![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is business research? |
An organized systematic inquiry or investigation into a specific problem. |
|
|
What are the two types of research |
Basic research : generates a body of knowledge - Applied research : Solves a current problem faced by the manager in the work setting, demanding a timely solution |
|
|
What are the four purposes of study? |
- Exploratory Undertaken when not much is known or no information is available - Descriptive Undertaken in order to be able to describe the characteristics of the variables of interest in a situation (correlation study= is there association between among variable) - Explanatory/analytical/causal Delineating one or more factors that are causing a certain effect - Predictive Aims to generalize from the analysis by predicting phenomena on the basis of hypothesized, general relationships |
|
|
What is deductive reasoning? |
Application of a general theory to a specific case (hypothesis testing) Most used in Causal and quantitative studies |
|
|
What is inductive reasoning? |
A process where we observe specific phenomena and on this basis arrive at general conclusions (all swans are white) Most used in Exploratory and qualitative studies |
|
|
What are some hallmarks/main distinguishing characteristics of scientific research? |
- Purposiveness - Rigor (strict) - Test ability - Precision and Confidence - Replicability - Objectivity - Generalizability - Parsimony (simplest assumption adoption) |
|
|
In methodology we have positivism and interpretivism, explain the different research options |
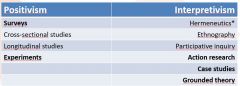
|
|
|
How to calculate the standard error? |
Sx (standard error) = S / (root) n S = stadard deviation n = sample size |
|
|
What are three different forms of validity? |
- Content validity : Face validity Expert validation of the instrument - Criterion-related validity Can you predict a criterion variable - Construct validity Validation of the construct by assessing its relationships to other variables |
|
|
What is methodology (research strategy)? |
The manner in which we approach and execute functions or activities - Consist of approaches or guidelines, not specific of how we do the task (they are methods) |
|
|
What is single and multi cross sectional design? |
•In single cross-sectional designs, there is only one sample of respondents and information is obtained from this sample only once. •In multiple cross-sectional designs, there are two or more samples of respondents, and information from each sample is obtained only once. Often, information from different samples is obtained at different times. |
|
|
What is longitudinal? |
•Longitudinal studies examine the dynamics of a research problem by investigating the same variables or group of people several times (or continuously) over the years. |
|
|
What is the difference between contrived and non-contrived experiments? |
In contrived the research has power over the variables, in non-contrived the researcher has not. |
|
|
What is ethnography? |
•The emphasis in ethnographyics on studying an entire culture. Originally, the idea of a culture was tied to the notion of ethnicity and geographic location (e.g., The culture of the Trobriand islands), but it has been broadened to include virtually any group or organization. That is, we can study the "culture" of a business or defined group (e.g., a rotary club). |
|
|
what is Participative inquiry? |
•Participativeinquiry is a methodology that involves the participants as fully as possible in the study, which is conducted in their own group or organization. The participants have control over the research agenda, the process, and actions. -Cooperative inquiry, all those involved are co-researchers -Action research, the main aim is to enter in a situation, attempt to bring about change and to monitor the results -Two goals: solve problem of client and contribute to science |
|
|
What is grounded theory? |
Grounded theory can be seen as a systematic set of procedures to develop an inductively derived theory from the data |
|
|
What is Triangulation |
•Triangulationis the use of multiple sources of data, different research methods and/or more than one researcher to investigate the same phenomenon in a study |
|
|
What is qualitative data and what methods can be used to get this? |
•Ingeneral, qualitative data is characterized by a high degree of validity and low degree of reliability. Methods: Interviews Focusgroups Observations Protocolanalysis Diary methods |
|
|
What is a theoratical framework? |
A theoretical framework represents your beliefs on how certain phenomena (or variables or concepts) are related to each other (a model) and an explanation on why you believe that these variables are associated to each other (a theory). |
|
|
What is a dependent and what is a independent variable? |
Dependent variable (DV)Is of primary interest to the researcher. The goal of the research project is to understand, predict or explain the variability of this variable. Independent variable (IV)Influences the DV in either a positive or negative way. The variance in the DV is accounted for by the IV. |
|
|
What ia a moderating variable? |
Moderator is qualitative (e.g.,gender, race, class) or quantitative (e.g., level of reward) variable that affects the direction and/or strength of relation between independent and dependent variable. |
|
|
What is mediating variable? |
surfaces between the time the independent variables start operating to influence the dependent variable and the time their impact is felt on it. |
|
|
Hypothesis |
A proposition that is empirically testable. It is an empirical statement concerned with the relationship among variables. Good: - Must be adequate for its purpose - Must be testable - Must be better than its rivals |
|
|
What is a non-directional research hypothesis? |
Reflects a difference, but the direction is not specified• Use a two-tailed test |
