![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Synapomorphy
|
A shared characteristic inherited from a common ancestor.
|
|
|
Cilia/Ciliate
|
External covering of fine hairs used to propel protozoan ciliate through water.
|
|
|
Flagellum
|
A long cellular appendage specialized for locomotion. The flagella of prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ in both structure and function.
|
|
|
Vacuole
|
A space surrounded by membrane filled with digestive enzymes. Amoeba use them to keep from overfilling with water and bursting.
|
|
|
Micro/Macronucleus
|
Paramecium have a larger and smaller nucleus. Each contains the DNA of the organism. The micro are important for generating genetic diversity by conjugation.
|
|
|
Antigenic Variation
|
a mechanism whereby parasites, such as trypanosomes, plasmodia, and Borrelia, are enabled to escape immune surveillance of a host by modifying or completely altering their surface antigens.
|
|
|
Psuedopod
|
Amoebas extrude regions of their cytoplasm to move around.
|
|
|
Fission
|
In cellular bodies, when a cell essentially tears itself in two, a form of asexual reproduction.
|
|
|
Conjugation
|
n prokaryotes, the direct transfer of DNA between two cells that are temporarily joined. In ciliates, a sexual process in which two cells exchange haploid micronuclei.
|
|
|
Merozoites
|
Stage of Malaria that takes residence in the red blood cells of the host, where they feed on hemoglobin. The popping of infected cells cause the fever associated with malaria.
|
|
|
Gametocytes
|
Some merozoites become these, and reproduce sexually when sucked out of the blood by another mosquito.
|
|
|
Plasmodial
|
Stage in slime molds where it is extemsive, slimy, shapeless mass of cytoplasm (the plasmodium).
|
|
|
Sporangial
|
Reproductive or fruiting body stage of the slime mold, is a fine, net-like structurethat forms an upright sporangium
|
|
|
Fruiting body
|
The upright sporangium of the fungi that holds the haploid spores.
|
|
|
Cytoplasm
|
The entire contents of the cell, exclusive of the nucleus, and bounded by the plasma membrane.
|
|
|
Saprophytic
|
Organism that obtains nourishment through absorption.
|
|
|
Lichen
|
The symbiotic collective formed by the mutualistic association between a fungus and a photosynthetic alga or cyanobacterium
|
|
|
Mycorrizhae
|
Mutualistic associations of plant roots and fungi. Can be endo-mycorrizhae or ecto-mycorrizhae.
|
|
|
Hyphae
|
Filaments that collectively makes up the body of a fungus
|
|
|
Mycelia
|
The densely branched network of hyphae in a fungus
|
|
|
D. Ascomycota
|
Large group of terrestrial and aquatic fungi. Over 30000 species identified to date.
|
|
|
D. Ascomycota
Ascospores -> Ascus -> Ascocarp |
Spores of the Ascomycota produced inside the ascus where meiosis occurs. The ascus(asci) is located inside a hyphal structure called an ascocarp.
|
|
|
D. Basidiomycota
Basidiospores -> Basidium -> Basidiocarp |
Terrestrial fungi. Mushrooms and toadstools are basidiomycota.
|
|
|
3 parts of a mushroom
|
1. Lamellae
2. Pilleus 3. Stipe |
|
|
Describe the moss lifecycle.
|
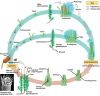
Duh
|
|
|
Describe the fern lifecycle.
|
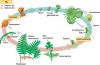
Duh.
|

