![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sensory input
|
Where the gathered information is received
|
|
|
Integration
|
The process and interpretation of the information received from the sensory input. Decides what should be done
|
|
|
Motor Output
|
The response that the brain – spinal cord interprets to do
|
|
|
Central Nervous System - Consists of what? Function?
|
consists of the brain and spinal cord – dorsal body cavity. It acts as the integrating command centers in the nervous system.
|
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System Consits of what? Function?
|
The part of the nervous system outside the CNS – Nerves that extend from the brain and spinal cord. Communication lines
|
|
|
The Spinal Nerves - How many? Names
|
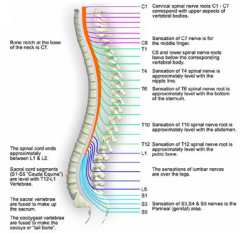
8 Cervical C1 -C8
12 Thoracic T1-T12 5 Lumbar L1-L5 5 Sacral S1-S5 1 Coccygeal |
|
|
Sensory Reception (Afferent) - Consists of what
|
Consists of nerve fibers that convey impulses to the central nervous system from sensory receptors. Sensory Fibers deliver the impulses from the skin, skeletal muslces, and joints – somatic
|
|
|
Motor Nerves (efferent)
|
Carries impulses from the CNS to effector organs the muscles and glands.
|
|
|
Motor Nerves in two subdivisions
|
Somatic (Voluntary)
Autonomic ( involuntary) |
|
|
Autonomic - 2 Parts Sympathic and Parasympathic
|
Has two parts the sympathic and parasympathic which bring opposite effects. What one stimulates the other inhibits.
|
|
|
Neuroglial cells
|
The supporting cells in the CNS that are “lumped together” – Nerve glue
|
|
|
Astrocytes
|
Form a living barrier between neurons and capillaries in the CNS. Help protect the neurons from harmful substances that might be in the blood and control the chemical environment in the brain by picking up excess ions and recapturing release neurotransmitters
|
|
|
Microglial
|
Spidelike phagocytes that dispose debris- ependymal cells
|
|
|
Oligodendrocytes
|
form myelin sheaths around nerve fibers in the CNS
|
|
|
Schwann Cells
|
form the myelin sheaths around nerve fibers that are found in the PNs
|
|
|
Satellite cells
|
Are the cushion and act as protective
|
|
|
Connection between Oligodendryte , Myelin, Satellite Cells, Schwaan
|
Oligodendryte form the myelin sheath Schwaan cells Myelin sheaths around he nerve fibers in the PNS Satellite Cells are protective
|
|
|
Nodes of Ranvier
|
the indentation and gaps that the myelin sheath is formed by many individual Schwaan
|
|
|
Saltatory Conduction - Action Potential
|
Action potentials traveling down the axon "jump" from node to node. This is called saltatory conduction which means "to leap." Saltatory conduction is a faster way to travel down an axon than traveling in an axon without myelin.
|
|
|
Reflexes
|
Are rapid involuntary responses to stimuli
|
|
|
Autonomic Reflexes
|
Regulate the activity of smooth muscles, the heart and glands
|
|
|
Somatic Reflexes include all reflexes that
|
stimulate the skeletal muscle
|
|
|
Neurons have two major functional properties
|
irritability the ability to respond to a stimulus and convert it into a nerve impulse and conductivity the ability to transmit the impulse to other neurons muscles and glands.
|
|
|
Polarized
|
the there are fewer postivie ions sutting on the inner face of the neuron’s plasma membrane
|
|
|
Repolarization
|
Outflow of positive ions from the cell restores the electrical conditions at the membrane to polarized or resting state
|
|
|
Depolarization
|
Inward rush of sodium ions changes the polarity of the neurons membrane at the site
|
|
|
Na+
|
• Major positive ions outside the cell
|
|
|
K+
|
Major positive ions inside the cell
|
|
|
Pump
|
uses ATP to pump potassium ions back into it
|
|
|
All or none response
|
either conducted over the entire axon or it doesn’t happen at all
|
|
|
Gyri
|
the elevated ridges of tissue on the entire surface of the cerebral hemispheres
|
|
|
Sulci
|
shallow groves
|
|
|
Fissures
|
: Less numerous deeper grooves
|

