![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
120 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many people lose a limb each year to an accident or disease?
|
150K
|
|
|
How many people in the U.S. currently have an amputation?
|
1.5 million
|
|
|
What are artificial limbs?
|
Prostheses
|
|
|
What are braces?
|
Orthoses
|
|
|
What 3 materials were originally used to make prostheses?
|
Metal
Leather Wood |
|
|
What is the primary concern of the rehabilitation team?
|
Patient education
|
|
|
When is it important to begin patient education?
|
Before or immediately after amputation
|
|
|
Recent surveys demonstrate that proper patient education occurs in what percent of the cases?
|
50%
|
|
|
Which are the most commonly used materials used for orthotics and prosthetics?
|
1. Leather
2. Metal 3. Wood 4. Thermoplastic and thermosetting materials 5. Foamed plastics 6. Viscoelastic polymers |
|
|
Which are the important characteristics that determine which material is used to create the orthotic or prosthetic?
|
Material Strength
Stiffness Durability Density Corrosion Resistance |
|
|
What is determined by the maximum external load that the material can support or sustain?
|
Material strength
|
|
|
What is the amount of bending or compression that occurs when a material is loaded?
|
Stiffness
|
|
|
What is determined by its ability to withstand repeated cycles of loading or unloading during functional activities?
|
Durability
|
|
|
What is the materials weight per unit of volume?
|
Density
|
|
|
What is the degree to which the material is susceptible to chemical degradation?
|
Corrosion Resistance
|
|
|
Where is material strength very important?
|
Lower limb devices due to loading forces associated with gait.
|
|
|
Where is durability especially important?
|
Hinges of an orthotic device
|
|
|
What will greatly influence the energy cost during function activities?
|
Density
|
|
|
What two things mentioned in lecture that break down some materials?
|
Perspiration
Urine |
|
|
What are advantages to using leather?
|
1. Protects skin from irritation
2. Good strength and resiliency 3. Breathability- good for shoe modification and foot orthotics 4. Very moldable |
|
|
What are different metals that are used?
|
Steel
Aluminum Titanium Magnesium Alloy |
|
|
Which metal has the following characteristics?
• Stong, rigid, durable • High density • Susceptibility to corrosion • High alloy steels difficult to fabricate |
Steel
|
|
|
Which metal has the following characteristics?
• Very high strength to weight ratio • Resistent to corrosion • Not as durable as steel |
Aluminum
|
|
|
Which metal has the following characteristics?
• Strong as steel with 40% less density • More resistant to corrosion than steel • Difficult to fabricate • More expensive than steel |
Titanium
|
|
|
Which metal has the following characteristics?
• Lighter than aluminum • Corrosion resistant • Not widely used |
Magnesium Alloy
|
|
|
Which material has the following characteristics?
1. Available 2. Strong 3. Light Weight 4. Easily Shaped |
Wood
|
|
|
Which type of plastic is formable when heated and becomes rigid when cooled?
|
Thermoplastics
|
|
|
What are examples of things added to thermosetting materials?
|
Fiberglass
Nylon Kevlar |
|
|
Which type of plastic is used over the skin?
|
Foamed plastics
|
|
|
What occurs when a materials that is subjected to a constant deformation requires a decreasing load with time to maintain a steady state?
|
Stress relaxation
|
|
|
What is increase in deformation with time to a steady state as a constant load is applied?
|
Creep
|
|
|
What are the steps to the fabrication process?
|
1. Make accurate measurements of the limb
2. Take a negative impression of the limb (cast) 3. Make a three dimensional positive model CAD/CAM - use of computer digitizing 4. Modify the positive model for desired controls 5. Create the socket for the positive model 6. Fit the device to the patient |
|
|
Which factors will compromise the fit of the orthotic or prosthetic?
|
1. Significant growth
2. Weight gain or loss 3. Muscle Atrophy 4. Edema 5. Trauma |
|
|
How often should check-ups be sceduled with the orthotist or prosthetist?
|
Annual or semi-annual
|
|
|
Moderate to excessive wear of the shoe at the ______ may compromise performance of the device
|
heel
|
|
|
What are the 7 stages of prosthetic gait?
