![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
166 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Examples of threatened and endangered species (since 2000)
|
-Baija River Dolphin
-W African Black Rhino -Golden Toad -Holdridges Toad -Spix Macaw -Po'o-uli -Hawaiian Crow -Pyrenian Ibex |
|
|
When was the Western Black Rhino declared extinct?
|
November 2013
|
|
|
How many Javan rhinos are left in the wild?
|
44
|
|
|
Date of the Committee on Rare and Endangered Wildlife Species? First list was called?
|
-1964
-Redbook |
|
|
Date of the Endangered Species Conservation Act?
|
1969
|
|
|
Date of the Endangered Species Act?
|
1973
|
|
|
Endangered species are...
|
a species in danger of becoming extinct throughout all or a portion of its environment.
|
|
|
Threatened species are...
|
a species likely to become endangered throughout all or a portion of its environment.
|
|
|
Who can list endangered or threatened species?
|
-Secretary of Interior (U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service)
-Secretary of Commerce (National Marine Fisheries Service) |
|
|
Endangered Species Act requires federal agencies, in consultation with the FWS, to ensure that actions they authorize, fund, or carry out are NOT:
|
-Likely to jeopardize the continued existence of any listed species
-Result in negative impacts to designated critical habitats to such species |
|
|
Critical habitats are...
|
geographic areas and ecosystems essential for the survival of a listed species
|
|
|
Endangered Species Act prohibits...
|
-Any action that causes a "taking" of any listed species
-Import, export, interstate, or foreign commerce of listed species |
|
|
CITES:
|
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wildlife Fauna and Flora (rhino poached of horns, violation of CITES)
|
|
|
What is the most endangered mammal in the world?
|
-White rhino, extinct in the wild
-2011 population: 5 male, 2 female |
|
|
What species was thought to be entirely extinct until a small population was discovered in Wyoming?
|
Black-footed ferret
|
|
|
What species had 22 remaining individuals in the wild in 1987?
|
-California condor
-As of 2012: 405 (226 in wild) |
|
|
ESA successes:
|
-American Alligator (1987)
-Eastern N Pacific Grey Whale (1994) -Brown Pelican (delisted due to ban on DDT) -Maguire Daisy (2011) -Red Kangaroo (1995) -Bald Eagle (2007) |
|
|
Bald eagles and golden eagles are protected under...
|
The Bald Eagle Protection Act
|
|
|
A habitat is...
|
A place where an organism lives, including abiotic and biotic characteristics.
|
|
|
Habitat classifications:
|
-Terrestrial (vegetation characteristics)
-Aquatic (structural characteristics) |
|
|
Major forms of terrestrial vegetation
|
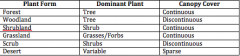
|
|
|
Biomes are...
|
large regions characterized by a type of vegetation
|
|
|
Types of Biomes
|
rainforest, temperate deciduous forest, taiga or boreal forest, chaparral, grassland, savanna, desert, tundra, and polar ice cap.
|
|
|
Major biomes in New Mexico:
|
-Alpine tundra
-Montane coniferous forest -Temperate deciduous forest -Temperate grassland -Chaparral -Desert |
|
|
Tundra:
(Where, Climate, Vegetation, Wildlife) |
-Arctic: far north, Alpine: high elevation
-Cold -Mostly herbaceous, few woody -Simple food chains, migratory or special adaptations for winter |
|
|
Boreal forest:
(Where, Climate, Vegetation, Wildlife) |
-Far north, below tundra (alpine)
-Warmer and more precipitation, soil thaws -Coniferous trees -Many birds use in summer, many mammals (boreal owl, American marten) |
|
|
Deciduous forest:
(Where, Climate, Vegetation, Wildlife) |
-South of boreal zone (NM-riparian zone)
-High precipitation, warm/humid summer; cool winter -Diverse & dense vegetation -Important game species, many migratory birds |
|
|
Grassland:
(Where, Climate, Vegetation, Wildlife) |
-Center of continent; between deciduous & desert
-Low rain; hot summer, cool winter -Grasses -Grazers, adaptations to no tree cover (burrows) |
|
|
Desert:
(Where, Climate, Vegetation, Wildlife) |
-Continental interior & rain shadow behind mountains
-Evaporation>Precipitation -Sparse vegetation -Special adaptations to arid environments (nocturnal) |
|
|
Chaparral:
(Where, Climate, Vegetation, Wildlife) |
-Coastal in temperate zone
-Stable (ideal) -Fire--Disclimax shrubs/trees -(California quail, California mule deer) |
|
|
Major freshwater types of aquatic biomes:
|
Lentic and lotic
|
|
|
Lentic systems are...
