![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
147 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What makes someone a person ? |
Change vs. stability Continuity vs. discontinuity |
|
|
|
Two basic development questions? |
1. Does age affect personality? 2. Or does personality affect age? |
|
|
|
What is personality? |
No one definition-but key uniting theme: -an organized and distinctive pattern of a combination of attributes, motives, values, and behaviors -characterizes a persons adaption to a situation. -endures over time, unique to individual, focus mainly on traits consistent across situations and time. |
|
|
|
What does personality involve? |
Processes by which we try to understand our self, others, and world |
|
|
|
What is the psychometric -individual differences approach to personality by Paul costa and ROBERT mcCrae? |
An empirical measurement approach using objective tests and questionnaires |
|
|
|
What’s the five factor(big five) theory of personality? |
Five universal and stable components make up an individuals personality. Tested longitudinally with adults over a 20 year interval |
|
|
|
What are the big five factor theory traits? |
OCEAN; -openness to experience -conscientiousness -extraversion -agreeableness -neuroticism |
|
|
|
OCEAN; Openness to experience? |
Imaginative vs practical Independent vs conforming Preference for variety vs routine |
|
|
|
Ocean; Conscientiousness |
Organized vs disorganized Careful vs careless Disciplined vs. impulsive |
|
|
|
OCEAN; extraversion? |
Sociable vs retiring Fun loving vs sober Affectionate vs reserved |
|
|
|
OCEAN; Agreeableness? |
Soft hearted vs ruthless Trusting vs suspicious Helpful vs uncooperative |
|
|
|
OCEAN; Neuroticism |
Calm vs anxious Secure vs insecure Self satisfied vs self pitying |
|
|
|
What are the hallmarks of adult personality? |
-stability and continuity -no frequent or extensive change -personality isn’t reorganized -basic personality remains stable through life and resists change |
|
|
|
What’s the cross age consistency (stability) of personality through adulthood? |
Personality resistant to environmental change But social and historical context can be influential. |
|
|
|
What happens in middle adulthood personality? |
Universal maturational change in achievement Less neuroticism, extraversion, and openness to experience More conscientiousness and agreeableness. |
|
|
|
What is self concept? |
Totality of the individuals thoughts and feelings A person refers to him/herself as an object The way that people view and evaluate themselves |
|
|
|
What does self concept include? |
Various aspects of self -self esteem is only one component |
|
|
|
Self concept also pertains to other important parts of the self... |
Self image Self perception Self efficacy Self mastery(control) Self identities |
|
|
|
In the first six months I the emerging self... |
Infants discover physical self Around 2-3 mo the infant shows personal agency An awareness that they can affect things and are also affected by things |
|
|
|
Infancy-the emerging self: Self awareness & self recognition? |
Psychological state in which self becomes an object of attention Fully develops at about 18 months |
|
|
|
Infancy-the emerging self: Joint attention? |
Difference in perceptions between self and others (parents) can be shared. |
|
|
|
Infancy-the emerging self; Categorical self? |
Emerges 18-24 months Babies classify self and others through social categories Age, sex, gender |
|
|
|
The self in childhood : Self in concrete terms... Kids self concept tends to be very concrete? |
Linked to specific traits, good or bad, possessions Wearing blue shirt, yellow balloon Im a good speller...but math is hard for me |
|
|
|
By age 2 kids use I and mine a lot... |
Many physical characteristics to describe themselves Terms as good, bad, nice, mean |
|
|
|
By age 8, kids focus on? |
Social identity; how other see them More abstract, descriptive, and personality traits terms are used. |
|
|
|
Self concept, kids (4-8)? |
Inflated self views View self as better then they are |
|
|
|
Around age 8 self concepts? |
Self ratings are consistent with actual competencies |
|
|
|
