![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the definition of Interstitial Lung Disease?
|
- Lung parenchymal disorder
- Common clinical, radiologic, physiologic, and pathologic features - Hallmark: involvement of interstitium |
|
|
What are the other terms for Interstitial Lung Disease?
|
- Infiltrative Lung Disease
- Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease (DPLD) - Restrictive Lung Disease |
|
|
What are the features of the term "infiltrative lung disease" (synonym of Interstitial Lung Disease)?
|
Infiltration of cellular and non-cellular elements w/in alveolar septa and alveoli
|
|
|
What are the features of the term "restrictive lung disease" (synonym of Interstitial Lung Disease)?
|
Reduced total lung capacity in presence of a normal or reduced expiratory flow rate
|
|
|
What are the types of Interstitial Lung Disease?
|
- Acute Interstitial Lung Disease - Acute Interstitial Pneumonia (ARDS)
- Chronic Interstitial Lung Disease |
|
|
What are the types of Chronic Interstitial Lung Disease?
|
- Fibrosing Lung Disorders (pneumoconioses)
- Granulomatous Disorders (sarcoidosis) - Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias (IIPs) |
|
|
What causes Interstitial Fibrosis?
|
- Alveolitis: damage to pneumocytes and endothelial cells
- Leads to leukocytes releasing cytokines - Mediates and stimulates interstitial fibrosis |
|
|
What are the impacts of Interstitial Fibrosis?
|
- ↓ Lung compliance and elasticity
- ↓ Lung expansion during inspiration |
|
|
What are the phases of Interstitial Lung Disease?
|
- Phase 1: Acute alveolitis - injury to parenchymal cells
- Phase 2: Chronic alveolitis - progressive alveolar injury - Phase 3: Derangement of collagen interstitial fibrosis - Phase 4: End-stage lung disease |
|
|
What are the modulating factors of Interstitial Lung Disease?
|
- Chronicity of exposure
- Effectiveness of lung defenses - Extent of injury - Intactness of basement membrane - Individual susceptibility (e.g., genetic factors) |
|
|
What are the clinical findings of Interstitial Lung Disease?
|
- Dry cough
- Dyspnea - Late inspiratory crackles, bibasilar = base of lung (Velcro crackles) - Cor pulmonale = R HF |
|
|
What would a chest x-ray for Interstitial Lung Disease look like?
|
Bilateral Reticulonodular Infiltrates
|
|
|
What are the causes of diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease?
|
- Occupational and environmental inhalants
- Drugs and toxins - Infections |
|
|
What occupational and environmental inhalants cause diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease?
|
- Inorganic dusts (silicosis, asbestos, coal workers' pneumoconiosis)
- Organic dusts (hypersensitivity pneumonitis) - Gases, fumes, aerosols (oxygen toxicity, sulfur dioxide, toluene) |
|
|
What drugs and toxins cause diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease?
|
- Chemotherapeutic agents (busulfan, bleomycin)
- Antibiotics (nitrofurantoin) - Other drugs (gold, penicillamine) - Toxins (paraquat) |
|
|
What infections cause diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease?
|
- Viral (influenza, cytomegalovirus)
- Bacterial (widespread TB) - Fungal - Parasitic (Pneumocystis carinii) |
|
|
What kind of Interstitial Lung Disease is caused by inhalation of mineral dusts in the workplace?
|
Pneumoconioses
|
|
|
What kind of disease is Pneumoconioses? Cause?
|
* Non-neoplastic lung reaction to inhalation of mineral dusts (often in workplace)
- Also includes inhalation of organic and inorganic particulates, as well as chemical fume- and vapor-induced non-neoplastic lung diseases |
|
|
Inhalation of what causes Pneumoconioses?
|
- Coal dust
- Silica - Asbestos - Beryllium (often in workplace) |
|
|
What percent of chronic Interstitial Lung Disease is caused by Pneumoconioses?
|
25% of cases
|
|
|
What determines the development and severity of Pneumoconioses?
|
- Amount of dust retained in lung parenchyma and airways
- Size, shape, and buoyancy of particles - Particle solubility and physiochemical reactivity - Other irritants may influence development (e.g., tobacco smoking) |
|
|
How does the size of particles inhaled that cause Pneumoconiosis affect what happens?
