![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
104 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an experimental group |
The group that receives a different treatment |
|
|
What is the control group |
The group that receives the same to no treatment |
|
|
Why is it important to have both |
To be able to compare results and data |
|
|
What is a hypothesis |
An educated guess |
|
|
What is a placebo |
A harmless pill, medicine, or procedure prescribed more for the psychological benefit to the patient then fire any physiological effect |
|
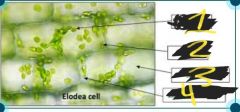
|
1) chloroplasts 2) cell wall 3) cytoplasm 4) plasma membrane |
|

|
1) central vacuole 2) cell wall 3) nucleus 4) nucleolus 5) chloroplast |
|
|
What is phenol red and how it reacts to Ph change |
Phenol red is a pH indicator which is red(out hot pink) under alkaline conditions (anove 8.2) and yellow unset acidic conditions (below 6.8) |
|
|
What is elodea and why it was used for the labs |
Elkdea is a common freshwater aquatic plant, used because.... |
|
|
Why'd would you expect the water to change color when it has the Elodea I it? |
?? |
|
|
Why did the color change occur? Whaybdoes that mean? Why were bubbles produced? |
The green extract should take on a burgundy red tint as the process of fluorescence occurs. In this reaction, the chlorophyll molecules absorb light energy which excites electrons |
|
|
Labor what seed germination and imbibition are |
Seed germination is the process of seeds developing into plants. Imbibtions is the uptakwnof water. It is a passive process that sweet the seeds, it activates the enzymes for cellular respiration to begin. Germination is the process of seeds developing into new plants. First, environmental conditions must trigger the seed to grow. Usually this is determined by how deep the seed is planted, water availabily, and temperature. When water is plentiful, the seed fills with water in process called imbibition. The water activates special proteins, called enzymes that begin the process of seeds growth. First the seed grows a root to access water underground. Next the shoots of growth above ground begins to appear. The seed sends a shoot towards the surface, where it will grow leaves to harvest engery from the sun. The leaves continue to grow towards then might source in a process called photomorphogenesis |
|
|
Know the scientific name of the plant you worked with in lab report 2 |
Phaseolus lanatus is the Liam bean. Grown in central America and California. Thigomorphogensis is the development in the plants response to touch. |
|
|
What is old xylem? |
In the center of the tree, no longer serves in conduction but serves only as structural support and waste dump |
|
|
What is phloem |
Phloem is a series of tubes like xylem but it is alive and transports organic nutrients like carbs |
|
|
Vascular cambium? Vascular cambium? |
A cylinder of meristematic tissue that produces additional xylic and phloic tissues. |
|
|
Do trees grow the same way as humans do? |
No trees have indeterminate growth, they grow forever, and humans stop growing. |
|
|
What is girdling? |
Cut through the bark all the way around (a tree or branch), typically in order to kill it or to kill a branch to make the tree more fruitful. |
|
|
Why did we use liquid nitrogen? What does it do? |
It will involve the use of liquid nitrogen flash freezing followed by grinding the frozen tissue with a mortar and pestle. This is to break open the tough cell walls with intense mechanical agitation. |
|
|
How is plant DNA different animal? |
The plant cell wall and the yields of DNA from plant tissues by these methods will generally be lower and of lower quality than for a comparable animal tissue extraction. |
|
