![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell Division |
G1: Cell increases its organelles and cytoplasm S: DNA Replication G2: Same as G1 M: The cell divides in two Mitosis = PMAT Meiosis = PMAT x 2 |
|
|
Mitosis |

|
|
|
Meiosis |
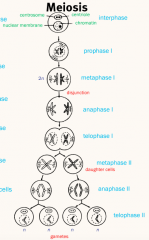
|
|
|
Sexual Reproduction |
Meiosis I and Meiosis II |
|
|
Meiosis I |
- Two pairs of sister chromatids form tetrads during prophase I. - Crossing over leads to genetic recombination in prophase I. - Homologous chromosomes separate during metaphase I. |
|
|
Meiosis II |
- Essentially identical to mitosis, but no replication. - Meiosis occurs in spermatogenesis (sperm formation) and oogenesis (egg formation). |
|
|
Four Stages of Early Development |
Cleavage: Mitotic Divisions Implantation: Embryo implants during blastula stage. Gastrulation: Ectoderm, Endoderm, and Mesoderm form. Neurulation: Germ layers develop a nervous system. |
|
|
Ectoderm |
Nervous System, Epidermis, Lens of Eye, Inner Ear. |
|
|
Endoderm |
Lining of Digestive Tract, Lungs, Liver and Pancreas. |
|
|
Mesoderm |
Muscles, Skeleton, Circulatory System, Gonads, and Kidney. |

