![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lisfranc
|
Evaluation requires AP, oblique, & lateral views
No gap 1st & 2nd MT bases AP view, lateral cortex of 1st MT must align perfectly with lateral cortex of medial cuneiform AP view, medial cortex of 2nd MT must align perfectly with medial cortex of middle cuneiform OBL view, medial cortex of 3rd MT must align perfectly with medial cortex of lateral cuneiform OBL view, medial cortex of 4th MT must align perfectly with medial cortex of cuboid OBL view, articular surface of 5th MT aligns with articular surface of cuboid; the nonarticular portion of the base of 5th MT projects laterally LAT usually normal, despite severe disruption; if abnormal, the MT's sublux dorsally 20-25% missed by radiographic evaluation |
|
|
Types of Arthritis
|
Chondropathic
Inflammatory Depositional Other |
|
|
Chondropathic
|
Osteoarthritis
CPPD Hemochromatosis Hemophilia Neuropathic |
|
|
Inflammatory
|
RA
JRA Psoriatic Reiter's AS Infection |
|
|
Depositional
|
Gout
Amyloid Hyperlipidemia Sarcoid PVNS |
|
|
Other Arthropathy
|
SLE
Scleroderma HOA Hyper PTH |
|
|
Chondropathic Arthritis Features
|
Cartilage degeneration caused by damage to the articular cartilage or subchondral bone
non-uniform joint narrowing osteophytes subchondral sclerosis and cysts |
|
|
Primary OA
|
DIP > PIP > MCP
1st CMC No erosions, BD N |
|
|
Typical OA
|
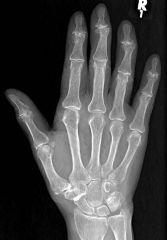
DIP > PIP > MCP
1st CMC No erosions, BD N |
|
|
Erosive OA
|
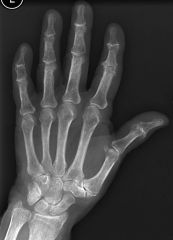
Chondropathic and erosive
Erosions typically central Ankylosis may occur Changes mainly IP joints Symmetric |
|
|
Charcot Features
|
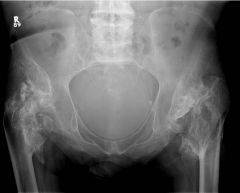
|
|
|
RA
|
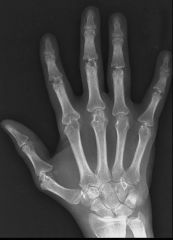
wrist, MCPs, PIPs
DIPs spared symmetrical osteopenia marginal erosions diffuse joint space narrowing fusiform soft tissue swelling subluxations |
|
|
RA Findings (Early)
|
Ulnar styloid
2/3 MCP Foot - 5th MCP affected 1st |
|
|
Chronic JRA
|
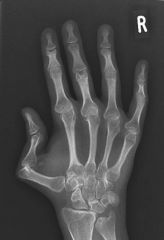
Tendency to involve wrist > MCP or IP joints
Imaging reflects changes to growing bones: Overgrowth at bone ends (ballooning of the ephiphyses) Accelerated bone age Ankylosis maybe a feature (carpals, tarsals. C-spine) |
|
|
Psoriatic
|
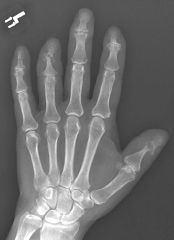
Hands > Feet
DIP (PIP and MCP) BD Normal Periosteal rxn, sausage digit pencil in cup Terminal tufts erosions |
|
|
Arthritis Mutilans – opera glass hands
|
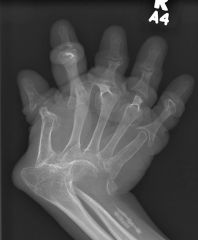
Psoriatic arthropathy
Rheumatoid arthritis Juvenile chronic arthritis Leprosy / Neuropathic arthropathy Reiter’s syndrome |
|
|
Sarcoid Arthropathy
|
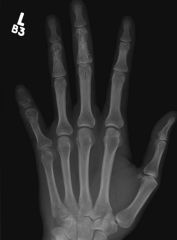
Granulomatous
deposition in bones and joints Soft tissue swelling Lacy pattern |
|
|
Scleroderma
|
tuftal acro-osteolysis
ST calcifications |
|
|
Hyperparathyroidism
|
Chondrocalcinosis
Tuftal resorption Sub____ erosions |
|
|
Inflammatory spondylitis
|
calcification in the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments
