![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Psychology?
|
The scientific study of human behavior and mental processes
|
|
|
What is Empiricism?
|
The view that knowledge comes from experience via the senses and that science flourishes through observation and experiment
|
|
|
What is Structuralism?
|
An early school of psychology that used introspection to explore the elemental structure of the human mind
|
|
|
What is Functionalism?
|
A school of psychology that focused on how mental and behavioral processes function – how they enable the organism to adapt, survive, and flourish
|
|
|
What is Humanistic Psychology?
|
It is historically significant perspective that emphasized the growth potential of healthy people; used personalized methods to study personality in hopes of fostering personal growth
|
|
|
Explain the Nature vs. Nurture Issue
|
It's the longstanding controversy over the relative contributions that genes and experience make to the development of psychological traits and behaviors
|
|
|
What is Natural Selection?
|
The principle that, among the range of inherited trait variations, those contributing to reproduction and survival will most likely be passed on to succeeding generations
|
|
|
What are Levels of Analysis?
|
The differing complementary views, from biological to psychological to social-cultural, for analyzing any give phenomenon
|
|
|
What is the Biopsychosocial Approach?
|
An integrated perspective that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis
|
|
|
What is Basic research?
|
It is pure science that aims to increase the scientific knowledge base
|
|
|
What is applied research?
|
It is scientific study that aims to solve practical problems
|
|
|
What is Counseling Psychology?
|
It is a branch of psychology that assists people with problems in living and in achieving greater well-being
|
|
|
What is Clinical Psychology?
|
A branch of psychology that studies, assesses, and treats people with psychological disorders
|
|
|
What is Psychiatry?
|
A branch of medicine dealing with psychological disorders; practiced by physicians who sometimes provide medical treatments as well as psychological therapy
|
|
|
What early contribution did Rene Descartes make to Psychology?
|
- Dissected animals and discovered nerves
- Correctly deduced they enabled reflexes - Incorrectly deduced they were tubes that carried animal spirits |
|
|
What was Francis Bacon known for?
|
- Considered to be a founder of modern science
- Felt people imagined a greater equality and order than actually exists |
|
|
What was John Locke know for?
|
- Wrote "An Essay Concerning Human Understanding"
- Founding father if imperialism |
|
|
What did Wilhelm Wundt do?
|
- He constructed the first psychological experiment
- Trained Bradford Titchener |
|
|
What did Bradford Tichener do?
|
- Founded Structuralism
- Believed nobody could know the mind better than its owner |
|
|
What did William James do?
|
- Founded Functionalism
- First/Early user of student evaluations - Admitted Mary Calkins as a grad student |
|
|
What did Mary Calkins do?
|
- First female to complete a PhD
- Wasn't awarded the title - Studied memory - First female president of the American Psychological Association |
|
|
What did John B Watson and B.F. Skinner do?
|
- Rejected the introspection as useful for studying the mind
- Redefined psychology as the scientific study of observable behavior |
|
|
What did Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow do?
|
- Helped develop Humanistic Psychology
- Rediscovered interest in mental processes |
|
|
What are the three main levels of the Biopsychosocial approach?
|
- Biological Analysis
- Psychosocial Analysis - Social-Cultural Analysis |
|
|
What are some of pychology's subfields?
|
- Basic Research
- Applied Research - Clinical Research - Clinical Application |
|
|
What is Critical Thinking?
|
Thinking that does not blindly accept arguments and conclusions. Rather it examines assumptions, discerns hidden values, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions
|
|
|
What is a Theory?
|
An explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes and predicts observations
|
|
|
What is a Hypothesis?
|
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
|
|
|
What is an Operational Definition?
|
A statement of the procedures used to define research variables. For example, human intelligence may be operationally defined as what an intelligence test measures
|
|
|
What is Replication?
|
Repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to to other participants and circumstances
|
|
|
What is Hindsight Bias?
|
The tendency to believe after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it
|
|
|
What is Critical Thinking?
|
Thinking that does not blindly accept arguments and conclusions. Rather it examines assumptions, discerns hidden values, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions
|
|
|
What is a Case Study?
|
An observational technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
|
|
|
What is a Survey?
|
A technique for ascertaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of people, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of them
|
|
|
What is the False Consensus Effect?
|
The tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share our beliefs and behaviors
|
|
|
What is a Population?
|
All the cases in a group, from which samples may be drawn for a study
|
|
|
What is a Random Sample?
|
A sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
|
|
|
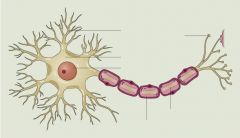
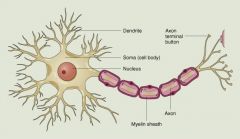
What is a Naturalistic Observation?
|
Observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is sensation?
|
The process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment.
|
|
|
What is perception?
|
The process of organizing and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events
|
|
|
What is bottom-up processing?
|
Analysis that begins with the sensory receptors and works up to the brain's integration of sensory information.
|
|
|
What is top-down processing?
|
Information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations.
|
|
|
What is psychophysics?
|
The sudy of relationships between the physical characteristics of stimuli, such as their intensity, and our psychological experience of them.
|
|
|
What is absolute threshold?
|
The minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time.
|
|
|
What is signal detection theory?
|
a theory predicting how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus amid background stimulation. It assumes there is no single absolute threshold and that detection depends partly on a person's experience, expectations, motivation, and level of fatigque.
|
|
|
What does subliminal mean?
|
Below one's absolute thresholk for consciousness or awareness
|
|
|
What is Priming?
|
The activation, often unconscious, of certain associateions. It predisposes one's perception, memory or response.
|
|
|
What is difference threshold?
|
The minimum difference between two stimuli required for detection 50% of the time.
|
|
|
What is Weber's law?
|
The principle that, to be perceived as different, two stimuli must differ by a minimum and constant ratio vice a constant amount.
|
|
|
What is sensory adaptation?
|
Diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation.
|
|
|
What is transduction?
|
Conversion of one form of energy into another. In sensation, stimulus energies are transformed into neural impulses.
|
|
|
What is wavelength?
|
The peak to peak distance of a wave.
|
|
|
What is the range of the visible spectrum.
|
400 to 700 nanometers
|
|
|
What is a hue?
|
the dimension of color that is determined by the wavelength of light. Also known as color.
|
|
|
What is light intensity?
|
The amplitude of the wave.
|
|
|
What is the pupil?
|
The adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters.
|
|
|
What is the iris?
|
A ring of muscle tissue that controls the pupil's dilation and gives the eye its color.
|
|
|
What is accommodation?
|
The process by which the eye's lens changes shape to focus objects on the retina.
|
|
|
What is the retina?
|
The light-sensitive inner surface of the eye containing the receptor rods, cones, and layers of neurons that begin the processin of visual information.
|
|
|
What is visual acuity?
|
The sharpness or resolution of vision.
|
|
|
What is nearsightedness?
|
A condition in which nearby objects are seen more clearly than distant objects.
|
|
|
What is farsightedness?
|
A condition in which far away objects are seen more clearly than nearby objects.
|