Self in adolescence; teens self descriptions? |
More trait focused Less on concrete and physical properties More abstract and psychologically complex Focus on deep personality characteristics |
|
|
|
Teens can distinguish between? |
Actual self (who I am) Future or possible selves (who I might become) Ideal self “who I would like to be” Feared self “who I dread becoming” |
|
|
|
Gordon Gallup jr? |
Self awareness in primates Mirror test, monkeys can’t but chimps can |
|
|
|
Michael Lewis and Jeanne brooks Gunn? |
Red dot on nose and mirror task Kids between 9-24 months rested Red dot on nose Younger kids touch dot on mirror as if not on their nose -behave like seeing another child, may wave, try to touch or kiss By 15-18 months; -child touches their own nose, most noticeable between 18-24 months |
|
|
|
William James (father of American psych) coined which term? |
Self esteem |
|
|
|
What is self esteem? |
Positive or negative orientation toward oneself Global evaluation of ones self worth |
|
|
|
Roy baumeister? |
Self esteem as an earned quantity and quality School aged kids: -self esteem earned not given A on test when cheating is less satisfying then earning it |
|
|
|
Development and adolescent self esteem? |
Self esteem tends to decline in early teens Then rises through late adolescence and emerging adulthood |
|
|
|
What influences teen self esteem? |
Having warm and democratic parents Receiving positive social feedback Achieving success in school Social support)peers, friends, siblings. |
|
|
|
Looking glass self? |
Perceptual reflection -the self view develops via social interactions |
|
|
|
Looking glass; -self as reflection? |
How person perceived way others see them |
|
|
|
False selves? |
Involves playing a role Acting out of character “Not the real me” |
|
|
|
Susan harter ? |
Self perception profile for adolescents -8 domains |
|
|
|
Susan harter, 8 domains? |
Scholastic competence Social peer acceptance Athletic competence Physical appearance Job competence Romantic appeal Behavioral conduct Close friendship |
|
|
|
Most important in teen overall self esteem? |
Social peer acceptance Physical appearance |
|
|
|
Morris Rosenberg? |
Defining aspects of self esteem Self esteem scale |
|
|
|
Morris Rosenberg? |
Defining aspects of self esteem Self esteem scale |
|
|
|
Rosenberg self esteem scale? |
Initially designed for teens Identifies two types of self esteem -baseline -barometric |
|
|
|
Morris Rosenberg? |
Defining aspects of self esteem Self esteem scale |
|
|
|
Rosenberg self esteem scale? |
Initially designed for teens Identifies two types of self esteem -baseline -barometric |
|
|
|
Rosenberg self esteem scale; baseline self esteem? |
Stable and enduring sense of self worth and well being |
|
|
|
Morris Rosenberg? |
Defining aspects of self esteem Self esteem scale |
|
|
|
Rosenberg self esteem scale? |
Initially designed for teens Identifies two types of self esteem -baseline -barometric |
|
|
|
Rosenberg self esteem scale; baseline self esteem? |
Stable and enduring sense of self worth and well being |
|
|
|
Rosenberg self esteem scale; Barometric self esteem? |
-fluctuating sense of worth and well being -changes as one responds to different thoughts, experiences, etc. -most prevalent in early adolescence. |
|
|
|
What is temperament? |
-Difference in children’s emotional reactivity -Emerge early in life |
|
|
|
What is temperament? |
-Difference in children’s emotional reactivity -Emerge early in life |
|
|
|
What’s temperament involve? |
-Constitutionally based individual differences -in quality and intensity of -emotional , motor, attentional reactions -ability to self regulate |
|
|
|
What is temperament? |
-Difference in children’s emotional reactivity -Emerge early in life |
|
|
|
What’s temperament involve? |
-Constitutionally based individual differences -in quality and intensity of -emotional , motor, attentional reactions -ability to self regulate |
|
|
|
Temperament is genetically based? |
Present at birth Shows consistency Relative stability over time |
|
|
|
Stella chess and Alexander Thomas? |
NY longitudinal study questionnaire Three temperaments in child |
|
|
|
Stella chess and Alexander Thomas? |