“squaring” of the vertebral bodies |
|
|
AS
|
-enthesopathy at ligaments
-shiny corners, squaring of VB Bamboo spine/Dagger sign |
|
|
Inflammatory spondylitis in the pelvis
|
sacroiliitis
enthesopathy degenerative change in hips |
|
|
Sacroiliitis
|
bilateral & symmetrical
ankylosing spondylitis Reiter’s syndrome enteropathic bilateral & asymmetrical psoriatic arthritis rheumatoid arthritis juvenile rheumatoid arthritis unilateral gout infection osteoarthritis |
|
|
Fracture Description
|
1. closed vs. open
2. simple vs. comminuted 3. extra-articular vs. intra-articular 4. path of the fracture line (transverse, oblique,spiral, longitudinal) 5. Position (Angulation, Displacement, Distraction, Impaction, Foreshortening) |
|
|
Fracture Position
|
Angulation - angular deformity created by fracture fragments (Varus and VaLgus ie lateral)
Displacement - Ant/Post/Sup/Inf/Med/Lateral Distraction - is a separation of fragments that have been pulled apart (shaft width) Impaction - occurs when fragments have been driven together Foreshortening - occurs when fragments override each other |
|
|
Kids Fracture
|
Plastic Bowing - fracture without disruption of cortex
Torus - buckled cortex Greenstick - cortex broken on one side of the bone and only bent or buckled on the other side Salter-Harris fracture - a fracture which involves an open growth plate |
|
|
Salter Harris
|
S - Slipped
A - Above L - Lower T - Through R - Ruined |
|
|
Hip Arthoplasty Types
|
Hemiarthoplasty (Unipolar, Bipolar) ***Keep native acetabulum
THA (Cement, NonCement, Hybrid) **** 3 parts (Femoral Stem, Acetabular component w/ liner, Cement) |
|
|
Complications
|
Fracture (Intraoperative, Late - Periprosthetic or Endoprosthesis)
Dislocation Loosening (Infection, Mechanical, Small Particle Dz) Heterotropic Ossification |
|
|
Approach to Hip Hardware
|
Prosthetic Position
Periprosthetic AbN Look at Acetabular Zone Look at Femoral zone |
|
|
Stress Shielding
|
Area with prosthesis is "shielding from stress", therefore by Wolff Law - it weakens
Remainder of limb distal become stronger ie denser |
|
|
Late Periprosthetic fracture and Endoprosthetic fracture
|
AbN stress and AbN bone
Stress - Trauma/Patient factors Bone - loosening/infection/small particle & Stress shielding/Reactive osteopenia Metal related fracture is rare |
|
|
Dislocation
|
Inadequate ST tension at surgery
Malpositioned prosthetic component |
|
|
Position of Prosthetic Components
|
1. Lateral inclination of acetabular component < 30 degrees
Draw transischial tuberosity line and bisect from head (ie how is femoral head in socket - eccentric is bad) 2. Anteversion of the cup < 25 degrees (use lateral) (ie cup needs to be in socket correctly) |
|
|
Loosening of Prosthetic
-Infection -Mechanical -Small Particle How to assess? |
Widening of interface:
1. Bone-Cement 2. Bone-Prosthesis 3. Cement-Prosthesis >2mm wide, periosteal rxn, cement fracture, malalignment or fracture Always compare to previous |
|
|
