![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The main driving force for protein folding is the hydrophobic effect. Describe this... |
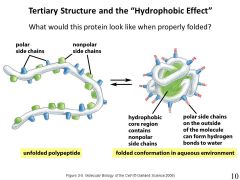
the hydrophobic effect is the tendency of hydrophobic effect is the tendency of amino acids to cluster together. In non-membrane bound proteins, the amino acids are segregated so that the hydrophobic amino acids are in the middle (core) and the hydrophilic amino acids face the outside. |
|
|
how does the hydrophobic effect contribute to the entropy of protein folding? |
-water molecules in contact with a hydrophobic side chain cannot form any type of non-covalent bond with that side-chain as its hydrophobic. -this results in water molecules forming tighter bonds with each other (water-water H bonds) and form "ice-like" structures. -this ice-like structure that surrounds each hydrophobic amino acid side chain can be released, and the water molecules allowed greater freedom---> greater entropy. thus the entropy increases---> 2.4kcalmol-1 increase in entropy for the hydrophobic effect |
|
|
H bonds don't contribute 3kcalmol-1 to the energy of folding- they contribute 1kcalmmol-1 because they also form weak H bonds with water molecules in the unfolded state. |
|
|
Do electrostatic interactions each contribute 5kcal/mol to the free energy of folding? |
no- because the charges are fully solvated (neutralised) by the water in the unfolded state. the entropic contribution of 1kcal/mol remains. |
|
|
The entropy of anything can be calculated by measuring the number of conformations you can have of something- how many different conformations something can adopt. Entropy can be related to the number of states or degrees of freedom of a system. |
S= K In W S=entropy K= boltzman constant In= natural log (inverse of e) W= number of states of a system. |
|
|
Entropy of the polypeptide greatly favours unfolded over the folded (ordered) state therefore... |
proteins are very easily destabilised by mutation or change in environment (pH, temperature etc). |
|
|
To conclude... |
the principle driving force for protein folding (or protein-protein interactions) in aqueous solution (biological systems) is the increased entropy of the water molecules that results from burying hydrophobic amino acid side chains---> HYDROPHOBIC EFFECT. |
|
|
How do proteins fold? |
The actual mechanism for protein folding is unknown. we know that protein folding is very rapid- infact it takes 1 second the amino acid sequence encoded structure and folding pathway. |
|
|
xx |
xx |

