![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the presenting symptoms of AML?
|
* Recent onset fatigue (anemia)
* Weakness (anemia) * Fever/infection (neutropenia) * Bleeding (thrombocyto.) |
|
|
What causes the presenting symptoms of AML?
|
Marrow infiltration and replacement of normal blood precursor cells.
|
|
|
What are the tell-tale signs of AML on a peripheral blood smear?
|
* High white cell count (may be normal or low)
* Leukemic blast cells (>20% is diagnostic) |
|
|
What is the diagnostic test for AML?
|
Bone marrow aspirate, showing a hypercellular blast count >20%
|
|
|
Other than blood, are other tissues involved in AML?
|
Yes. Leukemic infiltration of the GUMS (gingival hyperplasia), skin or CNS. Site tumors are CHLOROMAS.
|
|
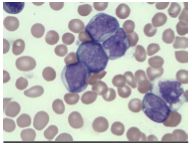
[Peripheral Smear] What are these cells called? What are their characteristics?
|
Myeloblast Cells from AML
* Mononuclear * Scant cytoplasm * Prominent pale nuclei |
|
|
What are the two classification schemes for AML?
|
1) French-American-British (FAB - Older)
2) WHO (newer) |
|
|
How are AML sub-type diagnoses performed?
|
1) Histologically (FAB)
2) Molecular subtypes 3) Cytogenetics (WHO) |
|
|
What two disorders often lead to AML
|
1) Myelodysplastic Sydrome
2) Myeloproliferative Disorders (P Vera, ET, etc.) |
|
|
What is the CR rate for AML treated with combination chemo?
|
60-80% within 9-15 months
|
|
|
What is the induction therapy used for AML?
|
1) Cytosine Arabinoside (antimetabolite)
2) Idarubicin or Daunorubicin (anthracycline) |
|
|
What is the consolidation therapy for AML?
|
High-dose Cytosine Arabinoside (HiDAC)
|
|
|
When would stem-cell transplant be used in AML?
|
During the FIRST REMISSION can achieve a 60% cure rate, however it is limited to 65 years or under, with an HLA-matched donor
|
|
|
What are indicators of a poor prognosis in AML?
|
1) Preceding myelodysplastic disease
2) Age >60 3) Certain cytogenetic problems (bcr-abl) 4) Failure to achieve CR with first round induction therapy |
|
|
What is the major factor used to predict AML outcome and the need for transplant?
|
Tumor cell cytogenetics
|
|
|
What is a potential complication of a very high WBC count?
|
Leukostasis may occur with WBC counts >100K. Large cells clog caps, cause tissue hypoxia.
|
|
|
What are the critical complications of LEUKOSTASIS?
|
1) CNS -> intracranial hemorrhage
2) Pulmonary -> respiratory failure |
|
|
What is the treatment for leukostasis?
|
Leukapheresis
|
|
|
What disease is responsive to All Trans Retinoic Acid?
|
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
|
|
|
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
|
All Trans Retinoic Acid (ATRA)
|
|
|
What critical complication often accompanies APL presentation?
|
DIC, likely due to the release of thrombogenic substances by the leukemic promyelocytes.
|
|
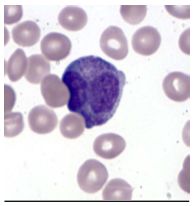
What disease is associated with this cell type? Describe the cell's characteristics.
|
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia.
* Azurophilic granues |
|
|
What is the main fungal infection in AML?
|
Aspergillus
|
|
|
What viral reactivations must be prevented in AML?
|
CMV and HSV. Run serology tests as part of an AML workup.
|
|
|
On the blood smear, what WBC cytoplasmic clue is closely linked with AML?
|
Auer Rods
|
|
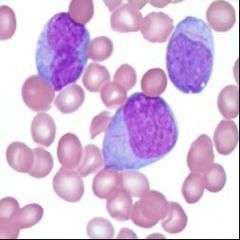
What disease may be diagnosed based on this finding?
|
These blast cells contain AUER RODS, indicating Acute Myelogenous Leukemia.
|
|
|
What monoclonal antibody drug may be given for good-prognosis AML?
|
Gemtuzumab (anti-CD33 antibodies)
|
|
|
What chromosomal translocation leads to Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia?
|
Specific t (15;17) translocation juxtaposes retinoic acid receptor gene (RARα) next to PML gene.
|
|
|
How is an allo stem cell transplant performed for AML?
|
High dose chemoradiotherapy:
* Cytoxan +Total body irradiation for 4 day OR High Dose Chemo: * Cytoxan + Busulfan |
|
|
What's the full name for the condition FAB-M3?
|
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
|

