![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pyogenic Granulomas |
- Rapidly growing lesion in response to local irritation -Erythematous, none-painful, smooth or lobulated mass that often bleeds easily when touched. - Occur in 5% of pregnant women (hormones) Treatment - Surgical excision (small chance of recurrence) |
|
|
Nicotine Stomatitis |
- Symmetric whitened hard palate with scattered punctate red papules - Painless and benign inflamed salivary ducts - Commonly seen in smokers, but could be due to hot food/beverage Treatment - Self-limited - Stop whatever caused it. |
|
|
Traumatic Ulcers |
- Ulcer with white border - May mimic deep fungal infections or SCC. Treatment - Biopsy if it does not heal in 2 weeks. |
|
|
Fibromas |
Fibroma - Soft white/pinkish nodule - hyperplastic fibrous connective tissue representing a reactive response to local irritation or trauma. Treatment - Excision (pathologic examination to rule out neoplasm) - recurrence after excision is not common |
|
|
Papillomas |
a small wartlike growth on the skin or on a mucous membrane, derived from the epidermis and usually benign |
|
|
Mucoceles |
- Collection of fluid (salivary mucin) from a traumatized duct. - More commonly occurs on lower lip Treatment - Excision with adjacent "feeder" salivary glands |
|
|
Leukoplakia |
WHO - “a white patch or plaque that cannot be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other disease." Medical term for a white, flat lesion that CANNOT be rubbed off. (not a diagnosis) - 1-20% develop into carcinoma w/in 10 years - best known pre-malignant oral lesion Treatment - Biopsy |
|
|
Erythroplakia |
- Red, flat lesion that cannot be rubbed off. - Erythroplakia and speckled leukoplakia are more likely than leukoplakia to exhibit dysplasia or carcinoma microscopically |
|
|
Leukoplakia vs. Erythroplakia |
Leukoplakia - White, flat lesion that cannot be rubbed off combined red and whitelesions are known as speckled leukoplakiaor erythroleukoplakia Erythroplakia - Red, flat lesion that cannot be rubbed off. - Erythroplakia andspeckled leukoplakia are more likely thanleukoplakia to exhibit dysplasia or carcinomamicroscopically Treatment - Biopsy |
|
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
Most common location is on the tongue, floor of themouth, and vermilion border of the lowerlip. - Tobacco andalcohol mayaccount forup to 80 percent of cases of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck - OSCC may also be HPV driven(primarily HPV 16) lesionsthat are p16+ may have a much betterprognosis Treatment - Guided by clinicalstaging. The overall five-year survival rate fororal cancer is 50 to 55 percent - Long-termfollow-up is advised because of the potentialfor recurrence or additional lesions |
|

|
Traumatic Ulcer - Ulcer with white border. Treatment - Biopsy if ulcer does not resolve in 2 weeks |
|

|
Mucocele (Ranula = floor of mouth mucocele) - Collection of fluid (salivary mucin, granulation tissue) from traumatized salivary duct. - Most commonly on lower lip - Common occurrence in children (lip-biting) - Cannot occur on gingiva (no salivary glands) Treatment - Excision with salivary gland to prevent recurrence. - Biopsy to rule out neoplasia |
|

|
Pyogenic Granuloma - Lobular proliferation of endothelial cells, blood vessels, andgranulation tissue - 75-80% occur on gingiva DDx: - Parulis, peripheral ossifying fibroma, peripheral giant cellgranuloma Tx: - Excision - Observation in pregnant women (common to resolve after birth) |
|

|
Nicotinic Stomatitis - symmetric whitened hard palate with scatteredpunctate red papules - Painless and benign inflamed salivary ducts - Commonly seen in smokers, but could be due to hot food/beverage Treatment - Self-limited - Stop whatever caused it. |
|

|
Fibroma - Soft white/pinkish nodule - hyperplastic fibrousconnective tissue representing a reactiveresponse to local irritation or trauma. Treatment - Excision (pathologic examination to rule out neoplasm) - recurrence after excision is not common |
|
|
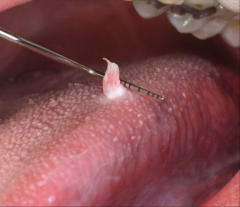
Squamous papilloma - Caused by HPV (50% HPV 6, 11) - Very low virulence & infectivity rate - Multiple lesions seen in childrenmay represent Heck disease |
|

|
Squamous papilloma - Caused by HPV (50% HPV 6, 11) - Very low virulence & infectivity rate - Multiple lesions seen in childrenmay represent Heck disease Treatment - Excision |
|

|
Leukoplakia (Sideof the tongue is very dangerous. Cantravel to lymphocytes). |
|

|
Erythroplakia |
|
|
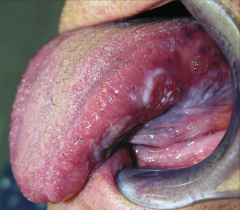
Squamous cell carcinoma - A malignancy characterized bythe invasion of epithelium into theconnective tissue - Most common malignancy of oral cavity Risk Factors - Tobacco and/or alcohol use |
|

|
Squamous cell carcinoma |

