![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Intelligence definition |
Ability to learn, ability to apply learned material to life. |
|
|
|
Meta cognition |
Ability to understand and control ones cognitive activity. Read your own mind. |
|
|
|
Intelligence definition 2 |
Traditionally defined as knowledge and reasoning. Verbal, problem solving skills Differs across culture |
|
|
|
Spearman initial view of intelligence |
Initially believed that individuals have a general intelligence, that is responsible for all mental test. The 'g' factor. |
|
|
|
Spearman two factor theory of intelligence |
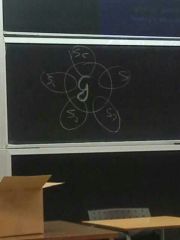
Factor analysis (satistical method to determine whether 2 or more items corralte. Thus forming a cluster)
G- general intelligence S- specific intelligence (specific tasks)
G-true intelligence Ultimately abandonded, for theories that looked into specific factor called multiple factor theories |
|
|
|
Lewis Thurstone (7) distinct components of intelligence |
Primary mental abilities Verbal comprehension Word fluency Numerical skill Spatial ability Associative memory Perceptual speed Reasoning |
|
|
|
Howard gaderners (8) aspects of intelligence |
Linguistic Logical-mathematical Musical Spatial Bodily-kinesthetic Interpersonal Intrapersonal Naturalistic (Spirtual Existential) Overcomplicated it, controversial |
|
|
|
Sternbergs triarchic theory |

-Practical (experimental) Apply knowledge to external world. New complex tasks.
-Analytic (internal) Specific Problem solving, something youve seen before. booksmarts
-Creative (external) How well we handle novel (new) situations and tasks |
|
|
|
Psychometric approach definition? |
-Measure intelligence through psycological testing
|
Iq test |
|
|
Mental age? |
Intellectual age at which a person functions. |
|
|
|
Intelligence quotent (IQ) |
Defined ad ratio of mental age to cronilogical age multiplied by 100 |
|
|
|
Standardization |
The use of uniform procedures to adminster, score and test. Individual scores are compared with sample scores. |
|
|
|
Reliability of tests. |
Consistancy in measurements -test-retest reliability: adminster the test more than once. -split-half reliability: divide the items on a single test amoung two groups. |
|
|
|
Validity of tests. |
Accuracy of measurments. Content validity: how well a test accuratly measures what it is intended to. Validity coefficient: correlation between measurment scores and external criterion Predictive validity: correlation between score and further behavior |
|
|
|
Caculating IQ |
Mode- value occurs most frequently Median- the middle value Mean- the average the sum of all scores divided by the number of cased. |
Mean, mode, median |
|
|
Galton theory of psychophysical performance. |
-Psychic energy and heightened sensitivity to external stimuli -Developed tests of an individual sensory processing, motor skills and reaction time. |
|
|
|
Alfrec Binet and Theodore Simon |

