![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
104 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the expected delivery date ? |
37 weeks after LMP
|
|
|
What is a term pregnancy ? |
37-42 weeks |
|
|
When are patients seen for booking visit, booking scan, anomaly/detailed scan ? |
Booking visit (8-12 weeks)
Booking scan ( 8-14 weeks)
Anomaly/detailed scan (18-20 weeks) |
|
|
At the booking visit, what is performed ? |
BP, BMI , blood glucose , urinalysis
Infections screen (TORCHeS)
ABO/rhesus status
|
|
|
What is performed at follow-up visits ? |
BP Urinalysis Preg abdo exam ( Fundus height, fetal HR) |
|
|
When can the uterus be palpated ?
what is the progression of growth thereafter? |
@ 12 weeks - at umbilicus
Growth= 1cm/week (36cm=36 weeks gestation @ xiphysternum) |
|
|
At the booking scan (8-14weeks) , what fetal measurement is used ? |
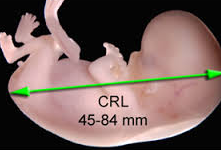
Crown-Rump length
|
|
|
At detailed/anomaly scan (18-20weeks) , What fetal measurement is used ? |
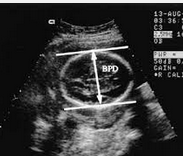
Biparietal diameter |
|
|
What factors determine the risk of down syndrome ? |
↑ maternal age
Nuchal thickness >6mm (@ Booking scan)
↑ hCG , ↓AFP/PAPP-A/oestriol |
|
|
What number is considered high risk for having a down syndrome baby ? |
1:250 |
|
|
Who is down syndrome screening offered too ? |
ALL women |
|
|
If a person is a high risk of having a down syndrome baby , what diagnostic tests can be performed ? |
-If < 14 weeks --> Chorionic villus sampling
-If > 14 weeks --> Amniocentesis
-If > 18 weeks - Cordocentesis |
|
|
What are the risk of miscarriage with chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis ?
What do they sample ? |
CVS = 2% (samples placenta)
Amniocentesis = 1% (samples amniotic fluid) |
|
|
If a person is at booking scan , describe
What gestational period is it? Down syndrome screening & diagnostic test ?
|
B/w 8-14 weeks gestation
Screening = USS + HCG/AFP maternal serology
Diagnostic = Chorionic villus sampling |
|
|
If a person is at anomaly scan , describe
What gestational period is it? Down syndrome screening & diagnostic test ? |
@ 18-20 weeks gestation
Screening = hCG/AFP/PAPP-A/estriol maternal serology
Diagnostic = Amniocentesis |
|
|
In which conditions is AFP elevated ? |
multiple pregnancies
Spina bifida Gastroschisis/ omphalocoele
Choriocarcinoma/ Dysgerminoma Hepatocellular carcinoma |
|
|
What is gastroschisis ? |
Bowel outside of peritoneal cavity
Lateral to umbilicus |
|
|
What is omphalocoele |
Bowel within peritoneal cavity
In midline
Associated w/ malformations |
|
|
What is characteristically seen on USS in a pt with spina bifida ? |
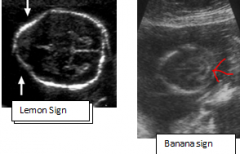
Lemon sign
banana sign |
|
|
When is a vaginal bleed considered antepartum hemorrhage ?
What about prior ? |
>24 weeks gestation
(If < 24 weeks gestation = threatened miscarriage) |
|
|
For Chromosomal analysis , which tests are used if you are looking for a specific mutation ? |
FISH
quantitative fluorescent PCR |
|
|
For chromosomal analysis, Which tests can be used if you want to look for general defects in DNA ? |
Karyotyping
Array CGH |
|
|
Which Chromosomal analysis testing is first line ? |
Array CGH |
|
|
What does hCG do ? |
Maintains Progesterone ( to maintain placental lining!) |
|
|
What can be used to measure fetal viability ? |
Oestriol |
|
|
What common conditions do pregnancy women get ? |
Reflux
HTN, oedema
Gestational DM
Gallstone
Urinary frequency
Hyperthyroidism |
|
|
What hormone mimics TSH during pregnancy ?