Small Particle Disease
|
Femoral head is ECCENTRIC in cup
-look for bony resorption -lobulated radiolucency |
|
|
Heterotopic Ossification
|
Common
Look for "islands of bone", bony spurs, ankylosis |
|
|
Lucent Bone Lesions
|
FOGMACHINES
F- Fibrous Dysplasia (No Periosteal rxn) O - Osteoblastoma (Mention w/ABC) G - GCT (Epiphyses closed, abuts articular surface, well defined NO sclerotic margin, eccentric) M - Mets/Myeloma A - ABC (expansile, <30) C - Chondroblastoma (<30, epiphyseal) H - Hyper PTH Browns (PTH) Hemagioma I - Infection N - NOF (<30, painless, cortical) E - EG (Younger than 30), Enchondroma (Calcs, Painless) S - SBC/UBC (<30, central) |
|
|
Malignant Bone lesions by Age
|
1 - Neuroblastoma
1-10 - Ewings 10-30 - Sarcoma 30-40 - Malignant GCT, Lymphoma, Fibrosarcoma >40 - Mets/MM/Chrondosarcoma |
|
|
Multiple lucent bone lesions
|
FEHMI
F- Fibrous Dysplasia E - EG/Enchondroma H - Hemangioma/Browns M - Mets/MM I - Infection |
|
|
DDX Solid Periosteal Rxn
|
Infection
Benign Neoplasm (Osteoid Osteoma) EG Hypertrophic Pulm Osteoarthropathy DVT |
|
|
Aggressive Periosteal Rxn
(Lamellated, Sunburst, Codman's Triangle) |
O/M
Malignancy -Osteosarcoma -Chondrosarcoma -Fibrosarcoma -Lymphoma -Leukemia -Mets |
|
|
Soft Tissue Calcification
|
Dystrophic (small to large calcium in damaged tissue - may progress to cortex)
CPPD Metastatic Calcification (finely speckled near bones) Tumoral Calcinosis (big globs near joint) Osteosarcoma (amorphous confluent calcs) |
|
|
AVN
|
A - Etoh
S - Sickle Cell, Steroids, SLE E - Ehrlenmeyer flask (Gaucher) P - Pancreatitis T - Trauma I - Idiopathic C - Caisson's |
|
|
Lucent Bone Lesion <30
|
EG
ABC NOF Chondroblastoma SBC |
|
|
DDx Lucent Bone Lesion
Automatics |
<30 - Infection, EG
>40 - Infection, Mets, Myeloma |
|
|
Lucent Epiphyseal Lesions
|
Infection
GCG Chondroblastoma Geode |
|
|
Osteomyelitis
|
Plain Film
Soft tissue abnormalities (Cellulitis, soft tissue mass) Mass may blur or obliterate fat planes Bone changes lag x 2weeks, indistinct cortex, permeative destruction, osteolysis, periosteal reaction Late osseous change: Sequestrum & involucrum Sequestrum: Necrotic bone, surrounded by purulent material or granulation tissue Sequestrum is usually NORMAL density (due to loss of blood supply), with surrounding osteopenia Involucrum: Bone shell surrounding purulent material & sequestrum (LUCENT) Cloaca: Cortical & periosteal defect through which pus drains from infected medullary cavity Late osseous change: Brodie abscess (Lytic, generally oval lesion with sclerotic, well-marginated rim), also has Surrounding osseous sclerosis and dense, regular periosteal reaction Best test is MR w/ Gad. Hard to tell between charcot and osteomyelitis (joint vs bone) |
|
|
GCT
|
◦Eccentric, lytic bone lesion
◦Well-defined borders ◦Expansile remodeling with apparent cortical permeation: 20-50% ◦Conspicuous peripheral trabeculae without tumor matrix ("soap bubble" appearance) ◦Septations ◦No marginal sclerosis ◦Periosteal reaction: 10-30% |