Developed first intelligence test. Idetified stindents wjo needed extra help Tests many normal children at each age Compared individual scores to "normal" scores
Mental age Chronological age |
|
|
|
The standford binet |
Comtqins items that require verbql / non-verbal responses -can be used on individual ranging from. |
|
|
|
Lewis terman |
Developed american version of the binet test called the stanford-binet test for ages to 2 -adult. Used ma/ca×100 David wechsler Eugenics |
|
|
|
Eugenics |
Terman believed that his IQtest could help determi5nethe fitness of individuals to reproduce -alberta in 1928 and BC in 1933 enacted laws requiring individuals deemed mentally retarded or ill sterilized. - these laws were repealed in 1972 -terman administered his test to new imgigrants to the united states. |
|
|
|
Wechler int test |
Vocabulary- what does ______ mean? Similarities- how are _____ and ______ alike? Information - where is france? Comprehension- why do pepple need birth certificates? |
4 catagories |
|
|
Flynn effect |
Rise in iq tests over time. However other standardized test have dropped |
|
|
|
Mental Retardation |
General intellectual functioning below average.
Sub average 70-85 iq (13.6%) Mild/profound retardation 70 and below ( 2.3%) Mild retardation- -usually regonized at school -benifits from schooling -linked to enviroment.
profound (2.3%)retardation- -diagnosed early -biological (genetics) |
|
|
|
Giftedness |
Natural ability, talent, or intelligence Top 1-2% of the population -evidance at young age -enviromental contributors -intrisically motivated -may occur in specific areas Example gifted at academics but not social situations. |
|
|
|
Psychodynamic view |
Conflict anxiety, defence Id, ego, super ego Freud psychoanalytic theory Petsonality and behavior are shabed by interacting or dynamic underlying forces.
Theory based on the unconcious. |
|
|
|
Humanistic view |
N |
|
|
|
Trait theory |
L |
|
|
|
5 factor theory |
L |
|
|
|
Personality definition |
A set of behavioral, emotion, and cognitive tendencies.
Unique characteristics, that account for reacurring habits |
|
|
|
Conscious, preconsious, unconscious, id, ego, superego |

Con- thought were activly aware of Pre- arn't consciously aware of but can easily be brought to mind Unconscious-holds memories feelongs that are unpleasant to activly think about and bring anxiety. (ID)
(ID) basic instinctual drives, Imoral, instant gratification, pleasure principle (WANTS NOW)
Ego (ego tries to balance the id and the super ego, tries to satisfy your wants, while understanding what is rationally and moraly possible reality principle)
Superego (preconsious/conscious we internilize and adapt the principles of others, develops in childhood, your morality that leads to guilt and anxiety.)
|
|
|
|
5 stage of psychosexual developmemt |
Freud 1. Oral (0-18 months) pleasure derived from feeding, suckling breats for milk 2. Anal (18-3years) derives pleasure from goin to the bathroom 3. Phallic (3-6y) seek genital stimulation attraction to oppisite sex parent, identification with same sex parent. (Girls stuck at stage 3) 4. Latancy (6-piberty) repression of sexual urges, tranfor urges to socially acceptable activities. 5. Genital (puberty-adult) form mature relationships, related to productive work. |
|
|
|
Defense mechanisms |

Distress cause by anxiety motivates people to rid themselves of anxiety. Defense mechanisms are in the unconcious
Repression Denial
|
|
|
|
Amygdala |
Emotional content Motivation Fear, avoidance Inhibited children may have an overstimulated amygdala. |
|
|
|
Hemisphere dominance |
Right hemisphere dominance- sadness, inhibition, withdrawl introversion Left hemisphere dominance- positive emotikns, traits, extraversion |
|
|
|
Hormones |
Dopamine- high levels- positive emotions, high energy Serotonin- low levels-depression, violance, impulivity Cortisol -high levels inhibition |
|
|
|
Gender and personality |
Female -more empathetic - more neurotic - more sociability -greater individuality -more agressive -more assertive. Strong enviromental factors, sociatal expectations. |
|
|
|
Birth order |
First- conscientious, neurotic Middle- identifies less with family Later-agreeable, extraverted, open to experience |
|
|
|
Sociocognitive |
Lotice of control - understanding that your choices will impact the outcome of external situations. -self efficiency |
|
|
|
Peronality inventories |