What hormone mimics GH during pregnancy ? |
TSH = hCG
GH = HCS/HPL |
|
|
How many umbilical arteries & veins are there ?
What type of blood do they carry ? |
2x Umbilical arteries ( Deoxygenated blood)
1x Umbilical vein (oxygenated blood) |
|
|
What secretes hCG during pregnancy ? |
trophoblastic cells --> placenta |
|
|
What does hCG do ? |
↑ progesterone -> development of decidual cells ( uterine mucous membrane - which provides nutrients to the embryo) |
|
|
How do the levels of hCG progress throughout pregnancy ? |
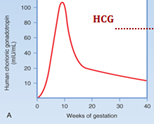
Doubles every 2 days
peaks @ 9-12 weeks |
|
|
In what condition is the hCG
Lower higher |
Lower = ectopic pregnancy
higher = Hydatidiform mole/Choriocarcinoma , multiple pregnancy |
|
|
What does HCS/HPL do ? |
Increases tissue development
-Breasts -Fetal tissue
(Leads to insulin resistance --> Gestational DM) |
|
|
What does Progesterone
promote ? Inhibit ? |
Promotes glandular development in Uterus & Breasts
Inhibits uterine contractions and lactation (REMEMBER IT RELAXES SMOOTH MUSCLES!)
Increases sensitivity to Carbon dioxide
|
|
|
What does estrogen
promote Inhibit ?
|
Promotes tissue development in uterus & breasts
Promotes uterine contractions
Inhibits lactation |
|
|
What CVS changes are there in pregnancy
|
↑ CO
hypotension --> ↑HR |
|
|
What heme changes are there in pregnancy |
↑Blood volume
Hemodilution
Hypercoaguability
|
|
|
What resp changes are there in pregnancy |
Progesterone increases carbon dioxide sensitivity --> ↑ RR |
|
|
What Urinary changes are there in pregnancy ? |
↑ GFR --> urinary frequency + oedema |
|
|
What GI changes are there in pregnancy |
Reflux
Gall stone
hemorrhoids |
|
|
What supplements should be given in pregnancy ?
|
400mcg folic acid ( 5mg if DM/epileptic)
300mg Ferrous fumarate 10 mcg vitamin D |
|
|
how do you Rx hyperthyroidism during pregnancy ?
Complications ? |
PTU ( Carbimazole is teratogenic & risk of agranulocytosis)
Complications: Thyroid storm, neonatal thyrotoxicosis |
|
|
Complications of hypothyroidism during pregnancy ? |
Cretinism |
|
|
What hormones inhibit lactation ? |
Oestrogen
progesterone
|
|
|
What hormone promote lactation? |
Prolactin
Oxytocin (via milk-let down reflect) |
|
|
What is the average weight gain during pregnancy ? |
11kg |
|
|
In what circumstance should a patient receive anti D ?
When should it be given ? |
When Mom (rhesus -ve) & fetus (rhesus +ve)
Anti D INJ @ 28 & 34 weeks |
|
|
What are the complications of rhesus incompatibility ? |
Neonatal anemia/jaundice --> kernicterus
Hydrops fetalis |
|
|
What is moulding ? |
Adjustment of fetal head after labour ( sutures are overlaping) |
|
|
How much is Full dilatation of the cervix ? |
10cm |
|
|
What is fetal lie ? |
Longitudinal axis of fetus cf. mom
-Longitudinal -Transverse -Oblique |
|
|
What is fetal presentation ? |
Presenting part of fetus
-Cephalic -Breech -Shoulder |
|
|
What is fetal position ? |
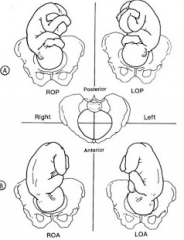
Orientation of presenting part
-Right/Left occipito Anterior/posterior |
|
|
What is fetal attitude ? |
relationship of fetal head to spine
-Vertex -Neutral -brow presentation -face presentation |
|
|
What is descent/station ? |
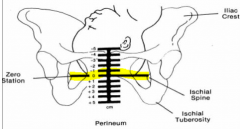
Depth of presenting part cf. Ischial spine
-described in cm or fifths
( - 5cm-->0 cm ) |
|
|
What does the pelvic opennings look like , from inlet --> mid cavity -> outlet |
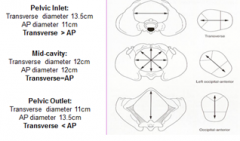
|
|
|
What is normal blood loss during labour ?