NY longitudinal study questionnaire Three temperaments in child |
|
|
|
Chess and Thomas three types of children(temperament) |
easy -difficult -slow to warm up |
|
|
|
Stella chess and Alexander Thomas? |
NY longitudinal study questionnaire Three temperaments in child |
|
|
|
Chess and Thomas three types of children(temperament) |
easy -difficult -slow to warm up |
|
|
|
Chess and Thomas; easy child temperament? |
Regular eating, sleeping, elimination cycles Positive approach response to new situations Good mood mostly, smiles often |
|
|
|
Stella chess and Alexander Thomas? |
NY longitudinal study questionnaire Three temperaments in child |
|
|
|
Chess and Thomas three types of children(temperament) |
easy -difficult -slow to warm up |
|
|
|
Chess and Thomas; easy child temperament? |
Regular eating, sleeping, elimination cycles Positive approach response to new situations Good mood mostly, smiles often |
|
|
|
Chess and Thomas; difficult child temperament? |
Irregular eating, sleeping and cycles Negative approach response to new situations Frequent, loud crying or tantrums Slow adoration to change, needs more time to get used to something |
|
|
|
Stella chess and Alexander Thomas? |
NY longitudinal study questionnaire Three temperaments in child |
|
|
|
Chess and Thomas three types of children(temperament) |
easy -difficult -slow to warm up |
|
|
|
Chess and Thomas; easy child temperament? |
Regular eating, sleeping, elimination cycles Positive approach response to new situations Good mood mostly, smiles often |
|
|
|
Chess and Thomas; difficult child temperament? |
Irregular eating, sleeping and cycles Negative approach response to new situations Frequent, loud crying or tantrums Slow adoration to change, needs more time to get used to something |
|
|
|
Chess and Thomas; slow to warmup child? |
Negative response of mild intensity when exposed to new situations Slowly accepts with repetitions Regular biological routine Variety with problems |
|
|
|
Mary Rothbart? |
Contemporary models of infant temperament |
|
|
|
Rothbarts Six key dimensions of temperament? |
Fearful and irritable distress Attention span Persistence Activity level Positive affect Rhythmicity |
|
|
|
Jerome Kagan? |
Behavioral inhibition |
|
|
|
Jerome Kagan? |
Behavioral inhibition |
|
|
|
Behavioral inhibition? |
Temperamentally based style of responding characterized by the tendency to be particularly fearful and restrained when dealing with novel or stressful situations. |
|
|
|
What impacts behavioral inhibition? |
Higher levels of limbic/autonomic nervous system reactivity Cerebral hemispheric differences (Nathan fox) |
|
|
|
What impacts behavioral inhibition? |
Higher levels of limbic/autonomic nervous system reactivity Cerebral hemispheric differences (Nathan fox) |
|
|
|
What did kagan find he could predict? |
Behavioral inhibition and excitation was a predictor of temperament Could predict temperament around 10-11 months |
|
|
|
Adolescence identity crisis? |
Erik Erickson |
|
|
|
Adolescents identity crisis? |
Exploration, turning point (crisis) |
|
|
|
Adolescence identity crisis? |
Erik Erickson |
|
|
|
Adolescents identity crisis? |
Exploration, turning point (crisis) |
|
|
|
Identity achievement? |
Establishing a clear and definite sense of who you are and how you fit into the world |
|
|
|
Adolescence identity crisis? |
Erik Erickson |
|
|
|
Adolescents identity crisis? |
Exploration, turning point (crisis) |
|
|
|
Identity achievement? |
Establishing a clear and definite sense of who you are and how you fit into the world |
|
|
|
Identity confusion? |
Failure to form a stable and secure identity |
|
|
|
Three principal areas of identity formation? |
Love, work, and ideology |
|
|
|
Identity exploration and formation; psychosocial moratorium? |
A period when adult responsibilities are postponed Young people experiment with various possible selves |
|
|
|
James Marcia’s known for? |
Identity achievement statuses |
|
|
|
James Marcia’s known for? |
Identity achievement statuses Classifying teens into one of four identity statuses |
|
|
|
What key adolescent issues does James Marcia’s identity achievement statuses address? |