|
- > 5-10 µm: unlikely to reach distal airways
- 1-5 µm: most dangerous, because they get lodged at the bifurcation of respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts - < 0.5 µm: move into and out of alveoli, often without substantial deposition and injury, phagocytosed by alveolar macrophages |
|
|
What are the types of FIBROGENIC (vs non-fibrogenic) Pneumoconiosis? What is inhaled to cause each type?
|
- Coal Workers' Pneumoconiosis (carbonaceous dust)
- Silicosis (crystalline silica) - Silicatosis (talc, kaolin, feldspar, mica, muscovite) - Asbestosis (asbestos fibers) - Metalloconiosis (berylliosis - beryllium dust; hard metal lung disease - tungsten carbide; aluminosis - aluminum) - Thesaurosis (hair spray) |
|
|
What are the types of NON-FIBROGENIC (vs fibrogenic) Pneumoconiosis? What is inhaled to cause each type?
|
- Siderosis (iron oxide)
- Baritosis (barium sulfate or barytes) - Stannosis (tin dioxide or cassiterite) - Zirconium lung disease - Antimony lung disease |
|
|
What are the three types of Coal Workers' Pneumoconiosis (CWP)?
|
- Pulmonary Anthracosis
- Simple CWP - Complicated CWP (progressive massive fibrosis) |
|
|
What are the features of the Pulmonary Anthracosis type of Coal Workers' Pneumoconiosis (CWP)?
|
- Simplest type / asymptomatic
- Anthracotic pigment accumulates in interstitial compartment and lymph nodes without a perceptible cellular reaction |
|
|
What are the features of the Simple type of Coal Workers' Pneumoconiosis (CWP)?
|
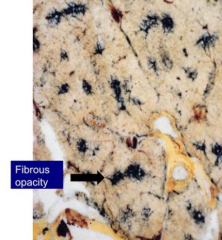
- Fibrous opacities < 1 cm
- Found in upper lobe and upper portion of lower lobe - Characterized by coal dust deposits adjacent to respiratory bronchioles - Accumulations of macrophages occurs with little to no pulmonary dysfunction |
|
|
Where are the fibrous opacities in Simple type of Coal Workers' Pneumoconiosis (CWP) found? Size?
|
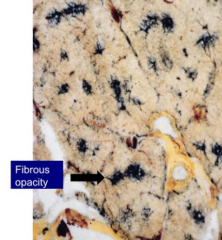
- Found in upper lobe and upper portion of lower lobe
- < 1 cm |
|
|
What are the features of the Complicated type of Coal Workers' Pneumoconiosis (CWP) / Progressive Massive Fibrosis?
|
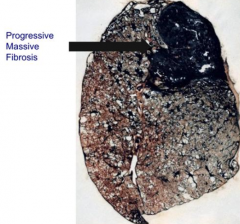
- Fibrous opacities > 1cm
- With or without central necrosis - Extensive fibrosis - crippling lung disease (black lung disease) - Compromised lung function - Caplan Syndrome - CWP w/ Rheumatoid nodules in lung |
|
|
Where are the fibrous opacities in Complicated type of Coal Workers' Pneumoconiosis (CWP) / Progressive Massive Fibrosis found? Size?
|
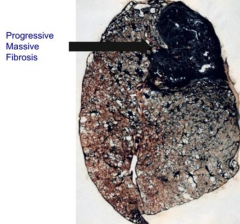
- Fibrous opacities are throughout entire lung
- > 1 cm |
|
|
Who gets Pulmonary Anthracosis (asymptomatic form of CWP)? Cause?
|
- Coal miners, urban dwellers, and tobacco smokers
- Caused by inhaled carbon pigment that is engulfed by alveolar or interstitial macrophages, which then accumulate in CT along lymphatics |
|
|
What kind of Pneumoconioses is characterized by multiple, intensely blackened scars larger than 2 cm?
|
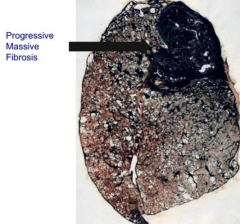
Complicated CWP / Progressive Massive Fibrosis - Black Lung Disease
|
|
|
What is Caplan Syndrome? What is it associated with?
