![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Actin is also known as the _____________ filament and Myosin as the ______________ filament. |
thin, thick |
|
|
The unit of contraction in a skeletal muscle cell is called a? |
Sarcomere |
|
|
The electrical impulse that is communicated to the entire heart muscle starts and is conducted by these specialized cells |
Pace maker cells |
|
|
In regards to the skeletal muscle contraction cycle, in order for a shape change to occur and the Myosin binding sites on Actin to be visible, ______________ needs to bind to Troponin. |
Calcium |
|
|
Select the characteristics unique to single-unit smooth muscle cells. (Select all that apply) A. These muscle cells are richly innervated with branches of the autonomic nervous system B. These muscle cells communicate through gap junctions which allows action potentials to travel to all cells C These muscle cells are found along the walls of hollow organs like the GI tract D Some of these cells have mechanically-gated sodium (Na+) channels that open when the muscle is stretched |
A. These muscle cells are richly innervated with branches of the autonomic nervous system B These muscle cells communicate through gap junctions which allows action potentials to travel to all cells C These muscle cells are found along the walls of hollow organs like the GI tract D Some of these cells have mechanically-gated sodium (Na+) channels that open when the muscle is stretched |
|
|
The contraction units in smooth muscle differ from skeletal muscle in which ways. (Select all that apply) A. The Actin and Myosin are not contained in a sarcomere B. The contraction filaments run diagonally through the muscle cell C. The contraction filaments attach to z-lines to stabilize them D. The Actin fiber lacks both regulating proteins |
A. The Actin and Myosin are not contained in a sarcomere B. The contraction filaments run diagonally through the muscle cell C. The contraction filaments attach to z-lines to stabilize them D. The Actin fiber lacks both regulating proteins |
|
|
In regards to the skeletal muscle contraction cycle, once the Myosin head has attached to the bonding site on the Actin fiber, what must happen to cause the Myosin head to bend inward, toward the center of the sarcomere?
|
ADP+P must be released off of the Myosin head |
|
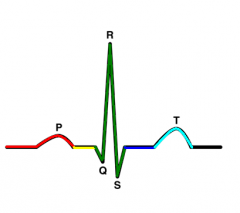
T wave |
ventricular repolarization |
|
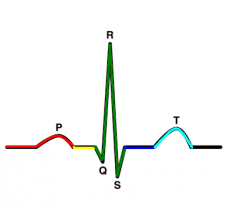
P wave |
atrial depolarization |
|
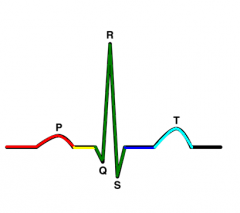
ST segment |
signal passing out of ventricles |
|
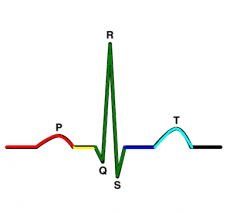
QRS Segment |
ventricular depolarization |
|
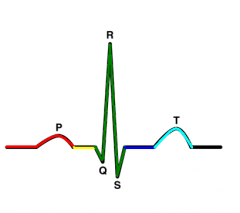
RS Segment |
Perkinje fibers |
|
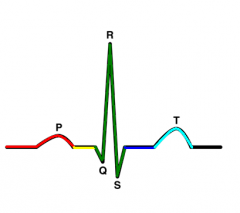
QR Segment |
Bundle Branches |
|
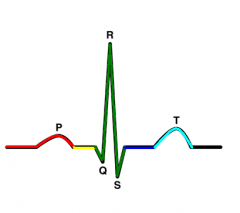
PQ Segment |
AV node delay |
|
|
Put the area of electrical conduction in order starting with the where the initial impulse happens all the way through until it ends
Bundle of His
Atrioventricular node
Sinoatrial Node
Purkinje Fibers |
Put the area of electrical conduction in order starting with the where the initial impulse happens all the way through until it ends __3__ Bundle of His __2__ Atrioventricular node __1__ Sinoatrial Node __4__ Purkinje Fibers |
|
|
The 2 functional motions of the GI tract muscles are peristalsis and fermentation T or F |
False The 2 functional motions of the GI tract muscle are peristalsis and segmentation |
|
|
In smooth muscle, if the outer longitudinal layer of the muscle contracts the organ will shorten and dilate. T or F |
True |
|
|
The specialized tiny tubes that run from the surface of the cellular membrane deep into the muscle cell are called the sarcolemma. T or F |
False- These tiny tubes are called the t-tubules |
|
|
In skeletal muscle the sarcoplasmic reticulum has voltage-gated calcium (Ca++) channels along its cellular membrane. T or F |
True |
|
|
Cardiac muscle cells have large numbers of ribosomes to generate protein that is used for energy.T or F |
False Cardiac muscle cells have large numbers of mitochondria to generate ATP that is used for energy. |
|
|
The pace maker cells all fire at the same time to ensure a strong contraction of the heart muscle. T or F |
False The pace maker cells initiate and distribute the electrical impulse along the conduction system in a way that allows the heart muscle to contract in an orderly fashion |
|
|
4 steps in the actin myosin contraction cycle |
1. attachment 2. pulling 3. detachment 4. reactivation
|

