![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
127 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
vasomotor (of medulla) does what to HR?
|
speeds it up
|
|
|
vagal center does what to HR?
|
slows it
|
|
|
what are the 2 places of baroreceptors for CV?
|
carotid body and aortic arch
|
|
|
the baroreceptors transmit information from the carotid body via what nerve?
|
glossophar
|
|
|
the baroreceptors transmit information from the aortic arch via what nerve?
|
vagal
|
|
|
Thyroid gland's effect on BMR?
|
raises it
|
|
|
What is the main hormone of glucose metabolism? Where does it occur?
|
insulin, myuscle/adipose tissue
|
|
|
Cortisol is released from what?
|
zona fascigulata of A.P.
|
|
|
What hormone controls ION and PROTEIN METABLOSIM?
|
cortisol
|
|
|
What hormone controls calcium/phosphate levesl?
|
pTH
|
|
|
If arterial pressure increases, the vessels stretch and it is sensed by...1... sending imulses to ...2...decreasing Q, and increasing...3...
|
1 - baroreceptors
2 - vasomotor center 3 - dilation of periph vessels |
|
|
The baroreceptor relays via glossopharyngeal nerve to what part of the brain?
|
brainstem
|
|
|
What is the downside to overlapping control mechanisms?
|
IT IS NOT ENERGY EFFICIENT
|
|
|
What syndrome is failure of Thymus to develop, resulting in no T cells? patients die early
|
digeorge
|
|
|
What type of NS response leads to MIOSIS?
|
sympathetic
|
|
|
what type of NS response leads to Mydriasis?
|
PNS
|
|
|
what muscle does MIOSIS?
|
radial
|
|
|
what muscle does mydriasis?
|
sphncter/ciliary muscle
|
|
|
What role does NE have in sweating?
|
none
|
|
|
what NT is invoved in sweating?
|
Ach
|
|
|
What is the main vasodilator of coronary blood vessels?
|
ADENOSINE
|
|
|
what stimulates ATP to release adenosine for vasodilator?
|
LOW O2 content
|
|
|
GI spnicter tone is decreased by what NS?
|
para
|
|
|
Peristalsis is increased with what NS?
|
para
|
|
|
body temperature goes up, chills.
body tempearture goes down, sweat |
SWEATING
|
|
|
what hormones does TG secrete?
|
t3 triiodo
t4 thyroxine |
|
|
What effect does testosterone have on O2 delivery?
|
It effects EPO, increasing RBC production
|
|
|
what is the hormone for increasing RBC production?
|
EPO
|
|
|
What arre APUD cells?
|
Secretory cells that secrete hormones into SURROUNDING area NOT into Lumen
|
|
|
what are secretory cells that DO NOT secrete into lumen, they secrete into the surrounding area?
|
APUD cells
|
|
|
What is polycethemia vera?
|
PRIMARY polyc., when the production of RBC;s is NO LONGER responsive to regulation
|
|
|
What is compensatory polycthemia?
|
normal response to an increased need for O2, so RBCs are produced more
|
|
|
what is a cause of 2ndary polycthemia?
|
increased altitude
|
|
|
do smooth muscles have a t-tubule?
|
NO- caveoli
|
|
|
what are caveoli?
|
rudimentary t=tubules of smooth muscle
|
|
|
What kind of muscle is in the esophagus?
|
striated top smooth bottom
|
|
|
APUD, DNES, ENTEROENDOCRINE CELLS...where do they secrtet hormones?
|
into surrounding area NOT into lumen
|
|
|
what is the purpose of the air-blood barrier of the lungs?
|
gas exchange
|
|
|
Where is auerbach's plexus located?
|
in between longitudinal and circumferential msucles
|
|
|
What controls the long loop of GI reflexes?
|
CNS
|
|
|
What type of secretion do the Parotid salivary glands have?
|
SEROUS
|
|
|
What part of the liver lobule carries lymph?
|
SPACE OF DISSE
|
|
|
What cells of the GI secrete HCL?
|
parietal cells
|
|
|
what do parietal cells secrete?
|
HCl
|
|
|
What cells of the GI secrete Intrinsic factor?
|
Parietal cells
|
|
|
What do the Parietal cells secrete?
|
HCl, Intrinsic factor
|
|
|
what do Chief cells of the Gi secrete?
|
PEPSIn
|
|
|
what cells of GI secrete pepsin?
|
Chief
|
|
|
what type of enterochromaffin like cells (ECL) secrete in GI?
|
histamine
|
|
|
when do chylomicrons enter circulation?
|
after they go through lacteals because htey are oto large to go through capillaries
|
|
|
Which nervous system increases motility AND gastric juice secretion?
|
PNS - rest and digest
|
|
|
What is the target site of Crohn's disease?
|
Terminal ileum, proximal colon
|
|
|
What is celiac's diseas?
|
hypersensitvity to gluten
|
|
|
what is the result of celiac's disease?
|
loss of intestinal mucosa , so MALABSORPTION
|
|
|
What happens to Na, Cl, Bicarb when salivary flow increase?
|
increase in conc
|
|
|
what happens to K when salivary flow increases?
|
decreases
|
|
|
What happens (overall) to the composiiton of saliva as flow rate increases?
|
it becomes more like plasma
|
|
|
what happens to each of the following as salivary flow increases?
