![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The primary visual cortex is also known as |
V 1 |
|
|
This is specialized for faces |
Fusiform gyrus |
|
|
She had symptoms that were consistent with left brain injury or hemispherectomy |
Genie |
|
|
The lower the SES the lower this is |
Laterality in the brain |
|
|
These are present before birth and become more pronounced in adulthood |
Cerebral asymmetries |
|
|
These two gyri are able to be seen ventrally |
Lingual and fusiform |
|
|
Has different functions |
Heterogeneous |
|
|
This has six layers like the rest of the cortex but layer 4 has a very distinct layers within it that are very thick. Also has blobs |
V one |
|
|
This is maintained in V2 |
Functional heterogeneity |
|
|
This doesn't have blobs , only stripes |
V2 |
|
|
What does a thin stripe represent? |
Color perception |
|
|
What does a thick stripe represent? |
Form |
|
|
What does a pale stripe represent? |
Motion |
|
|
What are the three types of stripes in V2? |
Thin, thick, pale |
|
|
Color vision is the primary job of |
V4 |
|
|
The primary visual cortex gets input from |
The lateral geniculate nucleus |
|
|
V5 is also referred to as |
Mt |
|
|
The dorsal stream goes to this lobe and is in charge of |
Parietal, visual guidance of movements |
|
|
The ventral stream goes to this lobe |
Temporal |
|
|
People who have lesions to this area are not aware of seeing but can act on visual information |
V1 |
|
|
More cortex is devoted to this than any other brain function |
Vision |
|
|
When you lose vision in one visual field there was an injury |
After the crisscross |
|
|
When you lose vision in an entire eye the injury |
Was before the crisscross |
|
|
More blind spots are present then just one in each eye |
Scotoma |
|
|
This patient was struck by a bullet in the back of the brain and World War II, lost sight in the right visual field. He could accurately guess about the presence or absence of light Kama had difficulty reading and recognizing faces |
P.m. |
|
|
There's no clear division on the lateral surface of the brain which separates the occipital cortex from |
The temporal or parietal cortices |
|
|
This separates the upper and lower visual fields and contains much of the primary visual cortex |
Calcarine sulcus |
|
|
V1 |
Primary visual cortex |
|
|
Lingual gyrus contain |
V2 and VP |
|
|
The fusiform gyrus contains |
V4 |
|
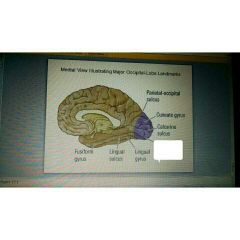
|
Collateral sulcus |
|
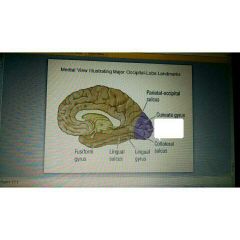
|
Calcarine sulcus |
|
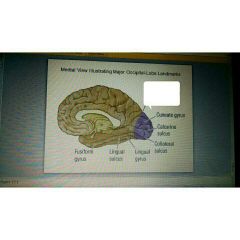
|
Parietal occipital sulcus |
|
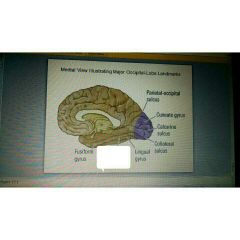
|
Lingual sulcus |
|
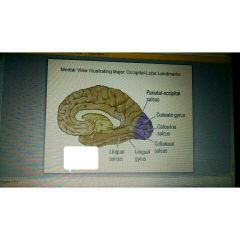
|
Fusiform gyrus |
|
|
Area V1 is functionally |
Heterogeneous |
|
|
Within V1 , layer 4 has how many distinct layers? |
4 |
|
|
What are cytochrome rich areas known as? |
Blobs |
|
|
What is used to separate blobs from inter blob regions? |
Cytochrome oxidase stains |
|
|
Blob cells are in charge of |
Color perception |
|
|
Inter blobs are in charge of? |
Form and motion perception |
|
|
It's functional heterogeneity maintained in V 2? |
Yes |
|
|
In v2 when these are Staind with cytochrome oxidase they are revealed |
Stripes |
|
|
A thin stripe represents |
Color perception |
|
|
A thick stripe represents |
Form |
|
|
A pale stripe represents |
Motion |
|
|
There's distribution of color function across these three areas and much of the occipital lobe |
V1 V2 and V4 |
|
|
Because of the distinct stripes the visual cortex is sometimes called |
The striate cortex |
|
|
Color vision is primarily the job of |
V4 |
|
|
This plays a role in detection of movement, depth and position |
Color vision |
|
|
This receives input from the lateral geniculate nucleus and send output to all other occipital levels |
V1 or primary visual cortex |
|
|
These two sections of the visual cortex send output to all other occipital levels |
Primary visual cortex and secondary visual cortex V1 and V2 |
|
|
After V2 there are these three distinct parallel pathways |
Output to the parietal lobe via the dorsal stream , output to the inferior temporal lobe via the ventral stream , multimodal output to the superior temporal sulcus via the ventral stream |
|
|
The dorsal stream leads to what lobe? |
Parietal |
|
|
The two ventral streams lead to what lobe? |
Temporal |

