![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Length of pregnancy |
40 weeks for gestational age 38 weeks for embryonic/fetal age |
|
|
Even though gestational age is more often used clinically than the fetal age, what would be a situation in which the fetal age would be used? |
in vitro fertilization or artificial insemination |
|
|
Viability definition |
ability of a fetus to survive in the extrauterine environment |
|
|
Difference between full-term neonates and pre-term neonates |
Full-term neonates have lower birth weight because of IUGR Pre-term neonates are underweight because of shortened gestation |
|
|
Postmaturity Syndrome |
When pregnancy is delayed 3-several weeks beyond expected date, fetus may experience dysmaturity (absence of subq fat, wrinkling of skin, or meconium staining, mortality) |
|
|
What is the embryonic period and why is it important? |
0-8 weeks after conception This is when the embryo is developing all of its major organs so it is the most susceptible |
|
|
Week 1 timeline |
Zygote starts dividing into 2 cells (30 hrs); 4 cell division to 8 cell division Morula forms days 3-4 which then becomes a blastocyst Late blastocyst forms Days 6-7; right before implantation |
|
|
Week 2 timeline |
Blastocyst implantation into the endometrium Bilaminar disc forms. |
|
|
Week 3 timeline |
-gastrulation (ie. neuralation & development of notocord) -heart and embryonic blood vessels start to form |
|
|
Week 4 timeline |
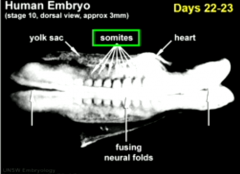
Everything starts developing -- major changes in body -neural tube forms inside somites -folding occurs -end of week 4 embryo has a C-shaped curvature |
|
|
Week 5 timeline |
-Minor changes in the body -Growth of head exceeds others (brain is developing) |
|
|
Week 6 timeline |
Upper limb starts to show regional differences Lower limb (4-5 days behind) is still a nub Umbilical herniation (intestines enter extraembryonic coelom) Spontaneous twitching mvmts of embryo that can't be felt by mom |
|
|
Week 7 timeline |
-notches between the digital rays in the hand plates (fingers) -ossification of upper limbs |
|
|
Week 8 timeline |
Digits of the hand then feet separate Purposeful movements of limbs Embryo has distinct human characteristics Intestines are still proximal potion of the umbilical cord |
|
|
Week 9 timeline |
-period of proliferation, differentiation, and increase in size -primordia of all major system have formed |
|
|
The fetal period is defined as.. |
weeks 9 to week 38 (birth) |
|
|
Weeks 9-12 (3 months) timeline |
-rapid growth in body length -upper limb is reach in relative length but not lower limb -primary ossification center appears -Week 11, intestines have returned to abdomen -Developing kidneys produce urine -erythropoiesis has begun in the spleen -Week 12 you can tell sex externally |
|
|
Weeks 13-16 (4 months) |
-fetus rapidly growing -skeletal ossification is active -limb movements become coordinated but not felt -eyes & ears are close to definitive positions -fetal ovaries differentiate & contain primordial ovarian follicles with oogonia |
|
|
Weeks 17-20 (5 months) |
-growth slows down -fetal movements (quickening) can be felt -vernix caseosa coats skin -eyebrows, head hair, and lanugo visible -testes begin to descend -uterus and vagina form |
|
|
Week 21-26 (6 months) |
-substantial weight gain -by (starts at 21 week but not sufficient) 24 weeks interalveolar walls of the lung to secrete surfactant |
|
|
What's the earliest a baby can be born to survive |
22 weeks via intensive care, however a premature baby after 32 weeks have a greater chance of survival |
|
|
Weeks 26-29 (7 months) |
-lung and pulmonary vasculature developed for adequate gas exchange -bone marrow becomes the major site of erythropoiesis -CNS matured to direct breathing and control body temp |
|
|
Weeks 30-34 (8 months) |
skin is pink, smooth and limbs are chubby |
|
|
Weeks 35-38 (9 months) |
Weight: ~7.5 lbs Nervous system mature enough testes in scrotum |
|
|
Effects on premature babies |
immature lung and CNS Undescended testes (cryptorchidism) |
|
|
malformation def |
defect resulting from an intrinsically abnormal developmental process (ie. chromosomal aberration--trisomy) |
|
|
Disruption |
defect resulting from extrinsic problem with an originally normal developmental process (not inherited---ie. teratogens) |
|
|
Deformation |
body defect resulting from mechanical forces (ie. intrauterine compression) |
|
|
Syndrome vs. association |
Syndrome: group of anomalies occuring together with a specific common cause (ie. down syndrome) Association: multiple anomalies occuring together randomly with unknown cause() (ie. VACTERL) |
|
|
Teratogen |
Any agent that can produce a congenital anomaly or increase incidence of a congenital anomaly |
|
|
Thaliodomide |
-sedative & Tranquilizer given as morning sickness Affects: -Meromelia, amelia or micromelia -absence of external and internal ears -heart defects -anomalies of urinary & digestive system |
|
|
What's the difference between meromelia, amelia, micromelia |
meromelia - absence of part of limbs amelia- absences of limbs micromelia- abnormally small or short limbs |
|
|
Thalomide caused severe limb defects when.. |
24-36 days post-fertilization (3.5-5 weeks) more severe during times of limb development |
|
|
Accutane |
-form of retinoic acid prescribed for severe cystic acne -Retinoic acid is synthesized from Vitamin A -It is a ligand that binds to receptors and in large amounts it will turn on Hox and Pax genes when it shouldn't be turned on during development -crucial exposure 3-5 weeks post fertilization Effects: -craniofacial dysmorphism -cleft palate -cardiovascular anomalies -neural tube defects -neuropsychological impairment |
|
|
Fetal Alcohol sydrome |
-severe end of the Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder -Effects: -thin upper lip, smooth philtrum, epicathal folds, short nose, growth deficits, CNS abnormalities (microcephaly), intellectual disabilities, cardiac anomalies -these features may be caused by cell death of structures derived from neural crest cells |
|
|
Cigarette smoking anomalies |
-can cause intrauterine growth restriction, premature delivery & low birth weight -nicotine constricts uterine blood vessels |
|
|
What are the TORCH infections? |
they are group of perinatal (time little bit before and after birth) infections with similar clinical presentation Toxoplasma Other (ie. Syphilis) Rubella Cytomegalovirus Herpes Simplex Virus |
|
|
Rubella virus can cause |
Sensorieural hearing loss Eye defects (cataracts & glaucoma) Cardiac defects Blueberry muffin lesions |
|
|
When should a baby be checked for rubella |
1st prenatal visit because it can cross the placenta |
|
|
Why is cytomegalovirus the most common viral infection in fetuses? |
It can be spread via contact with blodily fluids |
|
|
Clinical presentation of cytomegalovirus |
-low birth weight -hepatosplenomegaly -jaundice -microcephaly |
|
|
Late complications of cytomegalovirus |
hearing loss vision impairment intellectual disability delayed psychomotor development |
|
|
Do all fetuses with cytomegalovirus show symptoms? |
no 90% asymptomatic |
|
|
How can a mother be infected by toxoplasmosis? |
eating raw or poorly cooked meat close contact w/ infected domestic animals (cats--litter box) |