|
standing water habitats with little unidirectional water flow
|
|
|
Types of lentic systems:
|
-Natural lakes
-Impoundments: Ponds, small impoundments, and reservoirs -Other: Excavations |
|
|
Oligotrophic means...
|
low in nutrients
|
|
|
Eutrophic means...
|
high in nutrients
|
|
|
Lentic system habitat zones:
|
Littoral and limnetic (photic), profunal, benthic
|
|
|
Photic:
|
Light penetrates
|
|
|
Littoral zone:
|
Vegetation
|
|
|
Limnetic zone:
|
Over deep water
|
|
|
Profunal:
|
Unlighted
|
|
|
Benthic zone:
|
Bottom surface
|
|
|
Thermal stratification:
|
(Summer layers)
-Epilimnion -Thermocline -Hypolimnion |
|
|
Epilimnion:
|
Warm lighter water
|
|
|
Thermocline:
|
Prevents mixing
|
|
|
Hypolimnion:
|
Cool heavy water, often low in oxygen
|
|
|
Fall overturn:
|
when the layers are able to mix; same temperature as the hypolimnion
|
|
|
Winter inverse stratification:
|
Ice cover, then layers of water
|
|
|
Spring overturn:
|
Similar to fall overturn
|
|
|
Lotic systems are...
|
flowing water systems with strong unidirectional water flow
|
|
|
Characteristics of lotic systems:
|
-More uniform oxygen/temperature
-Shallower -Bottom less stable -Nutrients must be replaced -Productivity tied to terrestrial productivity |
|
|
Lotic habitat types:
|
-Riffles
-Pools -Runs -Backwater -Erosional zone -Depositional zone |
|
|
Types of transitional habitats (terrestrial-aquatic):
|
-Riparian zone (lotic)
-Shorelines of lentic systems -Beaches -Wetlands (coastal wetlands, marshes, bogs, swamps) |
|
|
Estuary:
|
place where a river enters the ocean
|
|
|
Characteristics of estuarine:
|
-Transition between fresh & salt water
-Extreme fluctuation in salinity -Salt wedge -High productivity |
|
|
Habitat degradation:
|
Human-induced changes that are negative in relation to native/desirable communities
|
|
|
Major kinds of habitat degradation:
|
-Air pollution
-Water pollution -Urbanization -Agriculture -Logging -Wetland loss -Habitat fragmentation -Channelization -Introduced organisms |
|
|
Type of air pollution:
|
Acid deposition (acid rain)
|
|
|
pH scale:
|
-Measures hydrogen ion concentration
-7 is neutral, below 7 is acidic, above 7 is alkaline |
|
|
Causes of acid deposition:
|
-Burning of fossil fuels
-Sulfur & nitrogen oxides released into atmosphere -Combine with water vapor-->sulfuric acid and nitric acid -Acidic precipitation falls to earth |
|
|
Effects of acid deposition on aquatic habitats:
|
-Reduced reproduction and survival in aquatic organisms
-Affect nutrient cycling -Release toxic heavy metals |
|
|
Effects of acid deposition on terrestrial habitats:
|
-Alter soil chemistry-->plant roots
-Essential minerals wash out -Heavy metals dissolve-->absorbed by roots in toxic amounts |
|
|
Acid deposition has more sever impacts on areas with...
|
low pH (forests)
|
|
|
Acid deposition causes how much damage in the U.S. annually?
|
$5 billion
|
|
|
Cause of global climate change:
|
-Release of greenhouse gas (e.g. CO2) in the forms of burning fossil fuels and deforestation
|
|
|
Global temperature due to global climate change:
|
-Last decade warmest on record
-1.5F increase since 1880 |
|
|
CO2 concentrations due to global climate change:
|
Highest in last 650,000 years
|
|
|
Arctic sea ice due to global climate change:
|
-Lose 11.5% per decade
-2007 lowest extent on record |
|
|
Land ice due to global climate change:
|
-Lose 24 cubic miles/year
-Greenland ice loss doubled 1994-2005 |
|
|
Sea level due to global climate change:
|
Global average sea level 4-8 inches over last century (3.3 mm/year)
|
|
|
Glaciers due to global climate change:
|
Slowly shrinking and disappearing
|
|
|
Weather and ocean due to global climate change:
|
-Extreme weather events
-Ocean acidification (carbonic acid) |
|
|
The ozone layer...