Pen and paper questionres designed to access personality Minnesota-useful in acessing abnormal peronality characteristics NEO |
|
|
|
Social psychology |
Seeks to understand, explain, predict, how peoples thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the presence of others. |
|
|
|
Milgram studies |
Shock Person of authority Teacher (subject) Learner (actor)
How far are people willing to follow given orders? Researchers predicted 1-2% go all the way. 2/3 go all the way to 400v lethal All go above 300v lethal Electrical socket 110v |
|
|
|
Social cognition |
How people percieve and interpret there own and others social behavior. |
|
|
|
Attitudes |
Attitudes are patterns, learned behavior, enduring, evaluations tovthings and people. reactions to specific situations. |
|
|
|
Implicit vs explicit attitude |
Implicit - an attitude we are unaware of. Fear is often a factor in implicit attitudes (donald trump fear reaction)
Explicit-attitudes we are aware of To change exposure to prejudice beliefs. |
|
|
|
Cognitive dissonance |
You have an attitude, but your behavior dosent follow said attitude.
(Out of charecter) Your brain trying to rationalize your actions |
|
|
|
Dissonance theory |
-Reducing mismatch between behaviors and feelings -Attempts to reduce cognative dissonance -when people who are not imoral act immorally they can: Change understanding (cheat on tax) Rationlize it by minimizing responsibility (I contribute in many otherways) Deny negatice consequences Blame, dehumanize victims |
|
|
|
Levels of cognitive dissonance |
Levels depend on two factors Personal responsibility (milgram shock experiment, nazis) Reason (ends justify the means.) Three ways to reduce dissonance Indirect stratagies Direct stratagies Trivialize inconsistencies (view it as unimportant, indifference) |
|
|
|
Self perception theory |
When people are uncertain they moniter and observe the behavior Meta cognition |
|
|
|
Persuasion |
The change of an attitude. Central route (working with facts, logic) Peripheral route (superficial, emotion) (making you feel good about something politicians) |
|
|
|
Foot in the door persuasion strategy |
Commitment, get them to agree to agree to something small so they will agree to something larger later. |
|
|
|
Door in the face persuasion method |
Ask for something big knowing you will get turned down, then adk for the smaller item you really wanted. Hey dad can I borrow, 100 $, no how about 10 $? |
|
|
|
Fear persuasion method |
Ad makes it seem like something bad will happen if you do not comply. |
|
|
|
Persuasion aspects |
Comunicator (crediability) (einstein once said)-expertiese (knowledgability) -similarity, likability
Comunicator (crediability) (einstein once said)-expertiese (knowledgability) -similarity, likabilityMessage (perceived honesty) less biased) (show a few negative aspects (buckleys tastes awful and it works)Fear (listerine)The audience Comunicator (crediability) (einstein once said)-expertiese (knowledgability) -similarity, likabilityMessage (perceived honesty) less biased) (show a few negative aspects (buckleys tastes awful and it works)Fear (listerine)The audience Message (perceived honesty) less biased) (show a few negative aspects (buckleys tastes awful and it works)Fear (listerine)The audience )
Fear (listerine) )Fear (listerine)The audience
The audience ( -high vs self monitoring -high self esteem (srong attitude hard to convince already made up the mind) -need for cognition (dont want to ne ignored)
|
|
|
|
Stereotypes |
Generlized impressions on social catagories May be positive or negative . Age, race, beliefs |
|
|
|
Prejudice |
Negative stereotypical attitudes towards all members of a group. Racism, sexism, ageism, homophobia |
|
|
|
Realistic conflict theory |
Amount of conflict bettween groups determines prejudice |
|
|
|
Social identity theory |
Emphasis social cognition factors in onset prejudice. Social categorization. |
|
|
|
Robbers cave study |
In, out group behaviour is learned. Camp eagles vs cougars. Everyone of the out group is bad Everyone of the in group is good |
|
|
|
Contact hypothesis |
Increase awarness of similarities Information inconsistent with stereotypes Challenge outgroup homogeneity Recategorization |
|
|
|
Attribution |
Attribution (an explanation for the cause of an event or behavior) 2 types Personal (internal) - peoples behaviour is causef by there own behaviour Situation (external) - situations and experiences cause behavior. |
|
|
|
Attribution |
Consistancy Distinctiveness Consensus |
|
|
|
Self serving bias |
Personal attribution for success (take credit for good exam) Situational attributiom for failures (blame proffesor) |
|
|
|
Correspondance bias |
Lessen others achievments. Underestimate impact of situational factors Overestimate role of personal factors. |
|