Na Cl K Bicarb |
inc
inc dec inc |
|
|
What are the 2 sites of the GI tract where most absorption occurs?
|
Duod/Jejunum
|
|
|
Name 2 membranes that digested nutrients must cross to get into circulation?
|
brush border, basolateral membrane
|
|
|
What are the 2 steps of glucose/galactose absorption?
|
1st - Na/K ATPase pumps Na out thru BL membrane.
2 - glucose/gala are absorbed with Na thru apical side |
|
|
SGLT-1-->Na/glucose transporter, 2Na for Each Glu/Gala
|
glu ala absorption
|
|
|
What INACTIVATES pancreatic protease precursors?
|
ACIDIC pH
|
|
|
what type of pH is needed to activate pancreatic protease precurosos?
|
neutral pH
|
|
|
what does 80% of synthesized cholesterol become?
|
bile acids
|
|
|
Maltose absorption into enteryocytes, what must happen?
|
Digested
|
|
|
Why is O2 pressure lower in SYSTEMIC vs. pulmonary?
|
bronchiole circulation
|
|
|
what effect does bronchiole circulation hafve on O2 pressure of pulmonary vs. systemic?
|
it makes pulmonary lower
|
|
|
What reacts in situation of SEVERE hemmorhaging to regulate arterial BP? its a hormone
|
vasopressin by PITUITARY
|
|
|
Von willebrand diseas? type of disorder, what is it
|
impaired platelet adhesion..excessive bleeding INHERITED
|
|
|
What is an inherited disease of platete adhesion?
|
von willebrand
|
|
|
Atherosclerosis causes MI T or F
|
MI
|
|
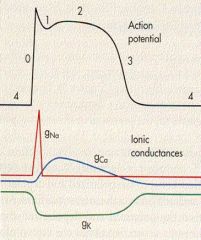
Where is absolute refractory?
|
0 to midway of 3
|
|
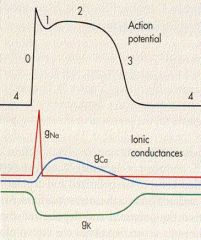
what is 1 due to?
|
efflux of K/Cl
|
|
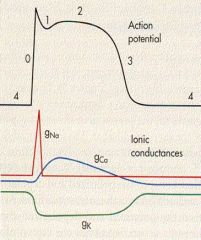
what is 0 due to
|
influx of Na via FAST VOLTAGE GATe
|
|
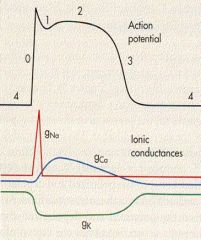
what is phase 2
|
calcium influx via SLOW Ca channels
|
|
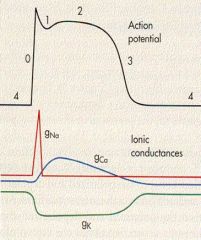
what causes the repolarization?
|
Efflux of K thru VOLTAGE GATED
|
|
|
Results of hypercalcemia: which isn't?
Kidney stone high plasma Ca Deposition of CaPO4 muscle spasm |
spasm
|
|
|
what effect does PNS have on heart?
|
slows rate
|
|
|
Hyperpolarization makes tissue MORE/LESS excitable?
|
less
|
|
|
How does Ach cause a DECREASE in HR?
|
it causes delay in conduction to Av node
|
|
|
How does Ach achieve a delay in condcution to AV node? what is the outcome?
|
increase K permeability, so K leaks out, slows HR
|
|
|
what nerve is involved in ventricular escape? what NS?
|
PNS - vagal
|
|
|
What is P wave caused by?
|
depolarized atria
|
|
|
what is QRS?
|
depolarized ventricles
|
|
|
whta is T wave?
|
repolarized ventricles
|
|
|
What is COMPLIANCE a ratio of?
|
volume/pressure (changes of)
|
|
|
Pulmonary fluid pressyre, systemic fluid pressure
|
pul - 15 mmHg
Syst - 100mm HG |
|
|
15 mm HG
100 mmHg which is pul, which is systemic fluid pressure? |
15 pul, 100 syst
|
|
|
What organ has the LOWEST cardiac output priority? 2nd lowest?
