![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sitting - Posteriorly rotated pelvis
|
1. increase in T/S kyphosis and C/S lordosis
2. protracted shoulder 3. forward head posture 4. subsequent anterior chest wall flattening 5. U/E IR and adduction |
|
|
Sitting - anteriorly rotated pelvis
|
1. reduced T/S kyphosis and C/S lordosis
2. shoulder girdle retraction 3. head in more neutral position 4. subsequent chest wall expansion 5. neutral or ER U/E |
|
|
Description of:
1. Anterior pelvic tilt 2. Posterior pelvic tilt 3. Left Lateral pelvic tilt 4. Right lateral pelvic tilt |
1. front of pelvis drops, back rises
2. front of pelvis rises, back drops 3. right side higher than left 4. left side higher than right |
|
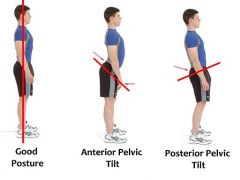
|
Anterior vs. Posterior pelvic tilt
|
|
|
Posterior pelvic tilt
1. Causes 2. muscles involved to create? 3. Muscles lengthened to allow? |
1. Tight hamstrings, short leg
2. rectus abdominus, hip extensors and trunk flexors 3. hip flexors, back extensors |
|
|
Optimal static posture
|
Body weight distribution such that there is normal resting tone in musculature and ligament tension is in balance with gravity
|
|
|
Optimal Dynamic Posture
|
Position of minimal effort with maximum efficiency which continually adapts to movement providing minimal strain to the body
|
|
|
Posture and habit
|
-body designed for good posture
-bad posture is a bad habit |
|
|
Assisting with bad posture requires understanding of:
|
1. body mechanics
2. causes of change in posture 3. Affect of posture change on E/C 4. Consequences of posture change |
|
|
What do we require to have good posture?
What do we need to have normal ROM? |
-normal ROM, more mobility, stability
-normal flexibility, joint movement, strength to attain and maintain |
|
|
Posture at birth
|
-entire spine is flexed at birth
-curves at birth = primary -those that maintain flexed position = primary -remaining curves = secondary |
|
|
Posture and standing
|
-standing = normal upright position
-see farther and move arms -increased stress on L/E, pelvis, spine -reduced stability -increased work on CV system |
|
|
Posture and neurosystem
|
-centre of gravity changes constantly
-tension in mm matches torque created at each joint imposed by body weight -coordination of neurosystem required -posture is largely reflexive |
|
|
Factors affecting posture
1. Mechanical/structural 2. neurophysiological 3. articular pathology 4. muscular control 5. fatigue 6. vision 7. hearing 8. respiratory conditions 9. Pain 10. Emotional 11. Social/Cultural 12. Age 13. Gender 14. Activity dependent |
1. length of leg difference
2. NS dysfunction 3. Z joint dysfunction 4. weak rhomboids, abs, gluts 5. sitting for many hours 6. forward head posture 7. side head flexion 8. COPD 9. disc herniation 10. stress (mm tone increase) 11. tall girl/boy 12. elderly degeneration 13. weight gains 14. habitual postures (sitting most of the day) |
|
|
Basic Pattern of Asymmetry
-Right hand dominant |
-Head RSF
-protracted and depressed R shoulder girdle -retracted and elevated L shoulder girdle -anteriorly rotated R pelvic girdle -posteriorly rotated L pelvic girdle -forward R ASIS -posterior L ASIS |
|
|
Anterior Line of Reference
|
-Tip of nose in line with manubrium, xiphisternum, umbilicus
-divides body L and R |
|
|
Lateral Line of reference
|
-Tip of the ear in line with tip of the shoulder and high point of iliac crest
-divides body anterior and posterior |
|
|
Abnormal lateral postures and effects on breathing
1. pigeon chest 2. funnel chest 3. barrel chest |
1. sternum forward and down
-increases A/P diameter -reduce vent volume 2. sternum posterior by rib overgrowth -reduced A/P diamter -displaced heart -respiration -may lead to kyphosis 3. sternum forward and upwards -Increase A/P diameter |
|
|
Abnormal Lateral postures and effects on muscle
1. pigeon chest 2. funnel chest 3. barrel chest |
1. Pigeon
-lengthen upper abs -shorten intercostals 2. Funnel -shorten upper abs, shoulder adductors, pec minor, and intercostals -lengthen T/S extensors and MFT/UFT 3. Barrel -shorten scapular adductors -lengthen intercostals and anterior chest muscles |
|
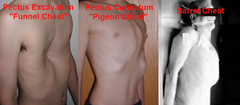
|
Funnel, pigeon, barrel
|
|
|
Posture and T/S kyphosis
|
-due to reduced anterior height of vertebral body
-Apex is at T7-T9 -Kyphosis in young often postural or result of Scheurermann's |
|
|
Posterior Line of Reference
|
-plumb line from SP of C7 through gluteal cleft
-divides body left and right |
|
|
Loading, positional change and the L/S
|
-Least load on disc in lying position
-increases progressively with: 1. standing 2. sitting 3. forward bending 4. forward bending with sitting -In lying with legs extended, psoas pulls on vertebral body -In sitting, pelvis rotates posteriorly reducing lumbar lordosis |
|
|
Muscle imbalance
|
-resting length of agonist or antagonist greater or less than normal
-Inert tissues react -arthrokinematics affected -common: shortened pecs with lengthened rhomboids |
|
|
Stressful Posture
|
-Posture maintained by sustained tension of musculature or passive loading of tissue
-fatigue and comfort -gives rise to ischemic conditions (reduced blood supply to tissues) |
|
|
Common Spinal deformities:
1. Pathological Lordosis |
1. Pelvic angle > or = 40 degreees (normal = 30)
-Elongated, weak abdominals -Elongatd hamstrings -Shortened, strengthened hip flexors, TFL, low back |
|
|
Common Spinal Deformities
2. Swayback Deformity |
2. Pelvic inclination of 40 degrees
-thoracolumbar spine exhibits kyphosis -anterior pelvic rotation so hip is in extension -Increase thoracic/lumbar curves in order to maintain C of G -Elongated and weak EO, Neck flexors, -Short and strong hamstrings, upper internal oblique |
|
|
Common Spinal Deformities
3. Kypohsis a. round back b. hump back c. flat back d. dowager's hump |
=exaggerated T/S curve
a. long rounded curve with pelvic inclination <30 b. sharp localized curve c. reduced pelvic inclination d. ? |
|
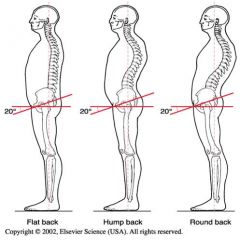
|
Kyphosis deformity
-Elongated and weak hip flexors -Short and strong hamstrings |
|
|
Common Spinal deformities
4. Scoliosis |
-Lateral spinal curvature
|
|
|
Posterior Posture
1. May occur... 2. Causes |
1. may occur in the T/S, T/L junction area or L/S alone
2. poor posture, nerve root involvement, inflammation of spine, LLD (leg length discrepancy), Hip contracture |
|
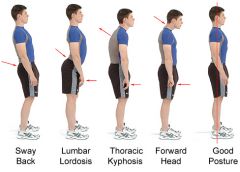
|
Common spinal deformities
|
|
|
Laterial View
|
1. Ear lobe to acromion
2. bisects chest 3. bisect abdomen/back ANTERIOR to SI Joint 4. ANTERIOR to midline of the knee 5. ANTERIOR to lateral malleolus 6. aligned with base of 5th metatarsal |

