![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Draw the symbol for Hinduism |

|
|
|
Draw the symbol for Buddhism |
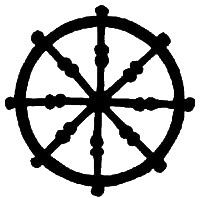
|
|
|
Draw the symbol for Sikhism |

|
|
|
2. The word “religion” comes from the Latin verb “religio.” Explain the meaning of the verb. |
The verb means to bind together. Religions bind people together through common beliefs, ethics, spiritual principles, etc. |
|
|
Secular |
non-religious or separate from organized religion. |
|
|
b. Monotheism- |
The belief that there is only one personal Supernatural Being. |
|
|
c. Omnipotent- |
All-powerful |
|
|
d. Omniscient- |
All-knowing |
|
|
e. Deism- |
The belief that the one God created the universe but does not affect the universe or people’s lives. |
|
|
Polytheism |
The belief that there are many Gods and Goddesses who are responsible for different aspects of life and nature. |
|
|
Pantheism |
The belief that everything is God and God is not a separate being from the universe. |
|
|
Anthropomorphism |
Giving human characteristics to something that is not human (depicting Gods in human form) |
|
|
Agnosticism |
A person who neither believes nor disbelieves the existence of God. |
|
|
Transcendent |
A dimension beyond the spatial/temporal limits of the universe. |
|
|
k. Immanent- |
Within space/time of the universe. |
|
|
4. Name and explain the three ways in which religion might view other religions |
1. Exclusivist- my religion is the only one true and good religion. Other religions are false and wrong. 2. Inclusivist- other religions can be included under my religion because my religion is the new and improved version of other religions, and therefore my religion is better. 3. Pluralist- There are many different good religions that have helped people and no one religion has a monopoly on the truth. |
|
|
What is the Latin name for the modern Catholic teaching on non-Christian religions? At which meeting of Catholic bishops was this document written? In which year? What does this document say about the attitude of the Roman Catholic Church toward non-Christian religions? |
Nostra Aetate, The Second Vatican Council. 1965. The Catholic church rejects nothing that is true and holy in non-Christian religions. |
|
|
6. Give 4 basic questions that religions try to answer. |
1. What is moral and immoral? 2. What makes us happy and fulfilled? 3. What happens to us after death? 4. What is ultimately real and true? |
|
|
7. What is the name of the calendar used by Orthodox and other eastern Christians? What is the name of the calendar used by Catholic and Protestant Christians? What do the letters “BCE” and “CE” stand for, and why do many non-Christians prefer them to “BC” and “AD”? How are the religious calendars used by Jews and Muslims similar yet different? What is unique about the Baha’i calendar? |
The Julian Calendar. The Gregorian Calendar. BCE= before the common era, CE= common era, many non-Christians prefer these to BC and AD specifically reference Christ as a marker of the year. Both are lunar calendars but the years in which the calendars start are different. The Baha’i calendar has 19 months with 19 days in each. |
|
|
8. What is the name of the basic ethical teaching found in all of the major religions? Give Confucius’ formulation of this teaching. Give Jesus’ formulation of this teaching. |
The Golden Rule. Do not do unto others as you would not have them done unto you. Treat others the way you want them to treat you. |
|
|
9. What are 6 basic commandments that all of the great religions teach? |
1. Do not kill 2. Do not commit adultery 3. Do not steal 4. Do not lie 5. Honor your parents &respect the elderly 6. Help the helpless |
|
|
10. Which religion teaches that there has been only one divine incarnation? Name a religion that teaches that there have been many divine incarnations. Name two monotheistic religions that do not believe in the possibility of incarnation. |
(Christianity), (Hinduism and some Buddhists), (Judaism and Islam) |
|
|
11. Name and explain three classical philosophical arguments for a monotheistic view of God. |
