![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Two conditions for a free vibration |
- No frictional forces present - Constant amplitude |
Friction |
|
|
Two examples of oscillation |
- Mass-Spring - Pendulum |
|
|
|
Formula For Phase Difference |

Objects must oscillate at the same frequency to apply this formula. ∆t = Difference in time for objects to pass the same point in the cycle |
|
|
|
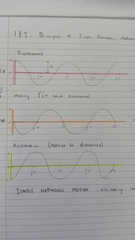
Draw Displacement, Velocity and acceleration time graph for 0<x<2T |
|
|
|
|
Define simple harmonic motion (SHM) |
Relationship between acceleration and displacement is: - Opposite - Proportional |
|
|
|
What two things decrease the frequency of oscillation for a mass-spring system? |
- Adding extra masses (increased inertia) - Weaker springs (smaller restoring/resultant force) |
|
|
|
What two things decrease the frequency of oscillation for a single pendulum? |
- Increased string length - Increased suspended mass
|
|
|
|
What's the equation for sum of Ek and Ep in an energy-displacement graph setup. |
½kA² |
|
|
|
Define "damped oscillation" and give an example of a force that causes this. |
- An oscillation where dissipative forces are present (e.g. air resistance, friction) |
|
|
|
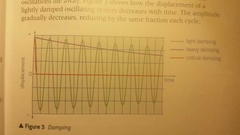
Draw a graph comparing light, heavy and critical damping. |
|
|
|
|
What is meant when a system is in resonance? |
When the periodic force in in phase with the velocity of the system and exactly ½π out of phase with the displacement. |
|
|
|
For an oscillating system experiencing a periodic force with little to no damping. At resonance _____________ |
Natural frequency = applied frequency |
|