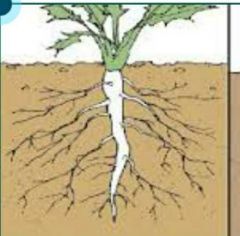
What kind of root is this? |
Taproot: Central, large dominant root in a plant. |
|
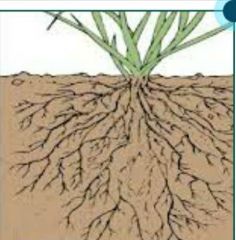
What type of root is this? |
Fibrous: It has moderately thin branches |
|
|
Why are roots important? |
Taking up air, water, and nutrients from the soil and moving them up into the leaves, where they can interact with sunlight to produce sugars, flavors, and energy for the plant. |
|
|
Be able to explain why some plants have different root structures. |
For nutrient and water uptake/storage depending upon the plant species/environment it lives in |
|
|
Why do some plants have shrunken stomata? |
Plants with sunken stomata are found in dry habitats and not even with the plant surface. The sunken stomata trap moist air, which reduces diffusion and reduces water loss. |
|
|
Why do some plants have thick cuticles? |
Like Cacti, these types of plants have thick cuticles to prevent water loss and trap more water in.
|
|
|
Why are leaves important for photosynthesis? |
During photosynthesis, plants trap light energy from the sun with their leaves and use that energy to change water and carbon dioxide into glucose. Leaves are usually thin to permit light penetration to all of the internal photosynthetic cells. Leaf pores can be opened to admit carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Leaves have conducting tissue in veins to transport the water to the cells and sugars to other parts of the plant as needed. |
|
|
What are trichomes? |
Trichomes are root/leaf hairs that absorb water and minerals, reflect radiation, lower plant temperature, and reduce water loss. |
|
|
Be able to tell the difference between leaves in sunlight and shade. |
A leaf in the sun would have thicker leaf structures to gather more sunlight for photosynthesis. A leaf in the shade would have thinner and broader leaf structure because it needs more leaf area to trap energy for photosynthesis. |
|
|
Why do some plants not produce seeds? |
Spore producing plants have a different life cycle than seed producing plants. |
|
|
What do they produce instead? |
They produce spores rather than seeds, which allows the spores to be dispersed to different locations by wind. |
|
|
What are some advantages/disadvantages of being a seedless plant? |
Advantages include that they can disperse spores for reproduction, can grow in various places, and some have a vascular system. Only disadvantages I could find were that seedless decreases biodiversity, which reduces plant species resistance to disease. |
|
|
What are the groupings of seedless plants pteridophytes, bryophytes, and lycophytes? |
Bryophytes are nonvascular, do not have specialized vascular tissue with lignin containing cell walls for conducting fluids and nutrients through the body. Lycophytes and pteridophytes are vascular. |
|
|
Be able to give examples and identify plants in each grouping.
|
Bryophytes: liverworts, hornworts, and mosses Lycophytes: club mosses, spike mosses, and quillworts Pteridophytes: whisk fern, horsetails, and ferns
|
|
|
Know how to correctly write scientific names. |
Genus species; or specific epithet |
|
|
Know the protection features seeds have. |
A seed consists of a protective seed coat that encloses an embryonic offspring plant and nutritive tissue. The nutritive tissue will provide the embryo with energy and nutrients needed during seed germination. |
|
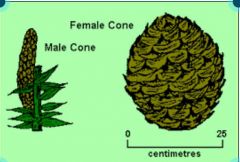
Be able to identify male vs. female cones (in pine trees). |
Male cones, pollen-bearing or staminate cones, are small and produce pollen grains. Female cones, ovule-bearing or seed cones, have ovules containing egg cells that later turn into seeds. |
|
|
What are conifers? |
Conifers are gymnosperm and cone bearers. |
|