|
1. Heel strike to foot flat
2. Foot flat to mid-stance 3. Mid-stance 4. Heel rise 5. Toe off 6. Swing through 7. Deceleration |
|
|
Which phase of gait is demonstrated by the following:
• Smooth and controlled plantar flexion • Knee remains stable • The stride length is equal to the uninvolved side |
Heel strike to foot flat
|
|
|
Which phase of gait is demonstrated by the following:
• Foot remains on line of progression during plantarflexion. • Trunk erect; 1” to 2” head sway toward prosthesis |
Foot flat to mid-stance
|
|
|
Which phase of gait is demonstrated by the following:
• Gait base should show 1 to 2 “ between medial heel borders • Ischium should remain over center of heel • Foot remains flat on floor |
Mid-stance
|
|
|
Which phase of gait is demonstrated by the following:
• Center of gravity follows smooth arc • Normal stride length of good side without excessive lumbar lordosis |
Heel rise
|
|
|
Which phase of gait is demonstrated by the following:
• Smooth hip and knee flexion with quad control of knee flexion and heel rise • Socket remains secure on stump; no pistoning. |
Toe off
|
|
|
Which phase of gait is demonstrated by the following:
• Smooth center of gravity • Summit of arc equal on both sides with ample toe clearance • No vaulting |
Swing through
|
|
|
Which phase of gait is demonstrated by the following:
• Smooth noiseless deceleration with swing to full extension • No goose stepping • Equal stride length |
Deceleration
|
|
|
What is characterized by excessive bending laterally from the midline, generally to the prosthetic side.
|
Lateral bending of the trunk
|
|
|
What is characterized by a very wide base with the prosthesis held away from the midline at all times?
|
Abducted gait
|
|
|
What is a swinging of the prosthesis laterally in a wide arc during swing phase?
|
Circumducted gait
|
|
|
What is characterized by a rising on the toe of the normal foot permitting the amputee to swing the prosthesis through with little knee flexion?
|
Vaulting gait
|
|
|
What is characterized by the arm on the prosthetic side held close to the body during locomotion?
|
Uneven arm swing.
|
|
|
What is characterized by steps of unequal duration, usually by a very short stance phase on the prosthetic side?
|
Uneven timing gait
|
|
|
What is characterized by the prosthetic heel rising quite markedly and rapidly when the knee is flexed at the beginning of swing phase?
|
Uneven heel rise gait
|
|
|
What is characterized by rapid forward movement of the shin piece allowing the knee to reach maximum extension with too much force before heel strike?
|
Terminal Swing Impact
|
|
|
Instability of the prosthetic ________ creates a danger of falling.
|
knee
|
|
|
When are medial or lateral whips observed best?
|
When the patient walks away from the observer.
|
|
|
Which whip is it when the heel travels medially on initial flexion at the beginning of swing phase?
|
Medial Whip
|
|
|
What is a too rapid descent of the the anterior portion of the prosthetic foot?
|
Foot slap gait
|
|
|
What is characterized by a downward movement of the trunk as the body moves forward over the prosthesis?
|
Drop-off at the end of stance phase
|
|
|
What is seen when the amputee takes a longer step with the prosthesis than with the normal leg?
|
Long prosthetic step
|
|
|
What creates an active lumbar lordosis?
|
Excessive trunk extension
|
|
|
What are prosthetic causes of lateral bending of the trunk?
|
Prosthesis may be too short.
An improperly shaped lateral wall may fail to provide adequate support for the femur A high medial wall may cause the amputee to lean away to minimize discomfort. A prosthesis aligned in Abduction may cause a wide-based gait, resulting in this defect. |
|
|
What are amputee causes of lateral bending of the trunk?
|
Amputee may not have adequate balance.
Amputee may have abduction contracture. The stump might be over-sensitive and painful. A very short stump may fail to provide a sufficient lever arm for the pelvis. Defect may be due to habit. |
|
|
What are prosthetic causes of abducted gait?
|
Prosthesis may be too long.
Too much abduction. may have been built into the prosthesis. A high medial wall may cause amputee to hold prosthesis away to avoid pressure on ramus. An improperly shaped lateral wall can fail to provide adequate support for the femur. Pelvic band may be positioned too far away from the patient’s body. |
|
|
What are amputee causes of abducted gait?
|
Patient may have an abduction contracture.
Defect may be due to habit. |
|
|
What are prosthetic causes of circumducted gait?
|
Prosthesis may be too long.
Prosthesis may have too much alignment stability or friction in the knee, making it difficult to bend the knee in swing through. |
|
|
What are amputee causes of circumducted gait?
|
Amputee may have an abduction. contracture of the stump.
Patient may lack confidence for flexing the prosthetic knee because of muscle weakness or fear of stubbing toe. Defect may be the result of habit. |
|
|
What are prosthetic causes of vaulting gait?
|
Prosthesis may be too long.
There may be inadequate socket suspension. Excessive stability in the alignment or some limitation of knee flexion such as a knee lock or a strong extension aid may cause this defect. |
|
|
What are amputee causes of vaulting gait?
|
Vaulting is a fairly frequent habit pattern
Fear of stubbing the toe may cause this defect. Stump discomfort may be a factor. |
|
|
What are prosthetic causes of rotation of the prosthetic foot on heel strike?
|
This defect may be caused by too much resistance to plantar flexing by the plantar flexion bumper or heel wedge.
