![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
__________ was the first person that concluded that blood must circulate around and around |
William Harvey (English Physician, 1578-1657 ) |
|
|
|
William Harvey’s work published in year _______ is considered the beginning of modern physiology and cardiovascular research |
1628 |
|
|
|
The Cardiovascular System(CVS) consists of the heart and the network of blood vessels in which the blood circulates. T/F |
True |
|
|
|
CVS in human is a open circulatory system. T/f |
False Closed |
|
|
|
The vascular network of CVS consist of what ? |
Aorta, Arteries, Arterioles, Capillaries, Venules, Veins and Vena cavae. |
|
|
|
The cardiovascular system has two main divisions; |
Systemic circulation (major division) Pulmonary circulation (minor division) |
|
|
|
_____________ involves transportation of blood and its constituents from the left side of the heart to the body tissues and back to the right side of the heart. |
Systemic circulation |
|
|
|
The _____________ is called the major circulation and it is a high pressure driven system. |
Systemic circulation |
|
|
|
The pump for the systemic circulation is the ________ |
Left ventircle |
|
|
|
The feeding venous system to the systemic circulation is the __________ |
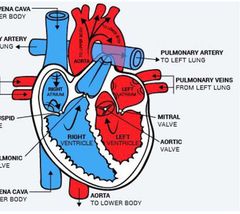
Pulmonary venous system |
|
|
|
Systemic Circulation Route are |

|
|
|
|
________ involves transportation of blood and its constituents from the right side of the heart to lung and back to the left side of the heart. |
Pulmonary circulation |
|
|
|
_________ is a low pressure driven system compared with systemic circulation. |
Pulmonary circulation |
|
|
|
The pump for the pulmonary circulation is the ______ . |
Right ventricle |
|
|
|
The feeding venous system to the pulmonary circulation is the _________ |
Systemic venous system. |
|
|
|
Highlight the Pulmonary circulation route |

|
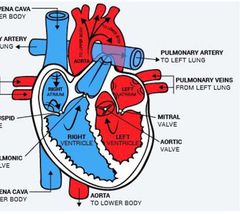
|
|
|
The functions of the cardiovascular system can be categorised into two; |
Mechanical function Electrical function |
|
|
|
The electrical activity initiates mechanical activities. T/F |
True |
|
|
|
Without electrical activity, there will be no mechanical activities. T/f |
True |
|
|
|
__________ is the Central pump through myocardial contractility Generates and propagates the cardiac electrical impulses |
Heart |
|
|
|
__________ is the Central pump through myocardial contractility Generates and propagates the cardiac electrical impulses |
Heart |
|
|
|
_____________Transport blood under high pressure and maintain blood flow at high velocities |
Arteries |
|
|
|
___________Maintains blood flow in response to tissue demand |
Arterioles |
|
|
|
__________ Exchange water, gases, nutrients, hormones, cytokines and other substances between the vascular system and interstitium |
Capillaries |
|
|
|
________ Transport blood from capillaries into veins |
Venules |
|
|
|
____________Transport blood under low pressure from venules into heart; |
Veins Also serve as controllable blood reservoir |
|
|
|
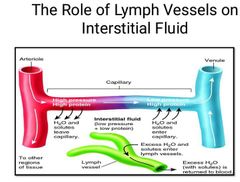
_________ refers to the movement of fluid between capillary and interstitium |
Capillary Fluid Exchange |
|
|
|
Capillary Fluid Exchange depends on pressure gradients between the capillary and the tissue at arteriolar and venular ends of the capillary as illustrated by Starling equation. T/f |
True |
|
|
|
In year ________, Ernest H. Starling, a British Physiologist derived an equation that shows relationship among forces that govern movement of fluid in and out of capillary |