|
Cedar |
|

|
Douglas Firs |
|

|
Cypresses |
|

|
Junipers |
|
|
Know the difference between angiosperms and gymnosperms. |
Gymnosperms are naked seeds that develop from ovules that are NOT enclosed in a structure, but rather EXPOSED on a cone scale or a stalk. Gymnosperms consist of conifers (pine, fir, spruce, cedar, etc.), cycads, ginkgo, and unusual gnetophytes. Angiosperms are flowering plants. Flowers include female structures called pistils, and male structures called stamens. |
|
|
What are cotyledons? |
A cotyledon is part of the embryo within the seed of a plant. Often when the seed germinates the cotyledon may become the first leaves of the seedling. Monocots – one cotyledon. Dicots – two cotyledons. Cotyledons are important for new plants as it begins to grow because they contain the stored food reserves form the seed to give the plant int initial burst of energy to grow. |
|
|
Why are common names not as useful as the scientific names? |
Scientists avoid using common names because they are often not specific enough to a particular species. Thank you Carl Linnaeus! Classification: Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. |
|
|
Why do plants produce flowers? What different adaptations do flowers have to attract pollinators? |
Flowers are the reproductive structures of flowering plants. The function of a flower is to produce a fruit that contains seeds. Every fruit has developed from a flower. Different adaptations to attract animals are visually or by smell. |
|
|
Know that everything we worked with in lab was a fruit. |
Everything we worked on with lab is a fruit. That includes: peanut, almond, walnut, strawberry, raspberry, apple, orange, corn, pineapple, coconut. |
|
|
Know why it is advantageous for plants to produce fruits. |
Fruits have seeds in them, and when eaten, they get pooped out (dispersed) in another location to begin growing a new plant. |
|
|
High power objectives have the working distance of about? High power objectives have the working distance of about? ? |
1 mm |
|
|
What is the apparent increase in size of an image. |
Magnification |
|
|
What is the name of the green organelles within which photosynthesis occurs? |
Chloroplast |
|
|
What is the diffusion of water across a membrane, moving to the side that has a lower water concentration. |
Osmosis |
|
|
What type of aquatic plant will we be using for this lab? |
Elodea |
|
|
What is a red pH indicator that we will be using in this lab. |
Phenol |
|
|
The green coloration of most plants is primarily the result of what pigments. |
chlorophyll |
|
|
Photosynthesis is a __ step process. |
2 |
|
|
What is an extremely important by-product of photosynthesis? |
Oxygen |
|
|
Angiosperms are what kind of plants. |
Flowering |
|
|
What are the naked-seeded plants that include conifers. |
Gymnosperms |
|
|
Attached to the embryo are one or more fleshy, nutrient rich structures called what? |
cotyledons |
|
|
The first step in the germination process is the uptake of water, called what. It is a passive process that swells the seed. |
Imbibition |
|
|
A particular seed will develop into a mature plant of a genetically predetermined form. |
True |
|
|
Phyton is a Greek word that means what? |
Plant |
|
|
A plant responding to various types of touch is called? |
thigmotrophisim |
|
|
Do plants grown in greenhouses usually have longer, thinner stems than another plant of the same species that is grown in a garden? |
True |
|
|
Do most plants require phosphorous? |
True |
|
|
Why are trees important? |
Provide shade, provide products, provide oxygen |
|
|
What kind of bud contains short, immature shoot with tiny immature leaves. |
Vegetative |
|
|
What are tough, shingle-like modified leaves covering a bud, used to protect the bud against damage and desiccation called? |
Bud scales |
|
|
What feature allows gas exchange on a twig? |
Lenticel |
|
|
You can tell the age of a tree from various features (ex: tree rings, and leaf scars). |
True |
|
|
You be extracting DNA from Hibiscus plant species. |
True |
|
|
Animal DNA is harder to extract and has a lower quality in most cases than extracted plant DNA. |
False |
|
|
We will be using what chemical substance to help break down the plant cell wall? |
Liquid Nitrogen |
|
|
Plants have tough cell wall made out of what. |
Cellulose |
|
|
Because plants are easy to manipulate, plant DNA is second only to what other DNA as a primary experimental subject for bioengineers. |
bacterial |
|
|
The what protects the root tip as it pushes through the soil. |
Root cap |
|
|
What is the method of killing trees by removing bark all along the trees trunk called? |
Girdling |
|
|
What are fungi called that engage in a mutually beneficial relationship with plant roots? |
Mycorrhizae |
|
|
Xerophytes are a category of plants that grow in what types of areas? |
Desert/Dry |
|
|
More than 90 % of the water lost from a plant is lost through stomata, in a process called? |
Transpiration |
|
|
The seedless plants include the liverworts, hornworts, and mosses, which are collectively referred to as? |
Bryophytes |
|
|
The ____ and pteridophytes are referred to as vascular seedless plants. |
lycophytes |
|
|
Plants spore-producing body is called? |
Sporophyte |
|
|
The zygote remains in place on the gametophyte to grow into the |
sporophyte |
|
|
Bryophytes are nonvascular plants. |
True |
|
|
In what do the naked seeds develop from ovules that are not enclosed in a structure, but rater are exposed on a cone scale or a stalk. |
gymnosperms |
|
|
Greek: gymnos means naked. |
True |
|
|
Confiners produce male (pollen-bearing) and female (ovule-bearing) cones. |
True |
|
|
A plant’s binominal scientific name consists of two words, the genus and the specific epithet. |
True |
|
|
Which is the correct way to rewrite the scientific name for pinus strobus? |
Pinus strobus |
|
|
Flowering plants are classified primarily on the basis of their what structure. |
Flowering |
|
|
What is the female structure on flowers (composed of stigma, style, and ovary). |
Pistil |
|
|
What is the male structure on flowers (composed of anther and filament). |
Stamen |
|
|
Every fruit has developed from a flower. |
True |
|
|
For this coming week’s lab, you will be dissecting flowers. |
True |
|

Terimial or apical bud |
Contains minture unelongated shoot The twig grows in length when the terminal grows |
|

Lateral or axillary bud |
Grows into a side shoot Present in every leaf axil, and above every leaf scar |
|

|
Tough, shingle-like modified leaves covering the bud Protects the bud blconyentd against damage and desiccation |
|

|
Thin scared left behind when the bud scales fall off during the spring |
|
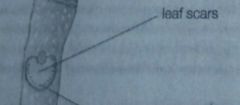
|
Scar left behind when a leaf falls off the twig |
|
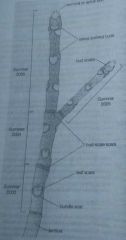
One year growth |
The length of twig from a terminal bud back to the closet but scar The lrmght of twig between two sets of bud scale scars |
|

|
Within a leaf scar The end of the vein that had entered the leaf |
|

|
Wart like break in the twig surface Allows gas exchange Is linear, across the twig in birch Is a round black dot in buckeye and maple |

