![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
introspection |
reporting on sensations and other elements of experience in reaction to stimuli. it sucks and is unreliable.
|
|
|
functionalism
|
studied thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. asked what function might they serve and how might they have helped our ancestors survive?
|
|
|
william james
|
founder of functionalism and wrote "the principles of psychology"
|
|
|
Mary Whiton Calkins
|
memory researcher and the first female president of the APA. was denied a PhD from harvard.
|
|
|
margaret floy washburn
|
PhD, 2nd female president of the APA. wrote "the animal mind". was barred from titcheners experiemental psychologist organization.
|
|
|
psychology
|
the science of behavior and mental processes
|
|
|
nature vs nurture
|
are people born a certain way or is it due to their environment growing up?
|
|
|
natural selection
|
useful in psychology because it explains animal behaviors as well as their structures.
|
|
|
hindsight bias
|
"i knew it all along"
|
|
|
overconfidence
|
mistakenly perceiving order in random events. "dice is fixed because you rolled 4 6's in a row"
|
|
|
scientific attitude
|
1. ask questions 2. be skeptic 3. be humble
|
|
|
naturalistic observations
|
range from watching chimps in the jungle to videotaping parent child observations.
|
|
|
neurons
|
nerve cells. each consists of a cell body
|
|
|
dendrite
|
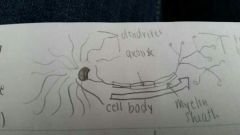
fibers recieve information and connect it toward the cell.
|
|
|
axon
|
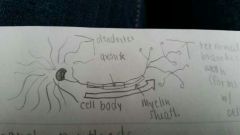
fibers pass the message through its terminal branches to other neurons or muscles or glands.
|
|
|
myelin sheath
|
fatty tissue that insulates the axons and speeds their impulses
|
|
|
action potential (neural impulse)
|

brief electrical charge that travels down the axon.
|
|
|
threshold
|
if the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity or threshold, the combined signals trigger an action potential
|
|
|
synapse and synaptic gap
|
•meeting point between neurons.
•gap between the axon and the receiving neuron. (dendrites and axons don't quite touch) |
|
|
neurotransmitters
|
chemical messengers that are released when the action potential reaches the terminal ends of an axon. they cross the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron.
|
|
|
reuptake
|
the sending neuron reabsorbs excess neurotransmitters.
|
|
|
sensory neurons
|
carry messages from the bodys tissues and sensory receptors inward to the brain and spinal cord for processing.
|
|
|
motor neurons
|
carry instructions from the central nervous system out to the bodys muscles
|
|
|
interneurons
|
forwards the message between the sensory input and motor output. the interneurons process the information in the brain
|
|
|
EEG
|
researchers present a stimulus repeatedly and have a computer filter out brain activity unrelated to the stimulus.
|
|
|
PET scan
|
positron emission tomography. depicts brain activity by showing each brain area's consumption of glucose. the patient recieves temporarily active glucose and the pet scan picks up the gamma rays as the patient preforms the given task.
|
|
|
MRI
|
aligns atoms, then allows atoms to return to normal which provides the scientists with an image of soft tissues including the brain.
|
|
|
fMRI
|
shows the functioning of the brain as well as its structure.
|
|
|
brainstem
|
begins when spinal cord swells slightly after entering the skull
|
|
|
medulla |
the slight swelling of the spinal cord right after entering the skull
|
|
|
thalamus |
egg shaped structures that receives all senses except smell and sends them to the brain.
|
|
|
reticular formation
|
lies between your ears. as the spinal cord's sensory input flows up to the thalamus, some of it travels through this which filters incoming stimuli and relays important information to other brain areas. also enables people to wake up.
|
|
|
cerebellum |
enables nonverbal learning and memory, coordinates voluntary movement, helps to judge time, modulate our emotions and discriminate sounds and textures. |
|
|
amygdala |
aggression and fear |
|
|
hypothalamus |
helps the body maintain a steady internal state |
|
|
cerebral cortex |
cover's the cerebral hemispheres. body's ultimate control and information processing center |
|
|
glial cells |
support, protect, and nourish neurons |
|
|
frontal lobe |
lies behind the forehead, involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgments. |
|
|
parietal lobe |
lies at the top of the head towards the rear, receives sensory input for touch and body position |
|
|
occipital lobes |
lies at the back of the head, includes areas that receive information from the visual fields |
|
|
temporal lobes |
lies roughly above the ears, includes auditory areas, each receives information primarily from the opposite ear. |
|
|
sensory cortex |
at the front of the parietal lobes, registers and processes body touch and movement sensations |
|
|
association areas |
areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions. involved in higher mental functions such as learning remembering thinking and speaking. |
|
|
plasticity |
the brains ability to change, especially during childhood by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience. |
|
|
corpus callosum |
large band of neural fibers connecting the 2 brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them. |