|
skin -- renal
|
|
|
Question of Venous resist/pressure -
Resistance to flow in large veins (compression via thorax, atmosph, abdominal organ) Collapse of veins/resistance = INCREASE in small vein pressure than RAP answer |
ALL OF THE ABOVE
|
|
|
What causes reduced RAP?
|
dehyrdation/hemorrhage
|
|
|
what does an increase in RAP cause in terms of veins, and flow resistance?
|
increased flow, collapse of veins
|
|
|
T or F, standing too long can cause significan decrease in CO and arterial BP
|
true
|
|
|
venous pressure of feet?
|
90 mmHG
|
|
|
90 mm Hg is venous pressure of your...
|
feet
|
|
|
what causes varicose veins/valce incompetence?
|
chronice excessive hydrostatic pressure DISTENDING veins of legs
thru pregnancy, standing or heart failure |
|
|
chronice excessive hydrostatic pressure DISTENDING veins of legs
thru pregnancy, standing or heart failure |
causes varicose veins
|
|
|
Lower capillary resistance
increased distention of capillaries recruitment of more capillarys helps what? |
BF thru lungs increase 3x w/ excercise
|
|
|
The PASSIVE lymph pump is caused by
|
excercise
skeletal muscle arterial pusaltions massage |
|
|
excercise
skeletal muscle arterial pusaltions massage cause what sort of lymph flow |
passive pump
|
|
|
Adenosine has what effect on coronary vessels?
|
vasoDILATIOn
|
|
|
what portion of the respiratory tract are ALVEOLAR SACS
|
respiratory
|
|
|
where does the conducting zone of respiration stop?
|
terminal bronchioles
|
|
|
Which portion of respiratory tract does gas exchange occur?
|
respiratory NOT conducting
|
|
|
how is surface tension reduced in lungs?
|
high surfactant
|
|
|
What is the importance of decreasing surface tension via surfactant?
|
equilbrating pressure between large and small alveoli
|
|
|
Restrictive or Obstructive:
Decreased compliance? Increased compliance work increased tissue resistance work? |
dec complioance - restrictive
tissue resistance - obstructive increased compliance work - restrictive |
|
|
Pulmonary arteries are diff from systmic how...
diameter walls thickness length amount of smooth muscle? |
larger dia
thinner wall shorter less smooth muscle |
|
|
Pulmonary volume increases with excercise through recruitment of capillaries and dialation
|
true
|
|
|
which part of the lungs is in most danger if there is a decrease in capillary pressre?
|
apex = zero flow (ZONE 1)
|
|
|
what can cause a decrease in capillary pressure? volume...
|
hypovolemia
|
|
|
Zones of lung
no flow? intermittent continuous? |
1 - no
2 - inter 3 - cont |
|
|
zone 1 flow
zone 2 flow zone 3 flow (OF LUNGS) |
1 - no
2 - inter 3 - continuous |
|
|
What is hypoxic vasconstriction? why and where doe sit occur?
|
ONLY in lungs. If obstruction, vasoconstriction so that blood isn't wasted there
|
|
|
what is unique of the interstitial space surrounding pulmonary capillaries?
|
it is MORE negative, so that fluid doesn't leak into alveoli, fluid movies into interstitial spacel
|
|
|
What is the A-a difference?
|
venous admixture...less o2 pressure because it comes from bronichiole veins going to pulmonary veins
|
|
|
Can hypoxemia occur in strenuous excercise?
|
NO
|
|
|
1.34, 15 g/dl, 20 ml O2/dL blood
which number is max o2 bound to hemo normal o2 conc normal bound o2 |
1.34 - max o2 bound
normal o2 conc - 15 normal bound o2 is 20 |
|
|
What type of hypoxia is ISCHEMIC hypoxia? it results in
|
transport, inadequate blood flow
|
|
|
What effect does Carb Anhydrase have on Co2 carrying capacity?
|
it LESSENS it
|
|
|
Diabetes Insipidus is a lack of response or lack of what hormone?
|
ADH
|
|
|
central chemoreceptors are stimulated by what?
|
H+
|
|
|
H+ stimulates what kind of receptors for acid/base
|
central cehmoreceptors
|
|
|
Macula densa cells meet up with what kidney part?
|
glomerulus
|
|
|
GFR = UV/P
125 = inulin C if value >125, what? what is an example? |
it is secreted/filtered, like creatinine
|
|
|
GFR = UV/P
125 = inulin C if value <125, what? what is an example? |
it is reabsorbed (UREA)
|

