systemic common = fever, malaise, anorexia, decreased weight |
|
|
|
skin signs of vasculitis : |
vasculitic rashes : non-blanching, widespread, palpable purpura livedo reticularis tender nodules digital infarcation and ulceration |
|
|
|
eye signs of vasculitis : |
red, painful, photophobic eyes (uveitis, episcleritis, retinitis) visual loss |
|
|
|
ENT signs of vasculitis : |
epistaxis nasal crusting nasal bridge collapse sinusitis hoarse voice stridor from laryngeal disease |
|
|
|
GI signs of vasculitis : |
mouth ulceration (genital) jaw claudication abdominal pain ( perforation and peritonitis) diarrhoea and PR bleeding |
|
|
|
renal signs of vasculitis ? |
hypertension, haematuria, proteinuria, renal failure (renal cortical infarcts; glomerulonephritis in ANCA+ive vasculitis |
|
|
|
cardio/resp signs of vasculitis: |
chest pain (pericarditis, pleuritis) SOB (due to pulmonary haemorrhage) haemoptysis fibrosis asthma |
|
|
|
neurological signs of vasculitis: |
numbness and paraesthesia ( peripheral neuropathy, mononeuritis multiplex, mononeuropathy) weakness headache and visual loss ( temporal arteritis) musculoskeletal ( myalgia , asymmetrical inflammatory oligoarthritis) |
|
|
|
investigations for vasculitis ? |
urinalysis to assess for renal involvement (U+Es, creatinine and ACR (high acr bad) ) LFTs, CRP/ESR raised, FBC WCC is decreased in SLE, normal in primary vasculitis , msy be eosinophilia in allergic GPA |
|
|
|
very general presentation of vasculitis ? |
nose bleeds,bloody persistent cough, muscle pain , bloody stool and abdo pain , joint pain , reduced visual acuity, palpable purpura and livedo reticularis, fever headache , weightloss, glomeurlonephritis , stroke, MI , hypertension |
|
|
|
other investigations for suspected vasculitis ? |
virus serology ( HIV, Hep B/C) CXR, sinus XR, CT scn , MRI and angiography and biopsy required for diagnosis , Echo scan - endocarditis
|
|
|
|
immunology for vasculitis |
RhF , complement, ANA, ANCA most important ( an IgG antibody tested for using immunofluorescence ) |
|
|
|
ANCA vasculitis ? |
has a predilection for kidney and resp tract cANCA (PR3) is cytoplasmic - seen in GPA pANCA is perinuclear = microscopic polyangitis and allergic GPA |
|
|
|
ANCA antibodies are also seen in ? |
IBD, autoimmune liver disease , SLE, INfection and malignancy - therfore not specific |
|
|
|
management of vasculitis ? |
remission induced with corticosteroids and or oral/ pulse IV cyclophosphamide highly toxic with s/e = myelosupression , alopecia , loss of fertilitiy maintenance = immunosupressant DMARD agent ( Azathiprinje, Methotrexate, MMF, SEptrin ) adjuvant therapy = pulses of IV corticosteroid, Rituximab, IV Ig, plasma exchange use these when symptoms persist despite the use of standard maintenance therapy |
|
|
|
allergic GPA name and triad ? |
Churg-Strauss syndrome eosinophilia vasculitis adult-onset asthma , happens in three phases , asthma / rhinitis is first |
|
|
|
GCA ? signs , presentation |
giant cell arteritis = temporal arteritis afffects > 50 symptoms include headache temporakl artery , scalp tenderness, tongue / jaw claudication , AMAUROSIS FUGAX ( sudden unilateral blindness probably due to clotting of vessels that supply optic nerve) raised ESR , cpr and platelets raised alp , decreased Hb, need a temporal artery biopsy within 14 days of starting steroids |
|
|
|
TTx of GCA ? |
prednisolone , 2 yr course then complete remission main death cause and morbiditiy is long-term steroid use give PPI, Bisphosphonate, Calcium and colecalciferol, consider aspirin |
|
|
|
Wegners GPA ? |
ANCA associated , p3 URT , LRT, joints , kidney nasal/ oral inflammation - ulcers, crusting , bloody discharge , sinusitis abnormal CXR = nodules , cavities or infiltrate urinary sediment gangrene |
|
|
|
Bechets syndrome ? |
oral , genital ulceration eye disease ulcers are painful cvs , GIT and MSK also affected needle prick test leads to papule formation within 48hrs |
|
|
|
polymyalgia rheumatica ? |
syndrome with pain or stiffness - neck shoulders , upper arms and hips - may occur all over body fatigue , appetite loss , decreasing weight, anaemia , flu-like symptoms , low grade fever can be sudden or gradual pain in muscles not a true vasculitis - pathogenesis is unknown 50% of GCA will have PMR |
|
|
|
features of PMR |
has GCA normally women over 50 bilateral aching , morning stiffness in shoulders, hips , proximal limb muscles subacute onset (<2weeks) bilateral aching , morning stiffness in shoulders, hips , proximal limb muscles fatigue , fever, anorexia, depression mild polyarthritis tenosynovitiscarpal tunnel syndrome no weakness or creatinine increase fatigue , fever, anorexia, depression mild polyarthritis tenosynovitis carpal tunnel syndrome no weakness or creatinine increase |
|
|
|
investigation findings in PMR |
raised crp/esr raised alkp in 30% creatinine normal |
|
|
|
differentials for PMR ? |
recent RA , polymyositis, hypothyroidism, primary muscles disease, occult malignancy or infection osteoarthritis (especially cervical spondylosis) shoulder OA neck lesions bilateral subacromial impingment spinal stenosis |
|
|
|
management of PMR ? |
prednisolone 15mg/d PO dramatic response - consider alternative diagnosis if not decrease dose slowly , by 1mg per month , according to symptoms/ESR investigate apparent flares most need steroids for 2 yrs , so give bisphophonates adding methotrexate nsaids not effective seek urgent review if symptoms of GCA develop |
|
|
|
complications of steroid therapy ? |
diabetes mellitus osteoporosis cataract avascular necrosis |
|