|
- CWP w/ rheumatoid nodules in lung (same nodules you see in RA)
- Associated with Complicated CWP |
|
|
Is there increased incidence of TB or Cancer in Complicated CWP?
|
No
|
|
|
What is the most common occupational disease worldwide?
|
Silicosis
|
|
|
What is inhaled in Silicosis? What causes exposure to this?
|
Crystalline silicon dioxide (quartz) - foundries (metal casting), sandblasting, silica mines
|
|
|
What is the process of inhaled silica / quartz causing Interstitial Fibrosis?
|
- Quartz activates alveolar macrophages after engulfment →
- Cytokine release → - Fibrinogenesis |
|
|
What are the morphological features of chronic Silicosis?
|
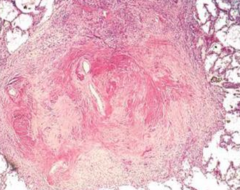
- Nodular opacities w/ concentric layers of collagen
- Polarizable quartz particles can be seen - Egg-shell calcification in hilar lymph nodes |
|
|
What are the complications of Silicosis?
|
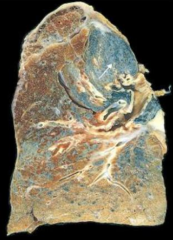
- Cor pulmonale
- Caplan Syndrome (Rheumatoid nodules in lung) - Increased risk for TB (silicotuberculosis) and cancer |
|
|
What are the forms of Asbestos?
|
- Serpentine (curly and flexible)
- Amphibole (straight and rigid) |
|
|
Where does Asbestos-related disease affect?
|
- Respiratory bronchioles
- Alveolar ducts - Alveoli - Lower lobes |
|
|
What are the sources of Asbestos-related disease?
|
- Insulation around pipes in old naval ships
- Roofing material used over 20 years ago - Demolition of old buildings |
|
|
What does tissue affected by Asbestos-related disease look like?
|
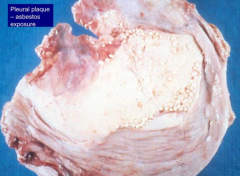
* Ivory white, calcified, benign pleural plaques
- Ferruginous bodies - macrophages phagocytose asbestos fibers and coat them w/ ferritin (iron and protein) - Diffuse interstitial fibrosis (asbestosis) |
|
|
What is Asbestos-related disease a risk factor for? How long after exposure does this occur? Additional risk factors?
|
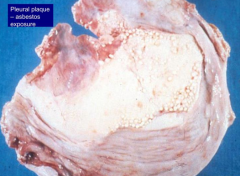
- Bronchogenic carcinoma (additional risk w/ smoking; occurs 20 yrs after first exposure)
- Mesothelioma (no relationship to smoking, arises from lining mesothelial cells of pleura, occurs 25-40 yrs after first exposure) - Not a risk factor for TB |
|
|
What are the complications of Asbestos-Related Disease?
|
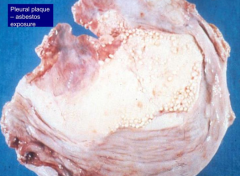
- Cor pulmonale
- Caplan syndrome (Rheumatoid nodules in lung) |
|
|
What is the appearance of Asbestos on microscopy?
|
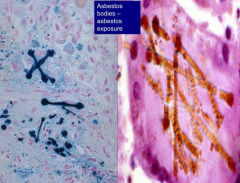
- Distinct golden brown fusiform rods that resemble dumbbells (color d/t iron)
- Navy blue with iron staining |
|
|
Where can you be exposed to Beryllium?
|
Nuclear and airspace industry
|
|
|
What does Beryllium exposure / inhalation cause?
|
Berylliosis:
- Granulomatous inflammation - Cor pulmonale - Lung cancer |
|
|
What is the differential diagnosis when you see granulomatous inflammation that makes you think of Berylliosis?
|
Must also consider TB and Sarcoidosis
|
|
|
What is Sarcoidosis? What percent of chronic interstitial lung disease is caused by it?
|
- Multi-system granulomatous disease of unknown etiology
- Causes 25% of chronic interstitial lung disease - Disorder of immune regulation * Diagnosis of exclusion * |
|
|
Where does Sarcoidosis occur? Who is affected by it?
