![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Follicular phase
|
High estrogen, tract conducive to sperm and egg transport
|
|
|
Luteal phase
|
High progesterone, tract conducive to pregnancy
|
|
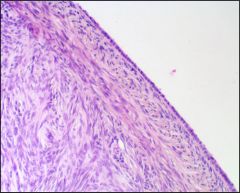
What is this?
Histology? |
Ovary
Simple cuboidal |
|
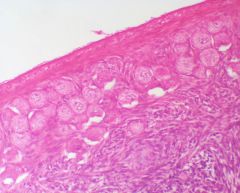
Name the three distinct tissue types in this picture from outer to inner
|
Tunica albuginea (connective tissue);
Cortex; follicles Medulla; fibroelastic tissue |
|
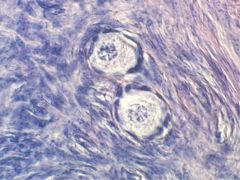
Follicle type?
Histology? |
Primordial;
Single layer of squamous cells |
|
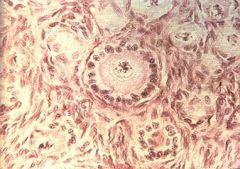
Follicle type? Histology?
|
Primary;
Single layer of cuboidal cells |
|
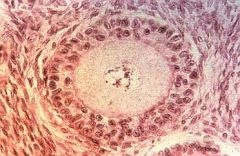
Follicle type? Histology?
|
Secondary; 2+ layers of follicular cells - NO antrum
|
|
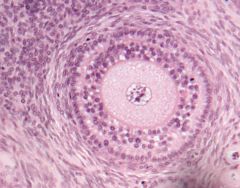
What lays between oocyte and follicular cells?
And what is the name for cells right outside zona pellucida? |
Zona pellucida;
Corona radiata |
|
|
Three layers of tertiary follicles?
|
Membrana ganulosa
Theca interna Theca externa |
|
|
What receptors are found in membrana granulosa? What does this layer produce?
|
FSH
Produces estrogen, inhibin, and follicular fluid |
|
|
Theca interna is under the influence of ___ and produces ______
|
LH; androgens
|
|
|
Theca interna is made of loose ______ and ______ the follicle
|
Connective tissue; supports
|
|
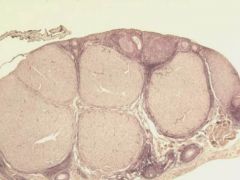
What layer makes up most of corpora lutea?
|
Membrana granulosa
|
|
|
LARGE luteal cells originate from ?
SMALL luteal cells originate from ? |
Granulosa
Theca |
|
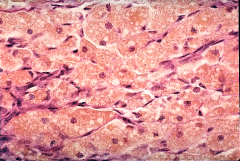
Small luteal cells are shaped how, where are they on this slide?
|
Flat and thin, dark stained cells
|
|
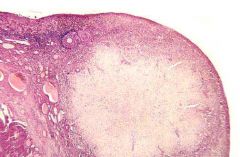
What is this?
This structure is made of what, and it takes the place of what structure? |
Corpus albicans
Made of connective tissue Takes place of CL |
|
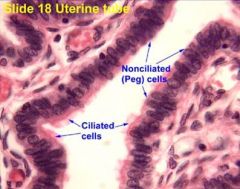
Histology of isthmus and ampulla?
|
Simple and pseudostratified columnar ciliated and non-ciliated together
|
|
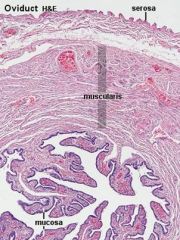
What is
|
Thing
|
|
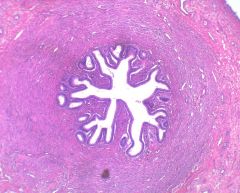
Isthmus
|
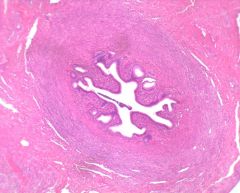
Isthmus
|
|
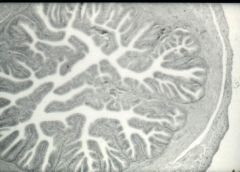
Ampulla
|
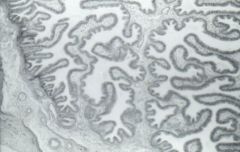
Ampull
|
|
|
Uterus histology?
|
Simple and psuedostratified columnar
|
|
|
Phase changes in uterus
|
Follicular: Uterine glands appear straight
Luteal: Appear coiled, tall epithelial cells |
|
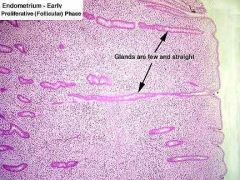
Uterus follicular
|
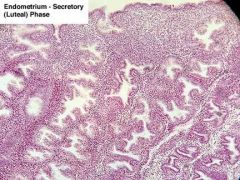
Uterus luteal
|
|
|
Cervix epithelium?
|
Simple columnar epithelium, Goblet cells
|
|
|
Phase changes in cervix
|
Follicular: Narrow lu
|