Too much toe out may have been built into the prosthesis. Socket may fit too loosely. |
|
|
What are amputee causes of rotation of the prosthetic foot on heel strike?
|
Patient may extend the stump too vigorously at heel strike.
Amputee may have poor muscle control of the residual limb. |
|
|
What are amputee causes of uneven arm swing?
|
Amputee may not have developed good balance.
Fear and insecurity accompanied by uneven timing will also contribute to this defect. Defect may be due to habit. |
|
|
What are prosthetic causes of uneven timing?
|
Improperly fitting socket may cause pain and a desire to shorten the stance phase on the prosthetic side.
A weak extension aid or insufficient friction in the prosthetic knee can cause excessive heel rise and thus result in uneven timing because of a prolonged swing-through. Alignment stability may be a factor, if the knee buckles too easily. |
|
|
What are amputee causes of uneven timing?
|
Amputee may have a weak residual limb.
Patient may not have developed good balance. Fear and insecurity may contribute to this defect. |
|
|
What are prosthetic causes of uneven heel rise?
|
Knee joint may have insufficient friction
There may be in inadequate extension aid |
|
|
What are amputee causes of uneven heel rise?
|
Amputee may be using more power than necessary to force the knee into flexion.
|
|
|
What are prosthetic causes of terminal swing impact?
|
Insufficient knee friction may be a factor
Knee extension aid may be too strong |
|
|
What are amputee causes of terminal swing impact?
|
Amputee may try to assure himself that the knee is in full extension by deliberately and forcibly extending the stump.
|
|
|
What are prosthetic causes to prosthetic knee instability?
|
Knee joint may be too far ahead of the TKA line
Insufficient initial flexion may have been built into the socket. Plantar flexion resistance may be too great causing the knee to buckle at heel strike. Failure to limit dorsiflexion can lead to incomplete knee control. |
|
|
What are amputee causes to prosthetic knee instability?
|
Patient may have hip extensor weakness.
Severe hip flexion contracture may cause instability. |
|
|
What are prosthetic causes of medial or lateral whip?
|
Lateral whips may result from excessive internal rotation of the prosthetic knee.
A medial whip may result from excessive external rotation of the knee. Socket may fit too tightly thus reflecting stump rotation. Excessive valgus or “knock” in the prosthetic knee may contribute to this defect. A badly aligned toe-break in a conventional foot may cause twisting on toe-off. |
|
|
What are amputee causes of medial or lateral whip?
|
Faulty walking habits may result in whips.
|
|
|
What are prosthetic causes of foot slap?
|
Plantar flexion resistance in usually too soft
|
|
|
What are amputee causes of foot slap?
|
Amputee may be driving the prosthesis into the walking surface too forcibly to assure extension of the knee.
|
|
|
What are prosthetic causes of drop-off at the end of stance phase?
|
There may be inadequate limitation of dorsiflexion of the prosthetic foot.
The keel of a SACH-type (solid ankle cushioned heel) foot may be too short, or the toe break of a conventional foot may be too far posterior. The socket may have been placed too far anterior in relation to the foot. |
|
|
What are amputee causes of drop-off at the end of stance phase?
|
There aren't any.
|
|
|
What are prosthetic causes of a long prosthetic step?
|
Insufficient initial flexion in the socket can cause this defect, when an irreducible stump flexion contracture is present.
|
|
|
What are amputee causes of long prosthetic step?
|
Amputee may have flexion contracture which cannot be accommadate prosthetically.
|
|
|
What are prosthetic causes of excessive trunk extension?
|
Improperly shaped posterior wall may cause forward rotation of the pelvis to avoid full weight-bearing on the ischium.
Insufficient initial flexion may have been built into the socket. |
|
|
What are amputee causes of excessive trunk extension?
|
Amputee may have hip flexor tightness.
Amputee may have weak hip extensors and may be substituting lumbar erector spinae. Weak abdominal muscles may contribute to this defect. Deviation may be due to habit pattern. Patient may be moving his shoulders backwards in an effort to obtain better |
|
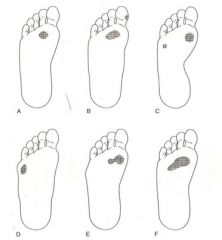
What is a?
|
Compensated rearfoot varus
|
|
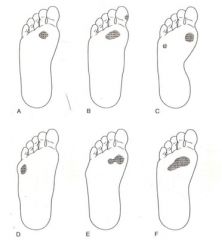
What is b?
|
Compensated forefoot varus
|
|
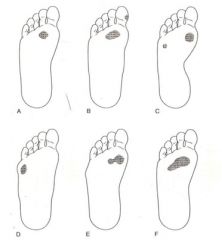
What is c?