1896 Jv = Kfc[(Pc-Pi)- σ(πp - πi)] Jv = Net rate of capillary filtrationn Kfc = Capillary filtration coefficient (a product of capillary surface area and capillary hydraulic conductance) Pc = Capillary hydrostatic pressure P i= Interstitial hydrostatic pressure σ = Osmotic reflection coefficient πp = Plasma oncotic pressure π i= Interstitial oncotic pressure |
|
|
|
Capillary fluid exchange is determined by four forces; |
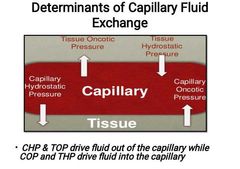
•Capillary Oncotic pressure (COP) •Capillary Hydrostatic Pressure (CHP) •Tissue Oncotic pressure (TOP) •Tissue Hydrostatic Pressure (THP) |
|
|
|
___________ is the osmotic pressure generated by plasma proteins. It draws fluid from interstitium into the capillary |
Capillary Oncotic Pressure (COP): |
|
|
|
_________ is the force generated by fluid within the capillary. It pushes fluid out of the capillary into the interstitium |
Capillary hydrostatic pressure (CHP) : |
|
|
|
________ is the force generated by interstitial proteins. It draws fluid from capillary into interstitium. |
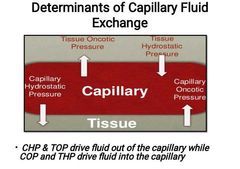
Tissue oncotic pressure (TOP): |
|
|
|
___________ is the force generated by interstitial fluid. It pushes fluid out of interstitium into the capillary |
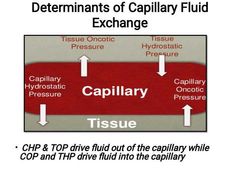
Tissue Hydrostatic Pressure (THP) : |
|
|
|
_____ = Net hydrostatic pressure - net oncotic pressure |
CFP |
|
|
|
COP-TOP = ________ |
Net oncotic pressure |
|
|
|
CHP-THP = _________ |
Net hydrostatic pressure |
|
|
|
_________ is the swelling of a tissue resulting from excessive accumulation of fluid within the tissue. |
Oedema |
|
|
|
________ is associated with imbalance of forces governing capillary fluid exchange with resultant fluid accumulation in the interstitial tissue. |
Oedema |
|
|
|
The pathophysiological mechanisms involved in oedema include; |
•Decrease plasma oncotic pressure: such as liver disease, nephrotic syndrome •Increase capillary hydrostatic pressure: e.g Congestive Heart Failure. •Increase capillary permeability: e.g Anaphylactic reactions, sepsis •Lymphatic obstruction: Filariasis |
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle consists of three groups; |
Specialized muscle; Cardiac electrical System. Atrial muscle Ventricular Muscle |
|
|
|
What is the Organization of Cardiac Electrical System |
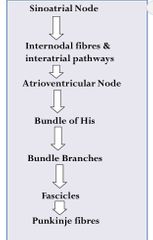
|
|
|
|
The Pacemaker of the heart is the ______ |
Sinoatrial Node |
|
|
|
The cardiac pace maker was Discovered in 1906 but first described(published) in 1907 in the countryside of Kent (UK) by __________ laboratory assistance; ______ and his (a young medical student). |
Arthur Keith Martin Flack |
|
|
|
The human sinoatrial node measures approximately 1.5cm long and 0.5cm wide. T/f |
True |
|
|
|
The cardiac pace maker (SA node) is Located in the upper wall of the right atrium, close to the interatrial septum at the entrance of superior vena cava into the right atrium. T/f |
True |
|
|
|
The cardiac pace maker (SA node) is Located in the upper wall of the right atrium, close to the interatrial septum at the entrance of superior vena cava into the right atrium. T/f |
True |
|
|
|
Potential exhibited by cardiac pacemaker cells is called ___________ |
Pacemaker potential |
|
|
|
The pacemaker is predominantly sinoatrial node action potential. T/F |
True |
|
|
|
The pacemaker is predominantly sinoatrial node action potential. T/F |
True |
|
|
|
What are the three phases of pace maker action potetials |
Pacemaker potential(prepotential), phase 4, Depolarization, phase 0 & Repolarization, phase 3. 403 |
|
|
|
Resting potential of a pacemaker cell ranges from _____-______ |
-60 to -70 mV |
|
|
|
The threshold for the pacemaker potential ranges from ___-____ |
-40 to -50mV |
|
|
|
What is the phase 4 of the sinoatrial action potential |