1. Argument from Purpose: without the possibility of union with God, human beings would have no purpose. 2. Argument from Miracles: A supernatural God must exist to explain supernatural events in human life. 3. Teleological Argument: There must be a great architect who designed the complex and well organized universe. |
|
|
12. Define “atheism.” Name three atheistic philosophers and give their reason for atheism. |
a. Atheism is the belief that a personal God or supreme being does not exist. b. Karl Marx- Religion is the opium of the people.c. Sigmund Freud – God is the need for a father-figure d. Albert Camus- I cannot believe in a God who lets innocent children suffer. |
|
|
13. How is religion different from science? According to Huston Smith, what “scientism”? Scientism is the belief that the only truth is what can be explained through science. |
Science relies on what can be proven, while religion relies on faith. Scientism is the belief that the only truth is what can be explained through science. |
|
|
14. Hinduism teaches that people want three things. What are they? |
a. Pleasure, Success (wealth, fame, and power), Ethical duty |
|
|
15. According to Hinduism, what do people really want? |
a. Moksha: liberation or release from anything which keeps us from Brahman so that we might be absorbed into Brahman. |
|
|
16. Explain the Hindu belief in Brahman. What are the names of the creative, preservative, and destructive aspects of Brahman? What is Krishna considered? |
Hindu name for Ultimate Reality or Universal consciousness. (Brahma), Vishnu, and Shiva.Krishna is considered an Avatar or an incarnation of God. |
|
|
17. What is meant by “Atman”? What do Hindus mean by “Namaste”? |
Brahman within all creatures. The Atman within me honors the Atman within you. |
|
|
18. What is the meaning of the word “yoga”? |
To join |
|
|
What is the purpose of yoga? |
To achieve God-consciousness |
|
|
What is the very first step of any kind of yoga? |
To remove all distractions. |
|
|
What is the Hindu name for the yoga that involves physical exercise? |
Hatha Yoga |
|
|
Give the Hindu names of the four kinds of spiritual yoga and then briefly describe each. |
a. Karma yoga- unselfish action, service and work b. Bhakti yoga- devotion and love c. Jnana yoga- knowledge about spiritual realityd. Raja yoga- meditation |
|
|
19. According to Hinduism, what are the four stages of human’s life? |
Student, Householder, Retirement, and Sannyasin |
|
|
20. What are the four basic castes in traditional India? |
a. Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, and Shudras. |
|
|
21. What is the name of the river in India that is considered to be sacred to Hindus? |
Ganges River |
|
|
22. Explain the Hindu belief in reincarnation. What is the law of karma? |
a. Many Hindus believe that the soul passes through many lives until union with Brahman is met. Karma is the moral law of cause and effect. |
|
|
23. What is the language in which the Hindu scriptures were written? |
Sanskrit |
|
|
24. What is the name of the Hindu holy man in the 19th century who practiced different religions? What are the three religions he practiced? Because of this experience, what did he conclude about the different religions of the world? |
Shri Ramakrishna. Hinduism, Christianity, and Islam. People of different religions can have the same mystical experience of God. |
|
|
25. Write the sentence from the Rig Veda that expresses the Hindu belief of accepting different religions as different approaches to Ultimate Reality, similar to different paths to the summit of a mountain. |
“Truth is one, Sages call it by various names” |
|
|
a. Moksha- |
absorption into Brahman |
|
|
b. Jiva- |
an individual soul |
|
|
c. Avatar- |
incarnation of God |
|
|
d. Harijan- |
God’s people |
|
|
e. Samsara |
reincarnation |
|
|
f. Maya- |
the illusion that we are separate from Brahman |
|
|
g. Japam- |
Constantly repeating divine names |
|
|
h. Puja- |
religious rituals and worship |
|
|
27. What does the word “Sikh” mean? |
Disciple or Student |
|
|
What does the word “guru” mean? |
Teacher or One who enlightens |