|
Rigid plantarflexed first ray
|
|
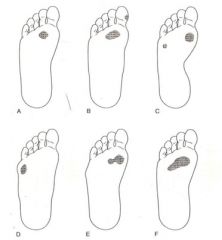
What is d?
|
Uncompensated rearfoot/forefoot varus
|
|
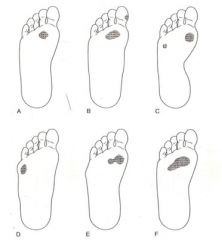
What is e?
|
Flexible plantarflexed first ray
|
|
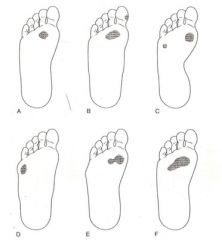
What is f?
|
Compensated equinus deformity
|
|
|
What are the goals for orthotic prescription?
|
1. Rest- patients will tend to rest an areas that has an orthosis
2. Immobilization- splint to protect an area 3. Joint Protection- as a result of a fracture or joint sprain 4. Control- negate unwanted movements 5. Assisting movement- rebound component on the orthosis 6. Provide feedback- improve proprioception 7. Correction- prolonged stretching of muscles and ligaments; breakdown of scar tissue |
|
|
Desired outcomes using orthotics are achieved by __________ of forces via the orthotic appliance.
|
Transmission
|
|
|
How do you avoid pain and skin breakdown with an orthotic?
|
Spread the pressure over as large of an area as possible
|
|
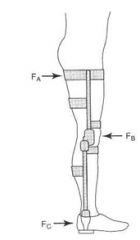
What is this an example of?
|
Three point force application
|
|
|
The forces at the posterior pad is ________ that of each anterior pad.
|
twice
|
|
|
Orthotic which distract may provide __________.
|
Stability
|
|
|
Orthotics which compress may _________.
|
Reduce pain
|
|
|
Which additional factors should one consider when designing or prescribing an orthotic?
|
1. Be aware of the sensitivity of the skin and underlying tissues
2. Allow adequate ventilation 3. Consider ease of cleaning 4. Be aware of bony prominences 5. Energy expenditure- paraplegic ambulating with bilateral KAFO’s with swing through gait pattern uses 16.3 ml/kg/min; 6.3 ml/kg/min in normal person (160% greater in paraplegic) 6. Impact on athletic performance 7. Ease of donning and doffing the appliance 8. Cost |
|
|
What is the first part of the biomechanical examination for orthotic prescription?
|
Static Exam
|
|
|
What gives information regarding shear and compressive forces during stance?
|
Callous patterns
|
|
|
What serves as a frame of reference to guide orthotic prescription?
|
Sub-talar joint
|
|
|
Structural deformities often occur as abnormal what?
|
Pronation or supination
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a common synonym for abnormal pronation?
Pes planus Flat foot Low-arched foot Valgus foot Talovalgus foot Pronated foot Calcaneovalgus foot |
Talovalgus foot
|
|
|
Pes cavus and high arched foot are synonymous with which abnormality?
|
Supination
|
|
|
Valgus is associated with _______ (supination or pronation), while varus is associated with ________.
|
Valgus- Supination
Varus-Pronation |
|
|
What are the 3 goals of foot orthotics?
|
1. support or balance the foot in order to eliminate the need for the foot to compensate for structural deformity or mal-alignment.
2. provide shock absorption 3. redistribute pressures on the plantar surface. |
|
|
Which "firmness" of orthotic has a limited life span and requires frequent replacement, and it used to provide cushion, improve shock absorption, decrease shear forces, and redistribute plantar pressures?
|
Soft/Flexible
|
|
|
Which "firmness" of orthotic provides shock absorption, is used to control the mal-aligned foot, and is good choice choice when control of supination or pronation is needed some shock absorption qualities?
|
Semi-rigid
|
|
|
Which "firmness" of orthotic primarily controls abnormal motion?
|
Rigid
|
|
|
Where would you add material to achieve support and control of the malaligned foot?
|
Plantar aspect
|
|
|
Studies have reported that __ % improvement can be seen with use of orthotics with patients who suffer from knee pain, plantar fasciitis, posterior tibial syndrome, shin splints, and IT band tendinitis.
|
75%
|
|
|
Which component of the shoe determines the maximum foot girth permitted in the shoe?
|
Throat
|
|
|
Which component of the shoe stabilizes the rear foot?
|
Heel counter
|
|
|
Which component of the shoe should be durable and provide traction?
|
Outersole
|
|
|
Which component of the shoe provides rigidity to the midsection of the shoe?
|
Shank
|
|
|
Which component of the shoe connects the upper shoe to the sole?
|
Last
|
|
|
Which component of the shoe should be the same shape as the foot?
|
Last
|

