![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
106 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List 3 uses of plants and explain |
Food- primary food source for humans Fuel-Burning of wood for heat Erosion Control |
|
|
What is the structure and function of Parenchyma? |
Structure: thin walled, flexible and sphere shaped Function:storage, photosynthesis, and gas exchange |
|
|
What is the structure and function of the Collenchyma? |
Structure: elongated cells, flexible, and spherical Function: support for surrounding cells, flexibility and tissue repair. |
|
|
What is the structure and function of the sclerenchyma? |
Structure- thick cell walls, contain lignin, lack cytoplasm Function: support for mature plant |
|
|
I am a waxy protective coating, what am I? |
Cuticle |
|
|
What is made up of transparent cells that allow light to pass through? |
Upper epidermis |
|
|
What do guard cells do? |
Control the opening and closing of the stomata |
|
|
A layer of loosely packed cells that allow for gas exchange |
Spongy Mesophyll |
|
|
Made up of elongated cells with many chloroplasts |
Palisade Mesophyll |
|
|
What is the epidermis' function? |
Prevents water loss, allows light to come through and site of gas exchange |
|
|
Mesophylls main duties are? |
Gas exchange and photosynthesis |
|
|
Is this a monocot or eudicot? Stem or root? |
Monocot Stem (herbaceous) |
|
|
What is this? |
Woody stem |
|
|
How are the xylem & phloem arranged in monocot and eudicot stems. |
Monocot- xylem and phloem in ring Eudicot- xylem in "x" shape and phloem between arms of X |
|
|
Characteristics of herbaceous stems? |
Green & flexible, contain chlorophyll |
|
|
Chracteristics of woody stems |
Hard and rigid |
|
|
What is the function of stems? |
Provide support for leaves. Storage area for water and food. Connect vascular tissue in roots to leaves. |
|
|
Structure of roots? |
Root tips containing meristem cells that allow for elongation |
|
|
Funtion of roots? |
Take in water and dissolved minerals from soil and anchor plants in soil |
|
|
Function of leaves? |
Absorb energy from sunlight through chloroplasts. Site of gas exchange. Protection from herbivores. |
|
|
How is water transported through plants? |
Moves into roots through osmosis, then moves into xylem at centre of root. After it moves up leaves through root pressure and transpiration pull. |
|
|
How is water transported through plants? |
Moves into roots through osmosis, then moves into xylem at centre of root. After it moves up leaves through root pressure and transpiration pull. |
|
|
What is root pressure? |
Pressure created as water particles diffuse into roots. There is an increase in positive pressure therefore column of water pushes up |
|
|
How is water transported through plants? |
Moves into roots through osmosis, then moves into xylem at centre of root. After it moves up leaves through root pressure and transpiration pull. |
|
|
What is root pressure? |
Pressure created as water particles diffuse into roots. There is an increase in positive pressure therefore column of water pushes up |
|
|
What process creates a negative pressure to pull water up? |
Transpiration Pull |
|
|
How is water transported through plants? |
Moves into roots through osmosis, then moves into xylem at centre of root. After it moves up leaves through root pressure and transpiration pull. |
|
|
What is root pressure? |
Pressure created as water particles diffuse into roots. There is an increase in positive pressure therefore column of water pushes up |
|
|
What process creates a negative pressure to pull water up? |
Transpiration Pull |
|
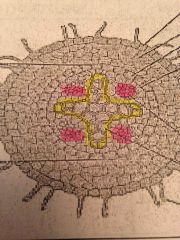
Is this a monocot or a dicot root/stem? |
Dicot Root |
|
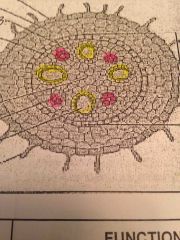
Is this a monocot or a dicot root or stem? |
Monocot root |
|
|
What is cohesion ? |
Cohesion causes molecules to stick together with H bonds pulling eachother up |
|
|
What is cohesion ? |
Cohesion causes molecules to stick together with H bonds pulling eachother up |
|
|
What is adhesion? |
Adhesion causes water to stick to side of xylem causing them to resist gravity. |
|
|
In what process does sucrose move from source to sink by water pressure in vacuoles of phloem? |
Translocation |
|
|
List common techniques for asexual reproduction |
Grafting, splitting, and air layering |
|
|
List common techniques for asexual reproduction |
Grafting, splitting, and air layering |
|
|
What is grafting? |
2 stems forced together through cutting |
|
|
List common techniques for asexual reproduction |
Grafting, splitting, and air layering |
|
|
What is grafting? |
2 stems forced together through cutting |
|
|
What is splitting? |
Split plant in two and plant somewhere else |
|
|
List common techniques for asexual reproduction |
Grafting, splitting, and air layering |
|
|
What is grafting? |
2 stems forced together through cutting |
|
|
What is splitting? |
Split plant in two and plant somewhere else |
|
|
What is airlayering? |
Placing a bag of soil around stem, it will turn into a root, then cut and plant |
|
|
List common techniques for asexual reproduction |
Grafting, splitting, and air layering |
|
|
What is grafting? |
2 stems forced together through cutting |