Teen rebellion Alienation Rejection of adult values Commitment to ideals |
|
|
|
Shifting horizons- viewpoints for self and personality in adulthood and old age? |
Gap between real and ideal self narrows |
|
|
|
Shifting viewpoints in old age? |
More self acceptance Later life losses aren’t seen as losses bc goals and expectations have changed |
|
|
|
Shifting viewpoints in old age? |
More self acceptance Later life losses aren’t seen as losses bc goals and expectations have changed |
|
|
|
In old age what happens with men and women in terms of personality issues? |
Older men focus on less manly things, focus more on emotions and nurturing feelings
Women focus less o emotions and more independence, control, autonomy |
|
|
|
Kansas City studies researchers? |
Neugarten, havinghurst, Tobin |
|
|
|
Kansas City studies researchers? |
Neugarten, havinghurst, Tobin |
|
|
|
What was the Kansas City study ? |
25 year longitudinal study showing changes in personality test scores Asked what their ember rod the test scores and used to evaluate how they imagined themselves |
|
|
|
Kansas City studies researchers? |
Neugarten, havinghurst, Tobin |
|
|
|
What was the Kansas City study ? |
25 year longitudinal study showing changes in personality test scores Asked what their ember rod the test scores and used to evaluate how they imagined themselves |
|
|
|
What is the illusion of personality change? |
People think they’ve changed more than they really have |
|
|
|
What does social cognition involve? |
Thinking of ones self and others in terms of: Perceptions Thoughts Emotions Motivations Behavior Also ability to understand psychological differences in others To be able to adopt another persons perspectives. |
|
|
|
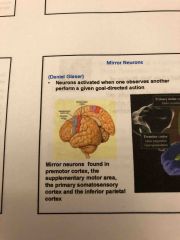
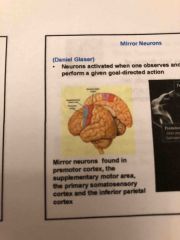
Mirror neurons? |
Neurons activated when one observes another perform a given goal directed action |
|
|
|
Mirror neurons found where? |
Mirror neurons found where? |
|
|
|
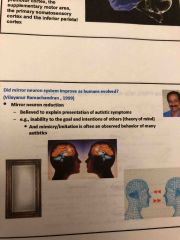
Mirror neurons and Gil ramachandran |
|
|
|
|
Why children lie? |
Ability to lie emerges early May be atrial part of intellectual development |
|
|
|
Michael Lewis research? |
Tested 3 yr olds Kids told not to peak at interesting toy Experimenter leaves room Upon return, about 70% lie about peaking |
|
|
|
Why is lying and deception viewed as adaptive and logical behavior? |
May indicate higher intelligence when observed very young. |
|
|
|
What is TOM? |
TOM involves understanding and making connections between other people’s perceptions, wishes, desires, and actions |
|
|
|
TOM: kids between 2 &5 |
Develop more sophisticated view of self and others Basic understanding of how others minds work How decisions are made and behavior influenced Occurs and develops often within context of play Called TOM |
|
|
|
TOM: kids between 2 &5 |
Develop more sophisticated view of self and others Basic understanding of how others minds work How decisions are made and behavior influenced Occurs and develops often within context of play Called TOM |
|
|
|
False belief tasks? |
Test kids understanding that other people will act in accord with their beliefs even when the child knows that these beliefs are incorrect. |
|
|
|
TOM: kids between 2 &5 |
Develop more sophisticated view of self and others Basic understanding of how others minds work How decisions are made and behavior influenced Occurs and develops often within context of play Called TOM |
|
|
|
False belief tasks? |
Test kids understanding that other people will act in accord with their beliefs even when the child knows that these beliefs are incorrect. |
|
|
|
False beliefs and autism? |
Problems with false beliefs tasks suggests they may have impaired mind reading mechanisms May interfere with their social functioning Also believed to have linguistic problems along with social. |
|
|
|
TOM: kids between 2 &5 |
Develop more sophisticated view of self and others Basic understanding of how others minds work How decisions are made and behavior influenced Occurs and develops often within context of play Called TOM |
|
|
|
False belief tasks? |