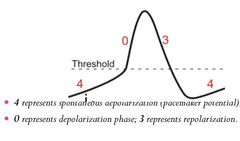
Phase 4 Spontaneous Depolarization
(Continuous K + efflux,Slow Na+ influx & Slow CA 2+ influx) |
|
|
|
What happens at the PHASE 0 of the sinoatrial Node Action potential |
Phase 0 Depolarization (Slow CA 2+ INFLUX) |
|
|
|
What happens at the PHASE 0 of the sinoatrial Node Action potential |
Phase 0 Depolarization (Slow CA 2+ INFLUX) |
|
|
|
What happens at Phase 3 of the sinoatrial node action potential |
Phase 3 Repolarization (K+ efflux) |
|
|
|
Individual cardiac muscle cells are separated from one another by |
intercalated discs |
|
|
|
Individual cardiac muscle cells are separated from one another by |
intercalated discs |
|
|
|
At Intercalated disc,the cells fuse with one another forming gap junctions which allow free ionic movement that facilitates intercellular communication. T/f |
True |
|
|
|
At Intercalated disc,the cells fuse with one another forming gap junctions which allow free ionic movement that facilitates intercellular communication. T/f |
True |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle fibres are arranged in a latticework with the fibres dividing,recombining form a syncytium. T/f |
True |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle fibres are arranged in a latticework with the fibres dividing,recombining form a syncytium. T/f |
True |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle consists of two syncytia; |
Atrial syncytium Ventricular syncytium |
|
|
|
The two syncytia are separated by a fibrous tissue of low electrical resistance. T/f |
False High electrical resistance |
|
|
|
Separation of atrial and ventricular syncytia allows for _______ |
Atrioventricular synchrony; |
|
|
|
Atrial excitation precedes ventricular excitation and thus the mechanical activities. T/f |
True |
|
|
|
__________ refers to the action potential of the myocardial cells. |
Myocardial action potential |
|
|
|
The resting membrane potential of myocardial cell ≈________. |
-90mV |
|
|
|
Duration of myocardial action potential ranges from _________ to __________ |
200ms (atrial muscle) to 400ms (ventricular muscle) |
|
|
|
The myocardial action potential has five phases( 0 - 5), Mention them |
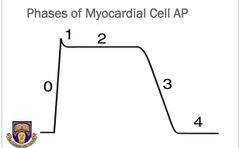
Phase 0 : Rapid depolarization Phase 1 : Early repolarization Phase 2 : Plateau phase Phase 3 : Late repolarization Phase 4 : Resting membrane potential |
|
|
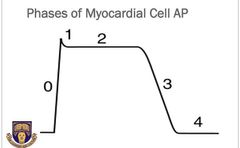
Discuss the ionic activity at each phase |
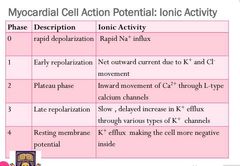
|
|
|
|
__________ is the interval during which the muscle does not respond to a stimulus. |
Refractory period |
|
|
|
_______ is the interval that the muscle does not respond to any stimulus no matter the strength. |
Absolute refractory period(ARP) |
|
|
|
________is the interval during which the muscle may respond to a stimulus of increased strength. |
Relative refractory period(RRP |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle has a long refractory period and therefore not prone to tetanic contractions. T/F |
True |
|
|
|
Excitation contraction coupling (ECC) is the process by which _______ |
An action potential triggers the contraction of cardiac muscle cells. |
|
|
|
____________ serve as the link between electrical excitation and mechanical activity (contraction). |
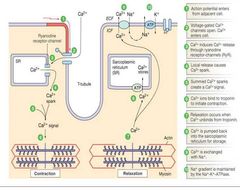
Calcium ions |
|
|
|
Cardiac electrical system or cardiac conduction system is structurally made up of the what components; |
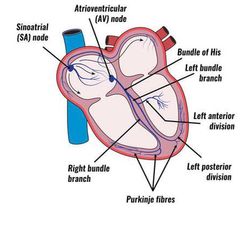
•Sinoatrial node •Internodal and interatrial pathways •Atrioventricular ( AV node) •His bundle(AV bundle) •Bundle branches •Fascicles •Purkinje fibres |
|

