![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Space |
The geometric surface of the earth |
|
|
Place |
A bounded area of some human importance (does not have to be inhabited) |
|
|
Toponym |
A place name |
|
|
Sequent occupancy |
The succession of groups and cultural influences throughout a place's history |
|
|
Map scale |
The ratio of distance on a map and distance in the real world |
|
|
Relative scale |
Aka scale of analysis Level at which things are grouped for examination Local, city, country, state, regional, national, continental, international, global |
|
|
Formal region |
Area of bounded space that possesses some homogeneous characteristic or uniformity U.S. and Australia are in the same linguistic region Dixie (dialect, food, architecture, climate, ethnicity, religion) Linguistic, culture, political, environmental |
|
|
Functional regions |
Aka nodal regions Areas that have a central place (node) as a focus, and its influence is strongest closest to it and dominishes as you get further away E.g. professional sports team |
|
|
Vernacular region |
Based upon the collective perspective of the residents E.g. Dixie - country music, Southern Baptist church, warm weather, etc. |
|
|
Absolute location |
A precise point identified by latitude and longitude coordinates |
|
|
Relative location |
The location of a place compared to a known place or feature |
|
|
Latitude |
Distance in degrees north or south of the equator |
|
|
Longitude |
Distance in degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian |
|
|
Absolute distance |
Distance between two places measured in linear units (miles) |
|
|
Distance decay |
The further away a place is from a place of origin, the less likely they are to interact with each other |
|
|
Friction of distance |
When distance inhibits the interaction between two points |
|
|
Tobler's law |
All places are interrelated, but closer ones are more related than further ones |
|
|
Space-time compression |
Decreased time and distance between places E.g. air travel, internet |
|
|
Central place |
A node of human activity (usually centers of economic exchange) |
|
|
Core and periphery |
One point is most central to a region (cultural, economic, political, environmental) but the periphery has the characteristics less concentrated |
|
|
Land survey patterns |
Metes and bounds - natural landscape features divide the land Township and range - based upon lines of latitude and longitude Long-lot patterns - narrow frontage along a road or waterway with a very long lot shape behind |
|
|
Arithmetic density |
Number of things per square unit of distance |
|
|
Agricultural density |
Number of people per square foot of land actively used for farming |
|
|
Physiologic density |
Number of people per square unit of arable land (actively farmed or not) |
|
|
Hierarchical diffusion |
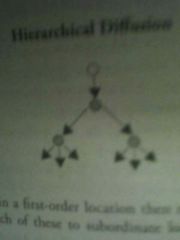
Starts with one, moves down to second order, then on to increasingly local |
|
|
Contagious diffusion |

Begins at a point of origin, moves outward to nearby locations |
|
|
Stimulus diffusion |
A general principle diffuses and stimulates the creation of new products or ideas |
|
|
Expansion diffusion |
The pattern originates in a central place and moves outward in all directions |
|
|
Relocation diffusion |
The pattern begins at a point of origin then crosses significant physical barriers then relocates on the other side |

