![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What provides the energy of pressure difference required for air movement?
|
Action of the so-called respiratory pump muscles
|
|
|
What process exchanges gases between the alveoli and capillaries?
|
Passive diffusion
|
|
|
What is the equilibrium position of the lungs?
|
Total collapse (because they are elastic structures)
|
|
|
What is the equilibrium position of the chest wall?
|
60% total lung inflation (because it is an elastic structure)
|
|
|
What do respiratory mechanics refer to?
|
Relationships between pressure changes within the respiratory system and resulting changes in airflow and lung volume
|
|
|
What are the three important pressures?
|
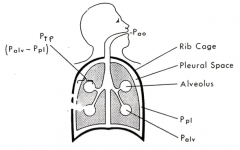
- Alveolar pressure
- Pleural pressure (within pleural space) - Transpulmonary pressure (difference between pleural and alveolar pressure) |
|
|
What causes air to flow between the atmosphere and the alveoli?
|
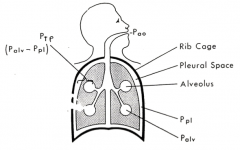
- Determined by a pressure difference between alveolar and atmospheric pressure
- Alveolar pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure during expiration - Alveolar pressure is less than atmospheric pressure during inspiration |
|
|
How do alveolar and atmospheric pressure compare during inspiration?
|
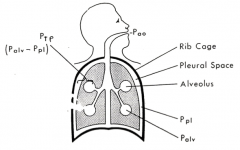
Alveolar pressure (negative) << Atmospheric pressure
|
|
|
How do alveolar and atmospheric pressure compare during expiration?
|
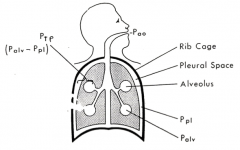
Alveolar pressure >> Atmospheric pressure
|
|
|
What causes alveolar pressure to change during inspiration?
|
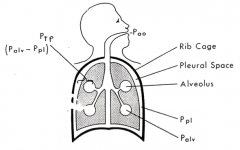
During inspiration, alveolar pressure is negative relative to the atmospheric pressure because pleural pressure becomes more negative during inspiration
|
|
|
What causes pleural pressure to change during inspiration?
|
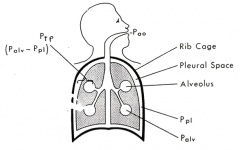
- Pleural pressure becomes more negative during inspiration as a result of contraction of the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles
- This increases the pleural space or volume and thereby reduces the pressure |
|
|
Why during inspiration and expiration does alveolar pressure change less than the change in pleural pressure?
|
Alveolar pressure changes less than pleural pressure because a portion of the pleural pressure (or energy) is required to overcome the lung elasticity.
|
|
|
What causes alveolar and pleural pressure to change during expiration?
|
- During quiet breathing in humans, alveolar and pleural pressure change as a result of the lung recoiling toward its equilibrium position
- During conditions of increased need for breathing, expiratory muscle contraction adds to the positive alveolar pressure generated by lung recoil |
|
|
What is the sequence of events that accounts for airflow throughout the respiratory cycle?
|
- Inspiratory muscles contract to expand the pleural space, thereby reducing pleural pressure
- A portion of the pressure change overcomes lung elasticity to expand the alveoli, which reduces alveolar pressure to subatmospheric and results in inspiration - Inspiration ends when inspiratory muscle activity ceases, and then the lungs recoil with or without expiratory muscle contraction and creates an alveolar pressure which is greater than atmospheric pressure |
|
|
What is the relationship between pleural pressure and lung volume during inspiration and expiration?
|
- Lung volume increases as pleural pressure becomes more negative during inspiration and it decreases as pleural pressure becomes less negative during expiration. The greater the pressure change, the greater will be the volume change. At the end of inspiration and expiration, there is no airflow; thus, alveolar pressure is zero. Pleural pressure thus reflects the lung elastic recoil pressure. Lung elasticity, also called lung compliance can be computed as ΔV/ΔPTP which becomes ΔPpl when airflow is zero. If a line is drawn to connect the zero flow values, the slope of that line reflects lung compliance. At any point on that line where Ppl exceeds PTP, the remaining pressure is PA, which will generate airflow. The amount of airflow for any PA is determined by airway resistance which can be computed as: R = PA/airflow.
|

