![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the presenting symptoms of AML?
|
* Recent onset fatigue (anemia)
* Weakness (anemia) * Fever/infection (neutropenia) pneumonia, UTI,cellulitis pharyngitis esophagatis * Bleeding (thrombocyto.) epistachis , exymosis, petechia, bleeding from pucnture sites splenomegaly hepatomegaly lymphadenopahty bone and joint pain( invasion of periosteum) CNS involvment( diffuse or local-- meningitis, seizures) testicular involvement( ALL) skin nodules( AML) |
|
|
What causes the presenting symptoms of AML?
|
Marrow infiltration and replacement of normal blood precursor cells.
|
|
|
What are the tell-tale signs of AML on a peripheral blood smear?
|
* High white cell count (may be normal or low)
* Leukemic blast cells (>20% is diagnostic) |
|
|
What is the diagnostic test for AML?
|
Bone marrow aspirate, showing a hypercellular blast count >20%
|
|
|
Other than blood, are other tissues involved in AML?
|
Yes. Leukemic infiltration of the GUMS (gingival hyperplasia), skin or CNS. Site tumors are CHLOROMAS.
|
|
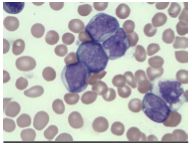
[Peripheral Smear] What are these cells called? What are their characteristics?
|
Myeloblast Cells from AML
* Mononuclear * Scant cytoplasm * Prominent pale nuclei |
|
|
What are the two classification schemes for AML?
|
1) French-American-British (FAB - Older)
2) WHO (newer) |
|
|
How are AML sub-type diagnoses performed?
|
1) Histologically (FAB)
2) Molecular subtypes 3) Cytogenetics (WHO) |
|
|
What two disorders often lead to AML
|
1) Myelodysplastic Sydrome
2) Myeloproliferative Disorders (P Vera, ET, etc.) |
|
|
What is the CR rate for AML treated with combination chemo?
|
60-80% within 9-15 months
|
|
|
What is the induction therapy used for AML?
|
1) Cytosine Arabinoside (antimetabolite)
2) Idarubicin or Daunorubicin (anthracycline) |
|
|
What is the consolidation therapy for AML?
|
High-dose Cytosine Arabinoside (HiDAC)
|
|
|
When would stem-cell transplant be used in AML?
|
During the FIRST REMISSION can achieve a 60% cure rate, however it is limited to 65 years or under, with an HLA-matched donor
|
|
|
What are indicators of a poor prognosis in AML?
|
1) Preceding myelodysplastic disease
2) Age >60 3) Certain cytogenetic problems (bcr-abl) 4) Failure to achieve CR with first round induction therapy |
|
|
What is the major factor used to predict AML outcome and the need for transplant?
|
Tumor cell cytogenetics
|
|
|
What is a potential complication of a very high WBC count?
|
Leukostasis may occur with WBC counts >100K. Large cells clog caps, cause tissue hypoxia.
|
|
|
What are the critical complications of LEUKOSTASIS?
|
1) CNS -> intracranial hemorrhage
2) Pulmonary -> respiratory failure |
|
|
What is the treatment for leukostasis?
|
Leukapheresis
|
|
|
What disease is responsive to All Trans Retinoic Acid?
|
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
|
|
|
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
|
All Trans Retinoic Acid (ATRA)
|
|
|
What critical complication often accompanies APL presentation?
|
DIC, likely due to the release of thrombogenic substances by the leukemic promyelocytes.
|
|
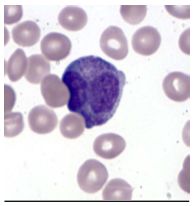
What disease is associated with this cell type? Describe the cell's characteristics.
|
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia.