Test kids understanding that other people will act in accord with their beliefs even when the child knows that these beliefs are incorrect. |
|
|
|
False beliefs and autism? |
Problems with false beliefs tasks suggests they may have impaired mind reading mechanisms May interfere with their social functioning Also believed to have linguistic problems along with social. |
|
|
|
Testing children’s theory of mind; smarties task |
Study preschoolers understanding of false beliefs Most three year olds answer as character in story does Suggests lack of understanding that actions are based on their own beliefs |
|
|
|
Ulta friths Sally Ann tasks |
Studies of autism Test kids understanding that other act according to their belief |
|
|
|
Autism? |
Is a syndrome involving a variety of intellectual and emotional difficulties Have problems with tasks that test other people’s perspectives such as false beliefs Bc autistic kids show more interest in objects, spatial and temporal (time) relationships than people; and lack of interest on social relationships |
|
|
|
Where’s TOM COME FROM? Theory of mind module??? |
Hypothesizes that brain mechanisms devoted to understanding others exists notions that TOMM matures over first five years |
|
|
|
Where’s TOM COME FROM? Theory of mind module??? |
Hypothesizes that brain mechanisms devoted to understanding others exists notions that TOMM matures over first five years |
|
|
|
TOMM evidence? |
Autistic kids have biologically impaired Brain Slows or prevents normal TOM development |
|
|
|
Where’s TOM COME FROM? Theory of mind module??? |
Hypothesizes that brain mechanisms devoted to understanding others exists notions that TOMM matures over first five years |
|
|
|
TOMM evidence? |
Autistic kids have biologically impaired Brain Slows or prevents normal TOM development |
|
|
|
Where does TOM come from? Psychosocial TOM theory? |
Emphasizes social interactions Not Brain development |
|
|
|
Where’s TOM COME FROM? Theory of mind module??? |
Hypothesizes that brain mechanisms devoted to understanding others exists notions that TOMM matures over first five years |
|
|
|
TOMM evidence? |
Autistic kids have biologically impaired Brain Slows or prevents normal TOM development |
|
|
|
Where does TOM come from? Psychosocial TOM theory? |
Emphasizes social interactions Not Brain development |
|
|
|
Psychological theory evidence? |
Older kids are better with false belief tasks then younger kids Maybe bc if experience |
|
|
|
Where’s TOM COME FROM? Theory of mind module??? |
Hypothesizes that brain mechanisms devoted to understanding others exists notions that TOMM matures over first five years |
|
|
|
TOMM evidence? |
Autistic kids have biologically impaired Brain Slows or prevents normal TOM development |
|
|
|
Where does TOM come from? Psychosocial TOM theory? |
Emphasizes social interactions Not Brain development |
|
|
|
Psychological theory evidence? |
Older kids are better with false belief tasks then younger kids Maybe bc if experience |
|
|
|
Where’s TOM come from? Informational processing (IT) TOM model? |
Emphasizes general info processing skill development for understanding beliefs. |
|
|
|
Where’s TOM COME FROM? Theory of mind module??? |
Hypothesizes that brain mechanisms devoted to understanding others exists notions that TOMM matures over first five years |
|
|
|
TOMM evidence? |
Autistic kids have biologically impaired Brain Slows or prevents normal TOM development |
|
|
|
Where does TOM come from? Psychosocial TOM theory? |
Emphasizes social interactions Not Brain development |
|
|
|
Psychological theory evidence? |
Older kids are better with false belief tasks then younger kids Maybe bc if experience |
|
|
|
Where’s TOM come from? Informational processing (IT) TOM model? |
Emphasizes general info processing skill development for understanding beliefs. |
|
|
|
IP model evidence? |
Autistic kids seem to lack certain IP skills Skills needed to multitask |
|
|
|
What’s the link between mirror neurons, TOM, and autism? |
Absence of mirror neurons and alternate Brain circuitry in autistic kids Tend to compensate with greater use of visual areas and motor areas but lack integration of emotions in limbic system. Possibly explains social impairment |
|

