![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
There are 3 main types of neurons:Sensory (afferent)- take messages from the sense organs to the central nervous system Interneurons-- receive messages from the sensory neurons- transfer messages within the CNS- pass messages to the motor neuronsMotor (efferent)- receive messages from interneurons and pass them to the muscles, organs and glands
|
|
|
|
Association areas:- The other space in each lobe that doesn’t have a specific function (the parts of the cerebral cortex that is not the motor, visual, auditory or somatosensory cortices). The main function of these areas is to “associate”. So association areas combine information from across the lobe and lobes and integrate it and combine it to allow a greater level of cognition to occur.- Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area are both association areas
|
|
|
|
Hippocampus:The Hippocampus is located in the medial Temporal lobe of the left and right hemispheres. The hippocampus plays a key role in the consolidation of declarative memory. It enables new learning to take place and new memories to form. E.g. a child learning to spell new words
|
|
|
|
The Amygdala is also located in the medial Temporal lobe of the left and right hemispheres. It regulates emotions such as fear and aggression and plays a role in the formation of emotional memory. E.g. if you are bitten by a dog the amygdala will process the event and increase your fear of dogs.
|
|
|
|
The hindbrain is the link between the spinal cord and the brain and is important for movement and balance.The midbrain coordinates movement, sleep and arousalThe forebrain is responsible for higher-order thinking processes including problem solving, planning memory, language, emotions and movement.
|
|
|
|
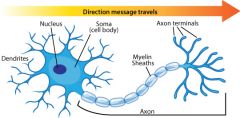
Dendrites- receive information from sense organs and pre-synaptic neuronsSoma- cell bodyNucleus- brain of the cellAxon- nerve fibre that carries information away from the cell bodyMyelin sheath- insulates and protects neural impulses Axon terminals- pass messages across the synapseSynapse- gap between two neurons leading to the post-synaptic neuronNeurotransmitters- pass messages across the synapse
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
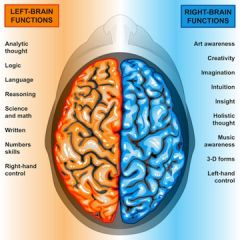
CORPUS CALLOSUM- the two hemispheres are connected by a structure called the corpus callosum, which allows them to communicate so that all the informations is accessible for both hemsipheres.
|
|
|
|
HEMISPHERIC DOMINANCE- although everyone uses both of their hemisperes, many people have been found to have a preference for tasks related top one hemisphere over the other. This is known as hemispheric dominance. |
|

