![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
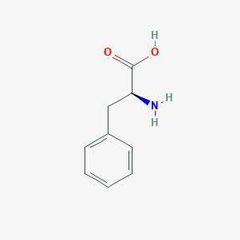
Essential amino acid (p) |
Phenylalanine |
Associated with a genetic disease requiring special protein supplements. |
|
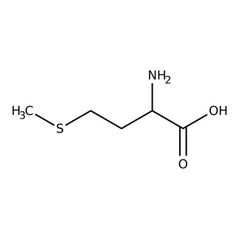
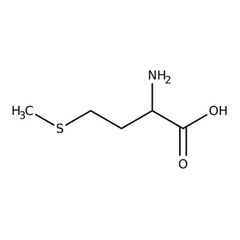
Essential amino acid (m) |
Methionine |
The first amino acid on any chain of protein in the body. |
|
Essential amino acid (T) |
Tryptophan |
People talk about it in relation to thanksgiving turkey. |
|
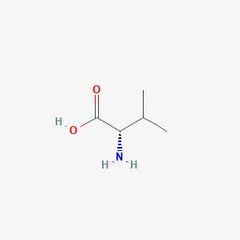
Essential amino acid (V) |
Valine |
|
|
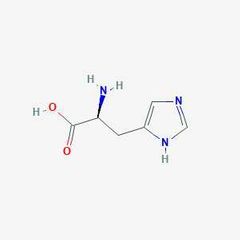
Essential amino acid (h) |
Hiatidine |
|
|
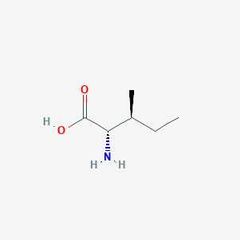
Essential amino acid (I) |
Isoleucine |
Associated with a different amino acid. |
|
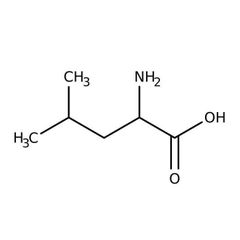
Essential amino acid (L) |
Leucine |
Offen claimed to be low in vegans. |
|
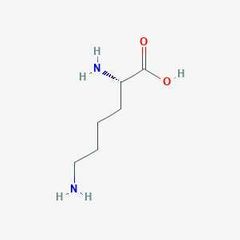
Essential amino acid (Ly) |
Lysine |
Often claimed to be the reason why vegans can't build muscle. |
|
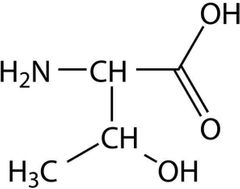
Essential amino acid (th) |
Threonine |
|
|
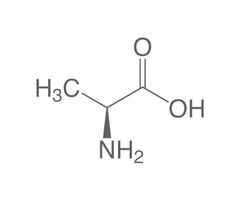
Non-essential amino acid (Al) |
Alanine |
|
|
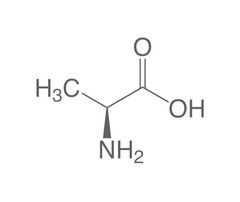
Non-essential amino acid (AA) |
Aspartic Acid |
|
|
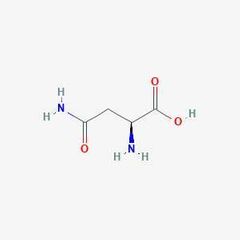
Non-essential amino acid (as) |
Asparagine |
|
|
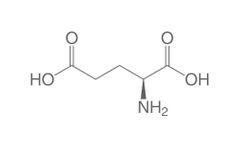
Non-essential amino acid (g) |
Glutamic acid |
|
|
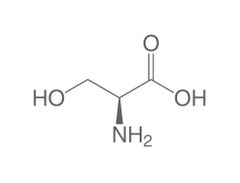
Non-essential amino acid (s) |
Serine |
|
|
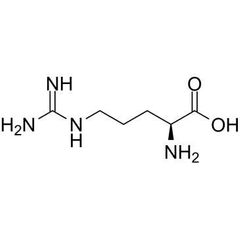
Conditionally essential amino acid (A) |
Arginine |
|
|
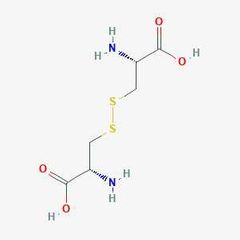
Conditionally essential amino acid (c) |
Cysteine |
|
|
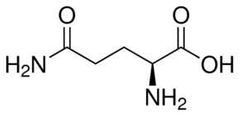
Conditionally essential amino acid (g) |
Glutamine |
People take this for their joints. |
|
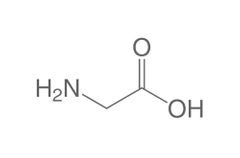
Conditionally essential amino acid (gl) |
Glycine |
Found in collagen |
|
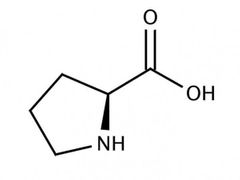
Conditionally essential amino acid (p) |
Proline |
Found in collagen |
|
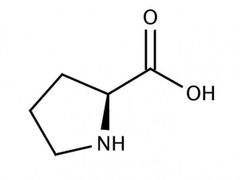
Conditionally essential amino acid (T) |
Tyrosine |
Has to be supplemented into vegan cat food. |
|
|
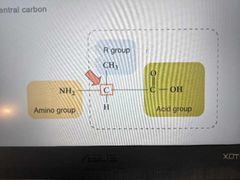
Four parts of an amino acid |