Vaginal? C-section? |
Vaginal (300-500mL)
C-section ( 750-1000mL) |
|
|
What are normal contractions during pregnancy called ?
Characteristics ? |
Braxton Hicks contractions ( irregular + painless) |
|
|
What are the signs of labour beginning ? |
-Show -Rupture of membranes -Regular painful contractions (>30 secs) -Cervical dilatation |
|
|
Labour is influenced by 3P's which are ? |
Power Passenger Passage |
|
|
What hormones increase uterine contraction ? |
Estrogen
Oxytocin |
|
|
Which hormone causes cervical dilatation ? |
PG |
|
|
What are the 3 stages of labour |
Stage 1 (Beginning of labour -> Full cervical dilatation)
Stage 2 (Stage 1 -> birth )
Stage 3 (Stage 2 -> Placental delivery) |
|
|
How long should stage 2 last ? |
1-2hrs |
|
|
How long should stage 3 last ? |
30 mins |
|
|
What does descent = 0cm mean ? |
Presenting part @ ischial spines |
|
|
What are the signs of placental separation ? |
High fundus
Gush of blood
Lengthened cord |
|
|
What is prolonged placental separation ?
Rx? |
Stage 3 > 30 mins
Rx : Brandt Andrew manoeuvre , Syntocinon/Syntometrin |
|
|
When is syntometrine contraindicated ? |
Pre-eclampsia ( b/c ergometrin vasoconstricts) |
|
|
What is brandt-Andrew manoeuvre ? |
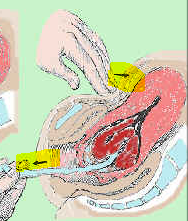
Pushing on abdomen + holding onto placenta |
|
|
What is normal contractions during labour ? |
1x contraction every 2-3 mins |
|
|
What is a good passage for pregnancy ? |
Short
No soft tissue obstruction
No bone dx
No pelvic trauma |
|
|
What is the best lie/presentation/attitude for a fetus for delivery |
Lie= longitudinal
Presentation = Cephalic
Attitude = vertex |
|
|
What is Bandl's ring a sign of ? |
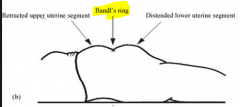
Obstruction during labour |
|
|
Describe the stages of delivery |
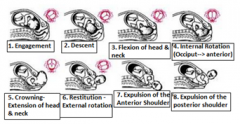
Fetal Engagement + full cervical dilatation--> occiput transverse --> flexion-->occiput anterior ->Extension -> crowning -> occiput transverse (i.e restitution) |
|
|
What are the analgesia's provided during labour ? |
- Entonox INH -TENS -Morphine -Remifentanil
-Pudendal nerve block -Epidural -Spinal |
|
|
What is in an epidural ? |
Lidocaine +/- opiates |
|
|
What nerve roots make the pudendal nerve ?
Where do you INJ for a pudendal nerve block ? |
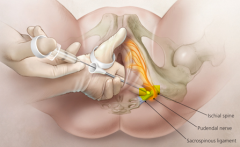
S2-4
INJ @ inferiormedially to ischial spines BILATERALLY |
|
|
What are the indications for pudendal nerve block ? |
Instrumental delivery |
|
|
What are the indications for spinal anaesthesia ? |
C-section
rotational delivery |
|
|
For an epidural..