|
|
What is a directional research hypothesis? |
Reflects a difference and the direction is specified• Use the one-tailed test |
|
|
What is Operationalizing |
reduction of abstract concepts to render them measurable in a tangible way. |
|
|
What are the four measurement scales? |
•Nominal is one that allows the researcher to assign subjects to certain categories or groups. •Ordinal not only categorizes variables, it also rank-orders categories in some meaningful way. •Interval lets us measure the distance between any two points on the scale. •Ratio overcomes the disadvantage of the arbitrary origin point of the interval scale. It has an absolute (in contrast to an arbitrary) zero point, which is a meaningful measurement point. |
|
|
Explain the different scales |
•Dichotomous scale (2 possible responses e.g. yes /no) •Category scale (answer categories) •Semantic differential scale (bipolar attributes: e.g. good-bad) •Numerical scale (bipolar adjectives, on numerical scale) •Itemized rating scale (1. very unlikely, … , 5 verylikely) •Likert scale (1. strongly disagree, … , 5. stronglyagree) •Fixed or constant sum rating scale (allocating points to aspects) •Stapel scale (+3to -3, direction and intensity of attitude) •Graphic rating scale (mark on graphic axis: e.g. faces) •Forced choice (rankobjects relative to each other) •Comparative scale (comparedto point of reference) |
|
|
What is probability sampling? |
•all elements in the population have a known and non-zero chance of being chosen |
|
|
What is uni, bi and multivariat analysis |
Univariate is relating to one variable, bivariate is relating to two variables and multivariate is relating to more than two |
|
|
Measurement |
the assignment of numbers or others symbols to characteristics (or attributes) of subjects according to a pre-specified set of rules. |
|
|
Operationalizing concepts |
Reduction of abstract concepts to render them measurable in a tangible way. Done by: A) Looking at the behavioral dimensions, facets, or properties denoted by the concept B) Translating them into observable and measurable elements so as to develop a way of measurement of the concept. |
|
|
Four steps of Operationalization |
1. Come up with the definition of the construct we want to measure 2. Think about the content of the measure, i.e. develop a measurement instrument that actually measures the concept 3. Come up with the response format, e.g. a seven-point rating scale 4. Assess the validity and reliability of the measurement scale |
|
|
Definition of the construct (concept) |
reduction of the concept from its level of abstraction, by breaking it into dimensions and elements: - Unidimensional, construct has only one dimension. - Multidimensional, construct has two or more dimensions. |
|
|
Dimensions of service quality |
Reliability, ability to provide what was promised Assurance, knowledge, and courtesy of employees and ability to convey trust Tangibles, physical facilities and appearance of personnel Empathy, degree of caring and individual attention Responsiveness, willingness to help customers and provide prompt service. |
|
|
Develop the measurement instrument (Scale) |
A valid measurement scale includes quantitavely measurable questions that adequalty rephresent all domains (or dimensions) of the construct. |
|
|
Come up with the response format, i.e. measurement scale |
- To be able to assign numbers to attributes of objects we need a scale - A Scale is a tool or mechanism by which objects are distinguished as to how they differ from one another on the variables of interest to study. |
|
|
Asses the validity and reliability of the measurement scale |
- Validity, does the instrument measure the concept you think you are measuring? - Reliability, is the instrument consistent in its measure? |
|
|
Validity |
Validity is a test of how well the instrument that is developed measures the particular concept it is intended to measure. |
|
|
Reliability |
Reliability of measure indicates the extent to which it is without bias and hence ensures consistent measurement across time (stability) and across the various items in the instrument (internal consistency). |
|
|
Experimental studies |
are used to investigate the relationship between variables, where the IV is deliberately manipulated to observe the effect on the DV |
|
|
Experimental designs |
- Independent-samples design, two groups are selected and compared - Matched-pairs design, pairs of subjects are matched and allocated to each group - Repeated measures, the experiment is repeated under different conditions - Singe subject design, single subject design compares the performance of an individual before and after a specified intervention. |
|
|
Ways of collecting qualitative data |
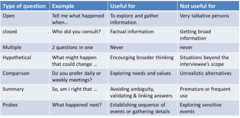
|
|
|
Focus groups |
a method whereby selected participants discuss their reactions and feelings about a product, service, situation or concept, under the guidance of a group leader. Focus groups combine interviews with observations. |
|
|
Procedure for a focus group |
1. Prepare a list of issues you want to cover 2. Invite a group of people with sufficient experiences in common on a neutral location 3. Create a relaxed atmosphere and explain the purpose. 4. Start the session with a broad, open question 5. Allow the group to discuss the issue(s) without intervention |
|
|
Sampling Process |
Sampling is the process of selecting a sufficient number of the right element from the population so that results from analyzing the sample are generalizable to the population. 1. Define the population 2. Determine the sample frame 3. Determine the sample design 4. Determine the appropriate sample size 5. Execute the sampling process |
|
|
Probability sampling |
all elements in the population have a known and non-zero chance of being chosen |
|
|
Non-Probability sampling |
all elements in the population do not have a chance of being selected for the sample |

