![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define Simple Harmonic Motion? |
An oscillation in which the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to its displacement from its equilibrium position, and is directed towards the equilibrium. |
|
|
Draw and explain the graphs for displacement, velocity and acceleration for an object moving in SHM |
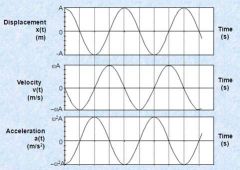
Displacement (x)= cosine graph with a maximum value A (the amplitude) Velocity (v)= gradient of displacement-time graph. Max at wA Acceleration (a)= Gradient of velocity-time graph. Max value w^2A |
|
|
Explain the phase difference between the 3 graphs |
Velocity is a quarter of a cycle ahead of x - so its pi/2 radians (90 degrees) out of phase. Acceleration is a further pi/2 radians ahead of velocity, and so it is in antiphase (pi radians) with the displacement. |
|
|
What is the amplitude of an oscillation? |
the maximum displacement |
|
|
How are frequency and period related to the ampitude |
They are independent of the amplitude - they are constant for a given oscillation. |
|
|
What is the 'mechanical energy' |
The sum of the potential and kinetic energy of the system and stays constant (if the motion isn't damped). |
|
|
What 3 variables can you change for a mass spring system in SHM? |
The Mass Spring constant, by using different combos of springs eg in parallel etc Amplitude (T doesn't depend on amplitude so there shouldn't be a change) |
|
|
What are free vibrations? |
They involve no transfer of energy to or from the surroundings. It will keep oscillating at the same amplitude forever (this doesn't happen in reality), but a spring vibrating in air is seen as a free vibration. |
|
|
What happens when the driving frequency is much less than the natural frequency? |
The driving frequency and the object will be inphase. Has very small amplitude |
|
|
What happens when the driving frequency is much greater than the natural frequency? |
The diving fr and the object will become completely out of phase - in antiphase. Has very small amplitude |
|
|
What is resonance? |
When the driving frequency is at the natural frequency, the system gains max energy and vibrates with a max amplitude. At resonance the phase difference between oscillator and river is 90 degrees or pi/2 radians. |
|
|
What is damping? |
A damping force causes an oscillator to lose energy to its surroundings, reduce the amplitude of its oscillations and rduce the sharpness of resonance. |