|
|
What is splitting? |
Split plant in two and plant somewhere else |
|
|
What is airlayering? |
Placing a bag of soil around stem, it will turn into a root, then cut and plant |
|
|
Unfertilized sperm cell, food source for zygote |
Endosperm |
|
|
List common techniques for asexual reproduction |
Grafting, splitting, and air layering |
|
|
What is grafting? |
2 stems forced together through cutting |
|
|
What is splitting? |
Split plant in two and plant somewhere else |
|
|
What is airlayering? |
Placing a bag of soil around stem, it will turn into a root, then cut and plant |
|
|
Unfertilized sperm cell, food source for zygote |
Endosperm |
|
|
What is an embryo |
Germinated haploid zygote. |
|
|
Explain how seeds can be dispersed? |
Wind or when it sticks to another organism |
|
|
Explain how seeds can be dispersed? |
Wind or when it sticks to another organism |
|
|
Apical meristems growth increasing plant height |
Primary growth |
|
|
Explain how seeds can be dispersed? |
Wind or when it sticks to another organism |
|
|
Apical meristems growth increasing plant height |
Primary growth |
|
|
Lateral meristem growth increasing plants girth |
Secondary Growth |
|
|
Factors that effect plant growth and development? |
Light quality, temperature, hormones, and soil quality |
|
|
Factors that effect plant growth and development? |
Light quality, temperature, hormones, and soil quality |
|
|
What are micronutrients? |
Nutrients needed in small amounts for cell processes |
|
|
Factors that effect plant growth and development? |
Light quality, temperature, hormones, and soil quality |
|
|
What are micronutrients? |
Nutrients needed in small amounts for cell processes |
|
|
What are macronutrients? |
Nutrients needed in large amounts |
|
|
Factors that effect plant growth and development? |
Light quality, temperature, hormones, and soil quality |
|
|
What are micronutrients? |
Nutrients needed in small amounts for cell processes |
|
|
What are macronutrients? |
Nutrients needed in large amounts |
|
|
The change of an environment from no life to one with life |
Primary Succession |
|
|
Factors that effect plant growth and development? |
Light quality, temperature, hormones, and soil quality |
|
|
What are micronutrients? |
Nutrients needed in small amounts for cell processes |
|
|
What are macronutrients? |
Nutrients needed in large amounts |
|
|
The change of an environment from no life to one with life |
Primary Succession |
|
|
The change of an ecosystem which as been diminished back into one with lots of life |
Secondary succession |
|
|
what are the two types of growth regulators? |
Stimulatory Hormones and Inhibitory Hormones |
|
|
what are the two types of growth regulators? |
Stimulatory Hormones and Inhibitory Hormones |
|
|
What do auxins do? |
Control growth of plant through elongation |
|
|
what are the two types of growth regulators? |
Stimulatory Hormones and Inhibitory Hormones |
|
|
What do auxins do? |
Control growth of plant through elongation |
|
|
What do cytokinins do? |
Stimulate cell division |
|
|
what are the two types of growth regulators? |
Stimulatory Hormones and Inhibitory Hormones |
|
|
What do auxins do? |
Control growth of plant through elongation |
|
|
What do cytokinins do? |
Stimulate cell division |
|
|
What do gibberellins do? |
Stimulate plant growth in cell walls |
|
|
What does ethylene do? |
Stops growth of plant, forces leaves to fall off and fruit to ripen |
|
|
What does ethylene do? |
Stops growth of plant, forces leaves to fall off and fruit to ripen |
|
|
What does abscisic acid do? |
Closes stomata to stop growth |
|
|
Movements independent of direction stimulus, reversable and repeatable, caused by changes in water |
Nastic Responces |
|
|
Movements independent of direction stimulus, reversable and repeatable, caused by changes in water |
Nastic Responces |
|
|
Dependant on direction of stimulus, permanent, caused by release of various growth regulators that bring about elongation. |
Tropic responses |
|
|
Movements independent of direction stimulus, reversable and repeatable, caused by changes in water |
Nastic Responces |
|
|
Dependant on direction of stimulus, permanent, caused by release of various growth regulators that bring about elongation. |
Tropic responses |
|
|
What is phototropism |
Growth in response to light |
|
|
Movements independent of direction stimulus, reversable and repeatable, caused by changes in water |
Nastic Responces |
|
|
Dependant on direction of stimulus, permanent, caused by release of various growth regulators that bring about elongation. |
Tropic responses |
|
|
What is phototropism |
Growth in response to light |
|
|
What is gravitropism |
Growth in response to gravity |
|
|
Movements independent of direction stimulus, reversable and repeatable, caused by changes in water |
Nastic Responces |
|
|
Dependant on direction of stimulus, permanent, caused by release of various growth regulators that bring about elongation. |
Tropic responses |
|
|
What is phototropism |
Growth in response to light |
|
|
What is gravitropism |
Growth in response to gravity |
|
|
What is thigmotropism |
Response to mechanical stimuli |
|
|
Is a leaf monocot or eudicot? |
Eudicot |