|
- Worldwide occurrence
- Highest in Scandinavia - AA:Whites - 10:1 - M:F - 1:2 - 70% < 40 years old - Non-smokers |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of Sarcoidosis?
|
- Unknown antigen interacts w/ CD4 T4 cells →
- Cytokine release and recruitment of monocytes / histiocytes → - Non-necrotizing granuloma formation |
|
|
What parts of the body are affected by Sarcoidosis?
|
- 95-100% of cases involve lungs
- 75-80% involve lymph nodes - 75% involve spleen - 50% involve liver - Alo skin, eyes, joints, nervous system, myocardium |
|
|
What happens to the skin in Sarcoidosis?
|
- Nodular granulomatous lesions
- Lupus pernio - Erythema nodosum |
|
|
What happens to the eyes in Sarcoidosis?
|
Uveitis
(inflammation of the pigmented layer of the eye: iris, choroid, and ciliary body) |
|
|
What happens to the liver in Sarcoidosis?
|
Granulomatous Hepatitis
|
|
|
What are the non-skin, -eye, and -liver features of Sarcoidosis?
|
- Enlarged salivary and lacrimal glands
- Diabetes insipidus - Bone marrow and splenic involvement |
|
|
What are the lab findings of Sarcoidosis?
|
- ↑ Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE)
- Hypercalcemia (5%) - Polyclonal gammopathy - Cutaneous anergy (lack of response to common skin antigens (candida) d/t consumption of CD4 T4 cells) |
|
|
What are the findings on chest x-ray for Sarcoidosis?
|
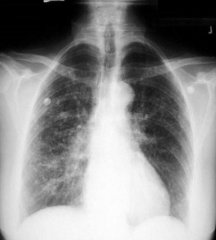
- Bilateral hilar adenopathy
- Reticulonodular shadows in lungs |
|
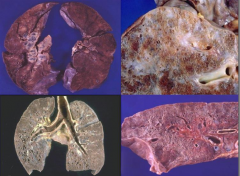
What do these images show?
|
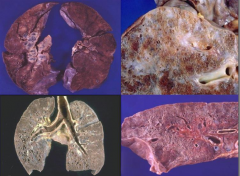
Sarcoidosis:
- UL: lung parenchyma is not that badly affected yet - UR: big patchy areas - LR: small cystic spaces - LL: honeycomb cysts |
|
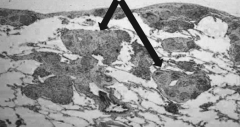
What do these arrows point out?
|
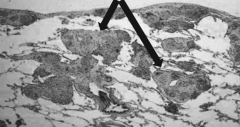
Sarcoidosis - Interstitial Granulomas found in lung parenchyma and also along pleural surface
|
|
|
What is the organization of the interstitial granulomas in Sarcoidosis?
|
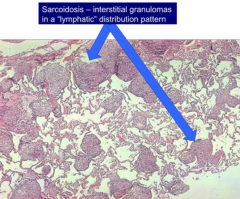
Lymphatic distribution pattern
|
|
|
If you see interstitial granulomas following a lymphatic distribution, what should you think of?
|
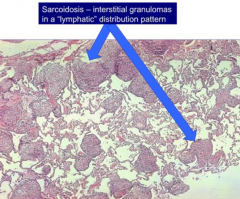
Sarcoidosis
|
|
|
What kind of cells form granulomas in Sarcoidosis?
|
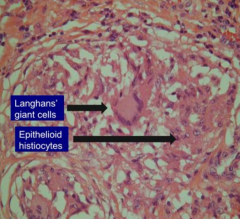
- Langhans' Giant cells (white)
- Epithelioid Histiocytes (purple) |
|
|
What is the prognosis of Sarcoidosis?
