![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Respiration
|
The exchange of gas between the outside air and blood, involving specifically the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide
|
|
|
Alveoli
|
Primary gas exchange units of the lungs which are interconnected and surrounded by capillary networks. They are separated from pulmonary capillaries by a very thin barrier, allowing faster gas exchange via diffusion
|
|
|
Trachea
|
Otherwise known as the windpipe, it directs air down into the lungs
|
|
|
Bronchi
|
Into which air from the trachea is directed to branch into both lungs
Plural: bronchus |
|
|
Bronchioles
|
The smaller branchings of the bronchus which have no internal cartilage
|
|
|
Respiratory Bronchioles
|
Provide the link between the lungs and the circulatory system for gas exchange. Each bronchiole leads to an alveolar duct which leads into an alveoli
|
|
|
Advantage of Bronchiole Tree
|
Provides an extremely large surface area across which gases can be exchanged
|
|
|
Oxygen Diffusion
|
Oxygen travels from the air in the alveoli across the alveolar-capillary membrane into the blood, combining with haemoglobin in RBCs
|
|
|
Carbon Dioxide Diffusion
|
Carbon dioxide travels from the blood (mainly from the plasma) across the alveolar-capillary membrane into the air in the alveoli
|
|
|
Alveolar Diagram
|
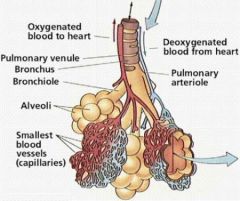
|
|
|
Lung Diagram
|

|