|
provides shield against ultraviolet radiation
|
|
|
Causes of ozone layer depletion:
|
-Use of CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) in air conditioners, refrigerators, and aerosol cans
-CFCs release chlorine with speed breakdown of O3 to O2 |
|
|
Effects of ozone layer depletion:
|
-To humans: skin cancer, eye cataracts, suppressed immune system, declines in agricultural production
-Retards plant growth -Reduced reproduction/survival -Add to global warming |
|
|
Causes of oxygen-demanding waste (water pollution):
|
-Biodegradable organic wastes
-Aerobic decomposers-use of oxygen -Anaerobic decomposers-release toxic substances |
|
|
Effects of oxygen-demanding waste (water pollution):
|
-Reduced reproduction, growth, survival
-Spread disease |
|
|
Causes of sedimentation (water pollution):
|
-Water-insoluble particles erode into water
-Natural causes -Human activities (roads, agriculture, livestock, logging) |
|
|
Effects of sedimentation (water pollution):
|
-Smother bottom-dwelling organisms
-Reduce water depth -Clog gills -Reduce light penetration -Transport excess nutrients, toxic metals, pesticides, herbicides |
|
|
Causes of organic chemicals (water pollution):
|
Oil, pesticides, detergents, gasoline
|
|
|
Effects of organic chemicals (water pollution):
|
-Cancer
-Added nutrients -Toxic -Coat bodies |
|
|
Causes of inorganic chemicals (water pollution):
|
-Mining--toxic metals, acids
-Agriculture--salts, nitrogens, phosphorous -Many others |
|
|
Effects of inorganic chemicals (water pollution):
|
-Excess nutrients-->excess algae/plants
-Reduce reproduction and survival |
|
|
Causes of heat (water pollution):
|
-Industrial cooling
-Reservoir releases |
|
|
Effects of heat (water pollution):
|
-Alters native fauna
-May lack oxygen |
|
|
Causes of urbanization:
|
-Human population growth
-Growth of cities |
|
|
Effects of urbanization:
|
-Loss of habitat
-Change in communities -Fragments habitats -Aquatic habitats severely affected -Change in climate -Negative wildlife-human interactions |
|
|
Habitat degradation-agriculture:
|
-Vast areas of temperate grassland & forest converted
-Soil erosion -Fertilizers and pesticides -Ground water depletion -Monoculture reduces diversity encourages disease/pests |
|
|
Habitat degradation-livestock:
|
-Reduce numbers and biomass of nutritious plants
-Destruction of riparian zones and steam beds -Increased erosion -Invasion of pests -Competition with wildlife |
|
|
Habitat degradation-logging:
|
-Impact related to scope and kind of logging
-Conversion to monoculture forest-reduces diversity -Habitat fragmentation -Soil erosion -Stream warming & destruction -Increased roads (increase erosion, stream damage, human access) -Fire suppression |
|
|
Habitat degradation-wetland loss:
|
-Viewed as wastelands (most productive & important)
-Loss of habitat -Increase disease outbreak -Reduced water purification |
|
|
Habitat destruction causes...
|
habitat fragmentation
|
|
|
Purpose of channelization:
|
Improve shipping or move water more rapidly
|
|
|
Methods of channelization:
|
Dredging, straightening, snag removal, etc.
|
|
|
Effects of channelization:
|
-Loss of habitat
-Dams change habitat & form barriers |
|
|
Causes of introduced species:
|
-Natural range expansion
-Intentional introductions -Accidental escape |
|
|
The Commons:
|
-Resources owned by everyone
-Activities on private land can impact the Commons or other peoples' private property |
|
|
Issues of the Commons:
|
-Should a person be able to do whatever they want on private property (without regards to other peoples rights?)
-U.S. law says no one has right to use property in a way that causes harm to other peoples rights |
|
|
The Takings:
|
Idea held by some private property owners that laws that are intending to protect the Commons (and other peoples private property) take away property rights & if these laws are enforced, they should be compensated.
