![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Motivation |
Set of factors ( innate& wants) that activate, direct and maintain behavior usually toward some goal. |
|
|
Emotion |
Subjective feeling that includes arousal, cognitions and expressive behaviors. |
|
|
Instinct Theory |
inborn, unlearned behaviors universal to species. explain motivation, human engage in reflexive behaviors |
|
|
Drive Reduction Theory |
Physiological need (lack) need that elicits a drive toward a behavior that will satisfy the original need. |
|
|
Arousal Theory |
People seek optimal level of arousal that max, their performance Too low: weak/ no behaviors Too High: anxiety/ errors in behaviors Optimal Level: is moderate level of arousal |
|
|
Sensation seeking |
Someone who needs more arousal than an average person. |
|
|
Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic |
In: Behavior itself is motivating ( self-intrest) Ex: motivation is separate from person and behavior from outside source ( rewards can lower motivation, is for reward) |
|
|
ERG: Mini Maslow |
Existence: physiological/ safety needs Relatedness: Belonging needs Growth: Self-esstem, self- actualization *does not have to move through each level sequentially* |
|
|
Incentive Theory |
Motivation results from stimuli that "pull" the organism in a certain direction. Toward desirable goals or undesirable goals |
|
|
Cognitive Theory |
motivation is directly affected by attribution or how we interpret or think about our own or others actions |
|
|
Maslow's Hierarchy of needs |
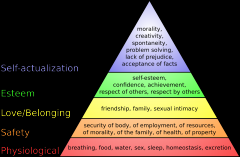
lower needs must be met in order to move up to higher needs. |
|
|
McClelland's Need Theory |
Need for achievement: desire to attain realistic & challenging goals. ( competitive, persistent, learned behavior) Need for affiliation: desire for social interaction and relationships with others. ( liked to be popular, accepted conform to group norms) Need for power: (need to be influential, prestige, lead and control others) |
|
|
Anorexia Nervosa |
eating disorder characterized by a severe loss of weight resulting from self- imposed starvation and an obsessive fear of obesity.( attack own organs, body waste away) |
|
|
Bulimia Nervosa |
consumption of large quantities of food followed by extreme vomiting, extreme exercise and or laxative use. ( chimpmuck cheeks bc of swollen glands, sores on knuckles) |
|
|
Female Athlete Triad |
Eating disorder Period stops bone loss |
|
|
James- Lange |
A stimulus leads 1st to bodily arousal, which is then interpreted as an emotion. I feel sad bc I'm crying. |
|
|
Cannon- Brad |
A stimulus sends signal to the brain to arousal the body & interpret the emotions at the same time. Im crying and feeling sad at the same time. |
|
|
Facial- Feedback |
A stimulus causes arousal and a facial expression. The facial expression provides feedback to brain about the emotion. |
|
|
Schacther- Singer Cognitive Arousal ( two- factor) |
A stimulus leads to both bodily arousal & labeling of that arousal which then leads to labeling & experience of the emotional reaction. |
|
|
Lazarus's Cognitive- Mediational Theory |
A stimulus causes an immediate appraisal cognitive appraisal first, then emotional response, then appropriate bodily response. |