* Azurophilic granues |
|
|
What is the main fungal infection in AML?
|
Aspergillus
|
|
|
What viral reactivations must be prevented in AML?
|
CMV and HSV. Run serology tests as part of an AML workup.
|
|
|
On the blood smear, what WBC cytoplasmic clue is closely linked with AML?
|
Auer Rods
|
|
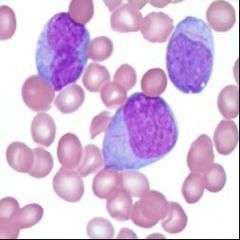
What disease may be diagnosed based on this finding?
|
These blast cells contain AUER RODS, indicating Acute Myelogenous Leukemia.
|
|
|
What monoclonal antibody drug may be given for good-prognosis AML?
|
Gemtuzumab (anti-CD33 antibodies)
|
|
|
What chromosomal translocation leads to Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia?
|
Specific t (15;17) translocation juxtaposes retinoic acid receptor gene (RARα) next to PML gene.
|
|
|
How is an allo stem cell transplant performed for AML?
|
High dose chemoradiotherapy:
* Cytoxan +Total body irradiation for 4 day OR High Dose Chemo: * Cytoxan + Busulfan |
|
|
What's the full name for the condition FAB-M3?
|
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
|
|
|
keywords for AML?
|
keywords for AML?
malignant disease of the bone marrow in which hematopoietic precursors are arrested in an early stage of development |
|
|
incidence of AML?
|
incidence of AML?
2.5/100'000, rising with increasing age |
|
|
what proportion of AML affects adults?
|
what proportion of AML affects adults?
80% |
|
|
median age in AML?
|
median age in AML?
60 years |
|
|
principal pathophysiology in AML?
|
principal pathophysiology in AML?
maturational arrest of bone marrow cells in earliest stages of development <-- in many cases activation of abnormal genes through chromosomal translocations and other genetic abnormalities |
|
|
major disease processes in AML?
|
major disease processes in AML?
marked decrease in production of normal blood cells --> anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia rapid proliferation of arrested cells with accumulation in the bone marrow, blood and frequently liver and spleen |
|
|
M:F in AML?
|
M:F in AML?
M>F, likely because MDS more frequent in men and advanced MDS often with progression to AML |
|
|
principal groups of clinical symptoms in AML?
|
principal groups of clinical symptoms in AML?
symptoms from bone marrow failure and/or symptoms from organic infiltration with leukemic cells |
|
|
major symptoms of bone marrow failure in AML?
|
major symptoms of bone marrow failure in AML?
anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia --> fatigue, history of persistent upper respiratory infections and bleeding |
|
|
most common sites of organic infiltration with leukemic cells in AML?
|
most common sites of organic infiltration with leukemic cells in AML?
spleen, liver, gums, skin |
|
|
organic infiltration most common in which forms of AML?
v |
organic infiltration most common in which forms of AML?
monocytic subtypes |
|
|
symptoms from splenomegaly?
|
symptoms from splenomegaly?
fullness in LUQ and early satiety |
|
|
symptoms from gum infiltration?
|
symptoms from gum infiltration?
gingiva hyperplasia, gingivitis, gum bleedin |
|
|
symptoms from leukostasis (hyperviscosity syndrome)?
|
symptoms from leukostasis (hyperviscosity syndrome)?
triad of bleeding diathesis, visual disturbances and focal neurologic signs bleeding: epistaxis or gingivorrhagia visual disturbances: decreased visual acuity, distended or thrombotic veins, papillary edema focal neurologic signs: dizziness, seizures, coma, stroke additionally respiratory distress altered mental status and priapism |
|
|
which of the hematologic disorders is the most ccommon risk factor for AML?
|
which of the hematologic disorders is the most ccommon risk factor for AML?
presence of antecedent hematologic disorder, most common of which is MDS others are aplastic anemia, MPN (myelofibrosis, PV) and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria |
|
|
congenital disorders presenting a risk factor for AML?
|
congenital disorders presenting a risk factor for AML?
Down syndrome Bloom syndrome Fanconi anemia neurofibromatosis --> usually AML during childhood |
|
|
types of chemotherapy as risk factor for AML?
|
types of chemotherapy as risk factor for AML?
alkylating agents often MDS then AML topoisomerase-II inhibitors no MDS before AML |
|
|
criteria for diagnosis of acute leukemia?
|
criteria for diagnosis of acute leukemia?
