![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the parts of the eye and what do they do? (Hint: CPILR) |
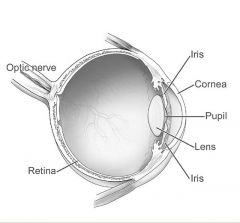
Cornea: Protection Pupil: Hole through which light enters Iris: Determines amount of light let in Lens: Keeps objects in focus Retina:(transduction) made up of neurons Extra: Optic Nerve sends images to the brain |
|
|
What is Transduction? |
Physical Stimuli being changed into neural impulses that the brain can understand. |
|
|
What are the three bones in the middle ear? (Hint: HAS) |
Hammer, Anvil, and Stirrup |
|
|
What are those three bones all together called? |
Ossicles |
|
|
How are sounds Received? |
Sound waves travel down ear canal and hit ear drum....this shakes/rattles the 3 bones in middle ear and jiggles the cochlea |
|
|
What is Gestalt? |
Hole |
|
|
What are the principles of Gestalt? (Hint: 5) |
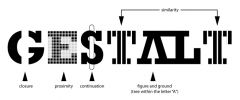
Closure: perceive objects with gaps as a whole Figure/Ground: figures against a background Proximity: grouping based on nearness Similarity: grouping based on alikeness Continuity: grouping based on pattern |
|
|
Which stage of sleep is the deepest? (deep sleep) |
Stage 4 |
|
|
What is amplitude? |
The height of the wave Sound: the pitch of something Vision: the brightness of something |
|
|
What is wavelength? |
Distance between crests Sound: the frequency of something Vision: the hue of something |
|
|
What is the sleep paradox? |
brain is awake yet body is paralyzed |
|
|
What is Stroboscopic Motion? |
rapid progression of images-looks like motion Ex: post-it flipbook |
|
|
What's the difference between relative size and relative shape? |
The size/shape of an object changes depending on where it is on the plane |
|
|
What is Pitch? |
Highness or Lowness (frequency) of a sound |
|
|
What is Hue? |

Color determined by wavelength of light |
|
|
What is Intensity? |
Amount of energy in a wave (higher the amplitude=the greater the intensity) |
|
|
Where does transduction happen in the ear? |
The Cochlea |
|
|
What are rods and cones and where are they located? |
Rods and cones are types of photo receptors located in the Retina |
|
|
What is Visual Acuity? |
Sharpness of vision |
|
|
What is Perception? |
The process of organizing and interpreting sensory information |
|
|
What is Retinal Disparity? |
perceiving depth based on the difference between the two images that the retina receives as an object moves closer or farther away (both images merged together) |
|
|
Monocular cues |
cues for distance that only require one eye to percieve |
|
|
Binocular cues |
cues for depth that require two eyes to percieve |
|
|
Olfactory Nerve |
Nerve that transmits information about odors to the brain |
|
|
Blind Spot |
Part of the retina that contains no photoreceptors |
|
|
Kinesthesis |
provides info about position and movement of individual body parts |
|
|
Sensation |
Stimulation of sensory reception & transmission of sensory info to the brain |
|
|
Fluid filled part of inner ear? |
Cochlea |
|
|
Light sensitive inner surface of eye that contains rods and cones and neurons? |
Retina |
|
|
Conductive Deafness |
~Damage to middle ear ~Can't hear quieter sounds (hearing aids can help) |
|
|
Sensorineural Deafness |
~Damage to neurons in Cochlea ~Can't hear sounds at certain frequencies ~Caused by disease or prolonged exposure to loud sounds (concert, iPod deafness) |
|
|
Sensory adaption |
Becoming more sensitive to low magnitude stimuli and less sensitive to constant stimuli |
|
|
Gate Control Theory |
Brain can only process so many messages at a time |
|
|
Consciousness |
Awareness of self and surroundings |
|
|
Preconscious |
Ideas we are not aware of in the moment |
|
|
Unconscious |
Unavailable awareness in most situations (of self or surroundings) |
|
|
Inner awareness |
Being aware of yourself |
|
|
What did Freud mean when he said that consciousness was like an iceberg? |
Most of what we do is unconsciouss |
|
|
Altered state of consciousness |
Type of consciousness other than normal waking consciousness |
|
|
Circadian Rhythm |
regular sequence of biological processes (biological clock) such as temperature and sleep that occurs every 24 hours |
|
|
How many stages of sleep are there? (including REM) |
5 stages (stage 1, stage 2, stage 3, stage 4, REM) |
|
|
What does REM stand for? |
Rapid Eye Movement |
|
|
What is the order of sleep cycles? |
1, 2, 3, 4, 3, 2, REM (then back to 1) |
|
|
How long is one sleep cycle? |
90 minutes |
|
|
Stage 1 of sleep |
Light sleep-drift in and out of sleep (awakened easily) |
|
|
Stage 2 of sleep |
Sleep Spindles (short burts of brain activity) - Eye movement stops and brain waves become slower |
|
|
Stage 3 of sleep |
Extremely slow brainwaves (delta waves) intersped with smaller faster waves |
|
|
Stage 4 of sleep |
Deep sleep-all delta waves (extremely slow brain waves)-no eye movement or muscle activity |
|
|
Stage 5 of sleep |
REM-breathing is rapid & irregular, eyes jerk rapidly under lids, muscles are temporarily paralyzed |
|
|
At what stage of sleep do nightmares occur? |
REM |
|
|
At what stage of sleep do night terrors, bed wetting or sleepwalking occur? |
Stage 4 |
|
|
What did Kleitman believe? |
That dreams don't have a point |
|
|
Meditation |
narrowing of attention that slows metabolism and produces feelings of relaxation
|
|
|
What are results of sleep deprivation? |
impaired brain activity, moodiness, memory problems, hallucinations, higher risk of chronic health problems and even death |