|
|
|
Goal of habitat management:
|
Change habitat (improve/degrade) in order to manipulate animal populations or communities
-Needs focal species -Increasing/maintaining biodiversity |
|
|
General methods of habitat management:
|
-Add/remove natural structures
-Add/remove artificial structures -Modify ecological succession |
|
|
Major approaches to terrestrial habitat management:
|
-Food
-Cover -Water |
|
|
Methods of food production:
|
-Propagation
-Release -Protection |
|
|
Propagation:
|
Plant seeds or transplant seeds
|
|
|
Release:
|
Reduce undesirable competitive plants
|
|
|
Methods of release:
|
-Mechanical
-Chemical -Burning |
|
|
Benefits of prescribed burns:
|
-Remove dead vegetation
-Free nutrients -Reduce invaders/encourage natives -Earlier green up |
|
|
Types of prescribed burns:
|
Reclamation burn and maintenance burn
|
|
|
Reclamation burn:
|
Convert damaged vegetation to healthier conditions
|
|
|
Maintenance burn:
|
Used as regular management practice to maintain conditions
|
|
|
Backfire:
|
Burn slower and more thoroughly
|
|
|
Headfire:
|
Burn rapid and less thoroughly
|
|
|
Protection:
|
-Protect plants from herbivores until mature
-Usually use fencing |
|
|
Examples of cover development:
|
-Plant or protect cover of plants
-Protect snags -Artificial nests -Exclude livestock -Build islands |
|
|
Methods of water development:
|
-Use where water is limited
-Enhance natural sources -Create new water |
|
|
Major methods of lentic habitat management:
|
-Dissolved oxygen
-Water level -Aquatic vegetation control -Terrestrial landscaping -Fertilization -Artificial structures |
|
|
Winterkill:
|
Ice causes loss of oxygen, increase toxins (more common in eutrophic waters)
|
|
|
Methods of managing winterkill:
|
-Reduce nutrient/sediment inputs
-Aeration systems (open water allows light penetration) -Manage as marginal water |
|
|
Summerkill:
|
Algal bloom death causes loss of oxygen (also low CO2 in hypolimnion)
|
|
|
Method of managing summerkill:
|
Aeration systems (prevent stratification)
|
|
|
Draw-downs:
|
-Use when stunted prey (concentrates predator & prey)
-Release nutrients in bottom-oxidation -Improve water clarity-compacts silt -Increase food/cover-terrestrial vegetation |
|
|
Flooding:
|
-Improve food/cover
-Increase water clarity -Dredging to deepen |
|
|
Aquatic vegetation control:
|
Need to maintain some vegetation (30%)
|
|
|
Methods of aquatic vegetation control:
|
-Don't build shallow lakes
-Mechanical -Chemical (temporary, expensive) -Biological (grass carp) |
|
|
Mechanical methods of aquatic vegetation control:
|
-Raking
-Harvesters -Dredging -Plastic sheeting -Winter drawdowns |
|
|
Other methods of aquatic habitat management:
|
-Terrestrial landscaping (reduces erosion, increases shade)
-Fertilization (increase k, use in areas with infertile soils that stay warm) -Artificial structures (creates fish cover) |
|
|
Purposes of regulations:
|
-Controlling overexploitation
-Achieve a particular management goal -Make resources available to more users -Psychological needs -Social/political concerns |
|
|
Fishery regulations:
|
-Usually include both number & size limits
-Can be released -Densities higher -Indeterminate growth-different sized individuals -Management units can be small |
|
|
Wildlife regulations:
|
-Usually include number limits
-Can not be released -Densities lower -Determinate growth-same-sized individuals -Need large management units |
|
|
Aspects that can be managed:
|
-Who
-What -Where -When -How |
|
|
Regulating who, means of limiting take:
|
-Resident only
-Hunter education certificate -Children only hunting/fishing areas -Limiting number of licenses |
|
|
Regulating who, means of encouraging use:
|
-Reduce fees for minors
-Reduced fees for senior citizens -Landowner benefits (reduced cost, increased portion of lottery) -Special considerations for persons with disabilities -Reduced fees for nonresident military & students |
|
|
Regulating what:
|
-By species
-By number -Lottery/drawing -Quotas -Creel/bag/possession limits -Point system -Lifetime limit -By sex -By size |
|
|
By species:
|
-Generally, non game & endangered species may not be harvested
-Take species with low population may be limited -Depends on location |
|
|
By number:
|
Set number of permits by area/unit
|
|
|
Lottery/drawing:
|
When demand exceeds permits available
|
|
|
Quotas:
|
-Allow harvest of set proportion of population
-Often difficult, expensive -Set permits per unit often equal to quota |
|
|
Creel/bag/possession limits:
|
-Must be very restrictive to prevent over harvest
-Usually set for political/social reasons -Can be used to distribute harvest equally & extend season -Reduce waste -Adds a perceived value |
|
|
Point system:
|
-Used for migratory waterfowl
-Various species worth different points, must stop when reach certain point total -Allows knowledgable hunters to take more common species -Allows reduction of excess males |