>20% blasts in the bone marrow |
|
|
what are the major WHO classification groups in AML?
|
what are the major WHO classification groups in AML?
AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities AML with myelodysplasia-related changes therapy-related myeloid neoplasms AML, NOS (not otherwise specified) |
|
|
object of induction therapy?
complete hematologic remission |
object of induction therapy?
complete hematologic remission i.e. blasts <5%, "normalisation " of peripheral blood count |
|
|
object of induction therapy?
|
common induction therapy in AML exc M3?
combination therapy ara-C plus anthracycline (eg daunorubicin, idarubicin) mnemonic: AML --> American Airlines = AA |
|
|
object of consolidation therapy in AML?
|
object of consolidation therapy in AML?
prevention of relapse |
|
|
options in consolidation therapy in younger patients in AML?
|
options in consolidation therapy in younger patients in AML?
chemotherapy, eg high-dose ara-C autologous stem-cell transplantation allogeneic stem cell transplantation |
|
|
what is AML M3 and what are characteristic findings?
acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) |
what is AML M3 and what are characteristic findings?
acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) cytogenetic findings are t(15;17) and the fusion gene PML-RAR alpha |
|
|
of what risk are the majority of AML?
|
of what risk are the majority of AML?
intermediate risk with either normal cytogenetics or abnormalities that do no confer strong prognostic significance |
|
|
what are cytogenetic finding confering poor prognosis in AML?
|
what are cytogenetic finding confering poor prognosis in AML?
monosomy 5 or 7 or complex cytogenetics with more that threee separate abnormalities |
|
|
what are cytogenetic finding confering poor prognosis in AML?
|
what are cytogenetic finding confering poor prognosis in AML?
monosomy 5 or 7 or complex cytogenetics with more than three separate abnormalities |
|
|
what is the treatment for the AML variant APL?
|
what is the treatment for the AML variant APL?
induction therapy with an anthracycline plus all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) |
|
|
what is the median age in APL?
|
what is the median age in APL?
40 years, thus considerably lower median age than other subtypes |
|
|
with what finding is bleeding in APL frequently associated
|
with what finding is bleeding in APL frequently associated
DIC |
|
|
what is the prognosis in AML for adults <60 years?
80% under age 60 with complete remission with high-dose remission therapy half of those with cure (40%) |
what is the prognosis in AML for adults <60 years?
mnemonic: 80-half-half 80% under age 60 with complete remission with high-dose remission therapy half of those with cure (40%) allogeneic bone marrow transplantation curative in half of cases |
|
|
what is the prognosis in AML for adults >60 years?
|
what is the prognosis in AML for adults >60 years?
50% over age 60 with complete remission cure rate in only 10% mnemonic: 50 + 10 = 60 |
|
|
what are the principle therapy steps particular in APL?
|
what are the principle therapy steps particular in APL?
induction therapy, followed by a consolidation therapy, also called postremission therapy and aditionally a maintenance therapy |
|
|
at does the maintenance therapy in APL consist of?
|
at does the maintenance therapy in APL consist of?
6-Mercaptopurin daily Methotrexat weekly ARTRA intervals every 3 months mnemonic: maintenance therapy with MiXed Martial ARTs = MMA |
|
|
what is the pathognomonic finding in the blood smear of AML?
|
what is the pathognomonic finding in the blood smear of AML?
Auer rods, which is an eosinophilic needle-like inclusion in the cytoplasm of blasts |
|
|
what are the phenotypic findings in AML?
|
what are the phenotypic findings in AML?
myeloid antigens such as CD13 or CD33 |
|
|
what is the method to determine the immunophenotype of the leukemia?
|
what is the method to determine the immunophenotype of the leukemia?
flow cytometry |
|
|
what are the histochemic findings in AML?
|
what are the histochemic findings in AML?
peroxidase in myeloid cells and butyrate esterase in monocytic cells |
|
|
what is the differential diagnosis to AML?
|
what is the differential diagnosis to AML?
other myeloproliferative disorders, such as CML and myelodysplastic syndrome |