|
- Variable: spontaneous remissions and relapses
- Progressive interstitial fibrosis w/ cor pulmonale and death in 10-15% of cases |
|
|
What causes Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
|
- Inhaled antigen (known or unknown)
- Produces granulomatous interstitial pneumonitis (extrinsic allergic alveolitis) |
|
|
What kind of hypersensitivity reaction occurs in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
|
- Starts as type III hypersensitivity reaction
- Chronic, granuloma formation leads to type IV hypersensitivity reaction |
|
|
What happens during the first exposure to antigen in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
|
Formation of IgG antibodies
|
|
|
What happens during the second exposure to antigen in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
|
IgG antibodies combine w/ inhaled antigens to form immune complexes → inflammatory response in lung (interstitial)
|
|
|
What happens when there is chronic exposure to antigen during Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
|
Granuloma formation (type IV hypersensitivity response)
|
|
|
What are the types of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
|
- Farmers' Lung
- Silo Fillers' Disease - Byssinosis |
|
|
What kind of disease is Farmers' Lung? Cause?
|
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- Caused by moldy hay: thermophilic actinomycetes bacteria (saccharopolyspora rectivirgula) |
|
|
What kind of disease is Silo Fillers' Disease? Cause?
|
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- Caused by inhalation of gases from plant material (oxides of nitrogen) |
|
|
What kind of disease is Byssinosis? Cause?
|
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- Caused by cotten, linen, hemp - Common in textile factory workers - "Monday morning blues" |
|
|
What are the degrees of clinical syndromes for Interstitial Lung Disease - Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
|
- Acute
- Subacute - Chronic |
|
|
How do you diagnose Interstitial Lung Disease - Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
|
- Symptoms and physical findings
- X-ray abnormalities - PFTs - Immunologic features (Abs to suspected Ags) - Lung biopsy may be needed |
|
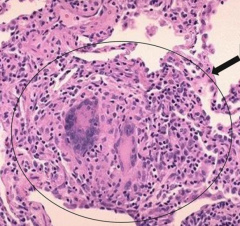
What is seen in this image?
|
Granuloma from Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- Random distribution |
|
|
What amount of Chronic Interstitial Lung Disease is caused by Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis?
|
15%
|
|
|
How long does Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis typically last? Who is affected by it
|
- 18-24 months
- M>F, 40-70 years old |
|
|
What are the clinical manifestations of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis?
|
- Dyspnea
- Non-specific constitutional symptoms: fever, weight loss, fatigue, arthralgias - Cough |
|
|
What causes Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis?
|
Repeated injury to lung → Alveolitis → Cytokine release → Interestitial Fibrosis → irregular dilation of adjacent airways → honeycomb lung (end stage interstitial fibrosis)
|
|
|
What is indicative of end stage interstitial fibrosis?
|
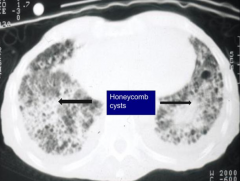
Honeycomb appearance of lung
|
|
|
What percent of cases of Interstitial Lung Disease are caused by Collagen Vascular Disease?
|
10%
|
|
|
What can cause Collagen Vascular Disease?
|
- Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) - Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma) |
|
|
How common is interstitial lung disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE)? What kind of pulmonary changes?
|
50% of patients
- Pleural effusion is the most common manifestation |
|
|
What should you suspect in a young woman w/ unexplained pleural effusion?
|
Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE)
|
|
|
What kind of pulmonary changes should you expect in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
|
Wide spectrum:
- Rheumatoid nodules (when associated w/ pneumoconiosis = Caplan Syndrome) - Interstitial fibrosis - Pleural effusions |
|
|
What kind of pulmonary changes should you expect in Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma)?
|
- Interstitial fibrosis w/ pulmonary vascular hypertrophy
- Commonest cost of death |
|
|
Case: 66 yo male smoker has increasing dyspnea for about a year. He is retired from construction business. Rales auscultated in both lungs on physical exam. Chest xray reveals bilateral diaphragmatic pleural plaques as well as diffuse interstitial lung disease. Sputum cytology shows no atypical cells.
These findings are most likely to suggest prior exposure to what environmental agent? |
Asbestos Fibers
|
|
|
Case: 50yo African American woman presents w/ increasing dyspnea, weight loss, and night sweats for 4 months. She is non-smoker. On exam, there are fine rales auscultated in all lung fields. Chest xray shows hilar lymphadenopathy and a reticulonodular pattern in all lung fields. Transbronchial biopsy demonstrates small pulmonary interstitial non-caseating granulomas.
What is the most likely diagnosis? |
Sarcoidosis
|