Where is it INJ? What nerves does it block ? When can it be injected ? |
INJ @ L3-4 , when Cervix > 3cm dilated
blocks T11-S5
|
|
|
What are the side effects of an epidural ?
|
Hypotension (prevented by giving 500mL haartmann's prior)
urinary retention ( prevented by catheterisation) Dural puncture --> headache Delayed stage 2 labour ( due to paralysis of pelvic floor) |
|
|
What is the difference b/w spinal & epidural anaesthetic ? |
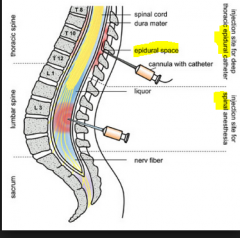
Spinal - paralysis + single INJ
Epidural - pain relief + Catheter in place for future top ups |
|
|
Contractions during labour have what effect on the fetus ? |
Cortisol/adrenaline release -> Surfactant + fluid reabsorption in lungs |
|
|
What do you do immediately after birth? |
Dry & keep baby warm
Give to mother |
|
|
What is normal weight loss in a newborn & when does this occur ?
|
10% weight loss within first 2 weeks of life.
|
|
|
What is used to monitor newborns after birth
|
APGAR
NEWS chart |
|
|
when is APGAR performed and what does it measure ? |
@ birth, 5min , 10 mins
Appearance - (Pink - Acrocyanosis- blue ) Pulse (>100 - <100- none) Grimace (pulls away - grimaces - none) Activity (Flexed- mild flexion- extension) RR ( Crying - weak cry - none) |
|
|
What is a normal APGAR ? |
9-10 |
|
|
For a newborn, what is a normal
RR HR BP Cap refill ? |
RR 20-60
HR 110-160 bpm
BP 90/60mmHg
Cap.refill <2-3s |
|
|
When should a neonate produce
urine Meconium |
Urine < 24 hrs
Meconium < 28 hrs |
|
|
In a newborn, what does
Nasal flarring mean ? Bilious vomitting ? |
Nasal flarring -> resp. distress
Bilious vomitting -> Malrotation -URGENT AXR/CT |
|
|
From ROM , when should labour be initiated ?
|
< 24 hrs
|
|
|
How long should a baby be breastfed? |
6 months |
|
|
Give advice on breastfeeding |
Good attachment Switch breasts Express milk prior to feeds
Watch out of Dx Avoid Alcohol/smoking
No guaranteed contraception |
|
|
What are the benefits of breastfeeding ? |
For baby - more nutritious, Immunity , warm, bonding
Contraception
Protection against breast CA
CHEAP! |
|
|
What are the cons of breastfeeding ? |
If poor attachment - Nipple trauma, engorgement, mastitis, poor feeding
No monitoring of feeds
Dx can spread to child |
|
|
What is engorgement ?
S/S
Rx |
Engorgement of breast due to poor feeding (milk left in breast!)
S/S - Swollen shiny breasts
Rx- ↑ breastfeeding (cold compress/hot shower) |
|
|
What is mastitis ?
S/S Rx |
Infection of breast
S/S: red hot swollen tender breasts
Pus or bloody discharge
Rx: ↑breast feeding , PO flucloxacillin |
|
|
What is full cervical dilatation ? |
10cm |
|
|
How often are contractions during labour ? |
1xcontraction every 2-3 mins ( due to risk of fetal hypoxia!) |
|
|
What is normal progression of cervical dilatation ? |
1cm/hr |
|
|
After ROM, when should labour occur ? Why? |
<24 hrs - due to risk of infection |
|
|
For induction of labour, what scoring system is used ?
What do the scores mean ? |
Bishops scoring system
If <5 --> PG + CTG If > 5 --> Artificial ROM + CTG |