|
|
28. Who is the founder of Sikhism? When did he live? |
Guru Nanak 1500AD |
|
|
29. What is the name of the Sikh scripture? |
Guru Granth Sahib |
|
|
30. As a blending of Islam and Hinduism, what are four things that Sikhism, in keeping with the Islamic revelation, rejected of Hinduism? Contrary to Islam, which Hindu belief does Sikhism accept? |
1. Avatars as divine incarnations 2. Images as aids to worship 3. Vedas (Hindu Scriptures) 4. Caste System Sikhism accepts Reincarnation |
|
|
31. What are the 5 Ks of Sikhism? Tell what each symbolizes. |
Kesa- uncut hair, accepting the way God made us Kangha- Wood comb, cleanliness Kara- Steel Bracelet, God's eternity Kacch- Long underwear, sexual purity Kirpan- Small Sword, defense of justice and sharpness of truth |
|
|
32. In which section of India did Sikhism develop? In which city is their Golden Temple? |
Amritsar, India. Punjab area |
|
|
33. What does the title “Buddha” mean? |
Enlightened or awakened one |
|
|
What are the first name and the family name of the Buddha? When did he live? Where did he live? |
Siddhartha Gautama, 500 BC, Nepal |
|
|
What did he do before he was 29 years old? What did he do from age 29 to 35? What did he do from age 35 to 80? |
Spoiled prince then wandering and denying himself pleasure then the middle path of pleasure and teaching his dharma to the sangha. |
|
|
34. Explain each of the Four Noble Truths which the Buddha discovered. |
1. Life is imperfect. it is a series of sufferings and frustrations. 2. Tanha is the cause of suffering. It is the desire for selfish things. 3. Suffering is cured by restraining selfish desires. 4. Enlightenment comes after following the eightfold path. |
|
|
35. List the eight areas of life that the Buddha called the “Eightfold Path” to enlightenment. |
Right Livelihood Right Intent Right Views Right Effort Right Speech Right Conduct Right Mindfulness Right Concentration |
|
|
36. What do Buddhists mean by “nirvana”? |
to blow out or to extinguish. Escaping the cycle of reincarnation or paranirvana. |
|
|
37. What is meant by the Buddhist teaching of “anatta”? |
No Atman, no permanent soul. the Soul and the Mind are verbs, not nouns. |
|
|
38. Huston Smith describes Buddhism as a “protestant” form of Hinduism. In contrast to the Hinduism of his day, what are five things that Buddha’s teaching was devoid of or lacked? What did Buddha emphasize in his teaching? |
Lacking or devoid of: Supernatural- rather focus on overcoming suffering Tradition- dropped Sanskrit as a religious language Authority- rejecting the need for the Brahmins Ritual- ceremonies in temples not considered neccesary Speculation- Buddha's parable of the poison arrow. Then Emphasizing intense self-effort. |
|
|
39. Name the major divisions within Buddhism and then tell in which part of Asia they are found. What is the difference between these groups concerning how they view the Buddha? What is an Arhat? What is a bodhisattva? |
Theravada (Southern Asia) and Mahayana (Northern Asia). Theravada views Buddha as a great teacher while Mahayana viewed him as a divine being. Arhat is a saint or ideal. Bodhisattva is to escape rebirth but return to help others. |
|
|
40. What is the title of the leader of Tibetan Buddhism? What is this person believed to be? How is this person chosen to fulfill this role? |
Dalai Lama. Reincarnation of the Buddha. Through a system that tracks the reincarnation of the previous Dalai Lama. |
|
|
41. Explain the special chant and form of meditation that some Tibetan Buddhist monks practice. |
Some monks have trained themselves to sing chords individually as a form of meditation. |
|
|
42. Explain what some Tibetan Buddhist monks do to learn patience and the Buddhist concept of impermanence. |
Some monks create Sand mandalas. |
|
|
43. What is Zen Buddhism? What is “zazen”? What is a “koan”? What is the purpose of koan training? Give an example of a Zen koan. |
Japanese and Korean form of Buddhism. Zazen is "seated meditation". Koan training is meant to cause a mental breakdown followed by a breakthrough. "What is the sound of one hand clapping?" |