1. Central carbon 2. Acid group 3. Amino group 4. R group |
|
|
|
Transamination |
The transferring of an amino group from one amino acid to a different one. |
|
|
|
Deamination |
The removal of an amino group when it doesn't get attached to a different carbon skeleton. |
|
|
|
Limiting amino acid |
The amino acid in the smallest supply. Limits the proteins the body can make. |
|
|
|
Bonds used to link amino acids |
Peptide bonds |
|
|
|
Primary structure of an amino acid |
Sequence of amino acids. This determines the protein's shape. |
|
|
|
Secondary structure of proteins |
The shape that the amino acid chain twists into, formed by weak bonds between the amino acids. |
|
|
|
Tertiary structure of proteins |
Three dimensional folding of twisted chains, overall shape. |
|
|
|
Quarter art structure of proteins |
2 or more peptides interacting. |
|
|
|
Nitrogen Balence |
Method to determine protein need. |
|
|
|
Negative nitrogen balence |
A person is eating less protein than they need. Can lead to diseases that increase protein breakdown. |
|
|
|
Positive protein balence |
Protein intake greater than losses Occurs durring growth, recovery and intense athletic training. |
|
|
|
RDA for protein |
0.8 g per kg bodyweight |
|
|
|
AMDR for protien |
10% - 35% of calories |
|
|
|
Stomach enzyme for protien breakdown |
Pepsin |
|
|
|
Hormones secreted when protein exits the stomach |
Secretin Cholecystokinin |
|
|
|
Enzymes for protein digestion |
Trypsin Chymotrypsin Carboxypeptidase |
|
|
|
Peptide absorption |
1. Active absorption absorption into cells 2. Continue to be digested 3. Transformed in the liver |
|
|
|
Uses for proteins |
1. Protein synthesis 2. Energy needs 3. Conversion to fat or carbs |
|
|
|
Function of albumin and globulin |
These proteins maintain fluid balance in the blood and can drop when people do not eat enough protein. |
|
|
|
How do proteins help acid-base balance? |
They pump ions into and out of cells by attracting positively charged hydrogen ions. |
|
|
|
How do proteins contribute to immune function? |
Antibodies are proteins and without enough of them your body's ability to fight infection is reduced. |
|
|
|
Retinal-binding protein |
Protein that carries vitamin A |
|
|
|
Transferin and ferritin |
Proteins that carry and store iron |
|
|
|
Ceruloplasmin |
Protein that carries copper. |
|