|
|
By sex:
|
-Species must be dimorphic
-Common in polygynous wildlife species -If male only-allows large harvests without hurting reproduction -Monogamous species must be managed more carefully |
|
|
By size:
|
(common in fisheries)
-Minimum length limits (release all under set limit) -Protected slot length limit (release all within set limit) -Reverse slot length -Reverse length limit -Catch & release (provide trophy fish opportunities) |
|
|
Appearance restrictions:
|
-By antler/horn structure
-Used in wildlife -Used to increase proportion of trophy animals (theoretically) -Could negatively impact genetics |
|
|
Regulating when:
|
-Time of year
-Time of day -After sunrise, before sunset |
|
|
Time of year:
|
-Usually restricts harvest to fall/winter when populations are at a high
-Protects breeding/spawning season -Reduces take -May be political/social -Can get reduction of harvest if close season during peak harvest activity times |
|
|
Time of day:
|
-Half-day hunts
-Reduces take -Reduces harassment |
|
|
After sunrise, before sunset:
|
Waterfowl most vulnerable before sunrise & after sunset
|
|
|
Regulating when:
|
-Sanctuaries
-Hunting units -Trespass -Safety units |
|
|
Sanctuaries:
|
-Areas off limits to hunting
-Used for waterfowl-can increases harvest on adjacent lands -Used for commercial marine fisheries |
|
|
Hunting units:
|
-Used where limited number permits
-Allows regulation of areas differently |
|
|
Trespass:
|
Legality of hunting on unmarked private land varies
|
|
|
Safety issues:
|
Shooting from roads, over roads, near houses
|
|
|
Regulating how:
|
-Some methods more efficient or more accessible than others
-Terminal tackle restrictions -Number of poles, lines, hooks, snagging -Weapon type and specifications -Use of "help" (dogs, boats, lights, baits, calls) |
|
|
The Lacey Act (1900):
(directed at the biota) |
-The Game and Wild Bird Preservation Act 1900
-Regulates interstate transport of illegally killed animals -Regulates international commerce in protected organisms -Prohibits importation of injurious species into US |
|
|
Migratory Bird Treaty Act (1918):
(directed at the biota) |
-US law to implement the Migratory Bird Treaty
-Made migratory birds under federal law -Supreme court upheld |
|
|
Other laws:
(directed at the biota) |
-Bald Eagle Protection Act (1940)
-Marine Mammal Protection Act (1972) -Fish and Wildlife Conservation Act (1980) -Fish and Wildlife Coordination Act (1934) |
|
|
Laws towards migratory bird habitats and wetlands:
|
-Migratory Bird Conservation Act (1929)
-Migratory Bird Hunting Stamp Act (1934) -Accelerated Wetlands Acquisition Act (1961) -North American Waterfowl Conservation Act (1989) |
|
|
Laws towards the environment:
|
-National Environmental Policy Act (1969)
-Federal Environmental Pesticide Control Act (1972) -Toxic Substances Control Act (1976) -Clean Water Act (1977) |
|
|
National Environmental Policy Act:
|
-Established Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Council on Environmental Quality
-Requires environmental impact statements (EIS) for all projects receiving federal funds |
|
|
Financial aid to states:
|
-Pittman-Robertson Act (1937)
-Dingell-Johnson Act (1950) |
|
|
Pittman-Robertson Act:
|
-Federal Aid in Wildlife Restoration Act
-11% tax on firearms and ammunition -Proceeds for use by states for wildlife restoration and management -Amendments include handguns and bow/arrows, some goes to hunter's safety |
|
|
Dingell-Johnson Act:
|
-Federal Aid in Sport Fish Restoration Act
-Importance of PR and DJ Acts -Provide additional funds (from users of resources) to support resource -Protects state license fees from diversion -Provides incentive to states to develop projects |
|
|
Management of federal lands laws:
|
-Taylor Grazing Act (1934)
-Multiple Use-Sustained Yield Act (1960) -Public Rangeland Improvement Act (1978) -National Forest Management Act (1976) -Wilderness Act (1964) |
|
|
Multiple Use-Sustained Yield:
|
-Legal basis for multiple use on National Forest Land
-Classification and Multiple Use Act (1964) similar but applies to BLM lands |
|
|
Public Rangeland Improvement Act:
|
-Improvement of federal lands to comply with NEPA and maintain diversity of native species
-Federal Land Policy and Management Act (1976)- similar but aimed at BLM |
|
|
Retirement of Agricultural Lands:
|
-Soil Bank Act (1956)
-Food Security Act [Farm Bill] (1985, 1990) -Water Bank Program (1972) |
|
|
Food Security Act [Farm Bill] (1985, 1990):
|
-Created Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) that provides funds to landowners who take highly erodible land out of production
-Swampbuster Provision -Sodbuster Provision |
|
|
Water Bank Program:
|
10-year agreements to protect wetlands and plant adjacent cover
|

