![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
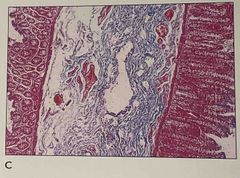
1.What is the problem shown 2. how do you prevent this problem 3. which layer is missing from the section |
1. The section of small intestine has rolled and is not oriented correctly 2. Gastrointestinal specimen should be opened and pinned 3. Muscularis externa cannot be seen |
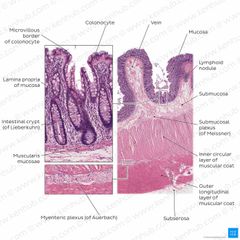
Small intestine has 4 layers that should be seen |
|
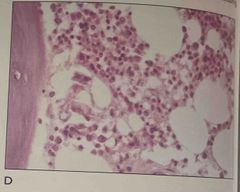
1. What is the tissue shown 2. What is the problem and how could it be prevented 3. The problem show is due to |
1. Bone marrow 2. Carefully monitoring the endpoint of decalcification 3. Overdecalcification |
|
|
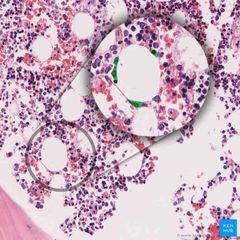
What is this specimen |
Bone marrow |
Notice red blood cells And (white) cavities |
|

1. What is the problem shown 2. How could it be prevented |
1. Improper embedding , tissue was not flat like in the block 2. Ensuring that both sections are embedded flat and at the same level |
|
|
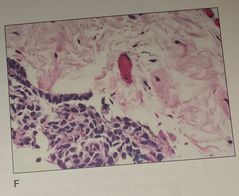
1. What is the problem shown 2. How do you prevent this 3. The problem occurred during which step |
1. Forcep metastasis , the tissue in the upper right is from another specimen 2. Prevent by better cleaning of forceps between specimen 3. Occurred during embedding |
|
|
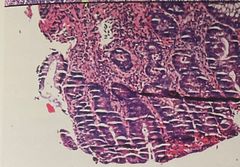
What is the problem and how to prevent |
Parched earth Cause: over dehydration Fix: soak in ice water before cut |
|
|
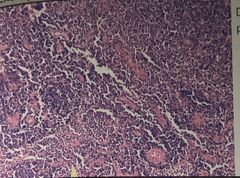
What is the Problem and how to fix |
Dry/ brittle powdery tissue Cause: over dehydration Fix: soak in water before cut |
|
|
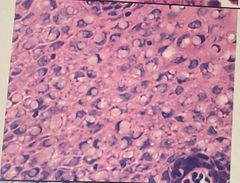
What is the problem and how do you fix it |
Nuclear bubbling Cause: incomplete fixation Fix: reprocess |
|
|
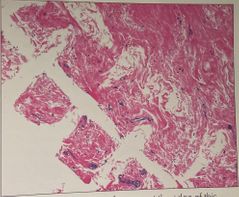
What is the problem and how do you fix it |
Crosshatching Sponge artifact Cause : Placing the tissue between 2 dry sponges |
|
|
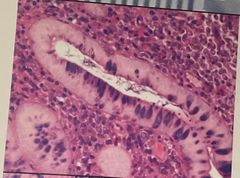
What is the problem |
Washed out epithelial nuclei Cause: contaminated(water) clearing/infiltration |
|
|
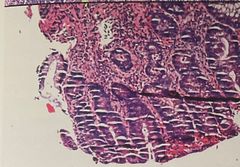
What is the problem |
Micro chatter Cause: over dehydration |
|
|
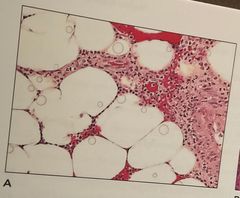
1. What is the problem shown, how to prevent it 2. Best corrected by removing cover glass and .. 3. The problem demonstrated is |
1. Dehydrating the section completely 2. Re-dehyrating and reclearing with fresh solution 3. Incomplete dehydration of section |
There are water droplets |
|
1. What is the problem and what is one possible cause 2. How to correct this |
1. Incomplete deparaffinization Causes: - Incomplete removal of paraffin - water left from incomplete drying 2. Treat w/ xylene and alcohol and decolorize and restain |
Notice White spots |
|
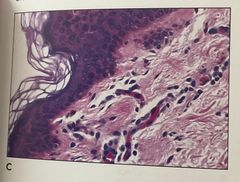
1. What is the problem and what is it caused by 2. How to correct in the future by decreasing .. 3. This problem would not occur if aluminum hematoxylin type had been 4. What is the tissue 5. What is the epithelium shown |
1. Inadequate differentiation 2. Hematoxylin 3. Mayer (difficult to overstrain) 4. Skin 5. Keratinizing stratified squamous |
Notice top is too Dark and nuclei is not reddish-purple or acidophilic |
|
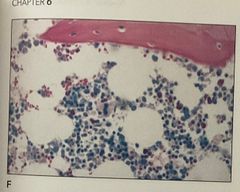
1. The cells showing intense red cytoplasm are 2. The stain shown is 3. The tissue shown is |
1. Erythrocytes 2. Giemsa 3. Bone marrow |
blood cells resemble little dots What stain is used for hematopoietic tissue |
|
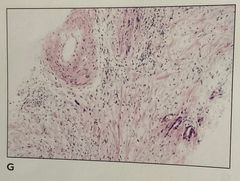
1. What is the problem 2. How can it be prevented 3.what is the tissue structure in the upper left part of the |
1. Eosin not showing 3 shades (not properly differentiated ) 2. Differentiating the eosin better in the lower dehydrating alcohol 3. Blood vessel |
|
|
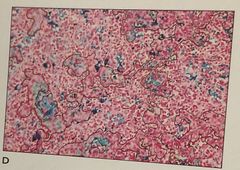
1. What is the problem 2. What could cause this 3. The problem can be corrected by using a mounting medium that is …
|
1. Evaporation of the mounting medium 2. Causes: - warped cover glass - mounting medium too thin 3. Corrected by using fresh mounting medium |
|
|
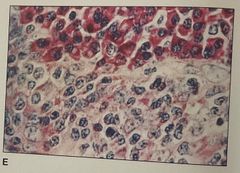
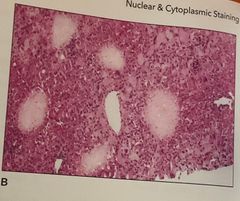
1. The cells that show intense pink cytoplasmic staining are most likely 2. the stain shown is 3. The intense rose color of the cytoplasm is due to |
1. Plasma cells 2. Methyl green - pyronin 3. Rough endoplasmic reticulum |
Stain shows red - RNA ( ribosome) Blue - DNA ( nuclei) |

