![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an X-ray? |
It is a high frequency, short wavelength electromagnetic waves |
|
|
What absorbs X-rays? |
Denser material such as bones and metal |
|
|
What are X-rays used for in hospitals? |
- Checking for broken bones - CT scans - Treating cancer |
|
|
What are CT scans? |
They are used to take images of soft and hard tissues, they work by having an X-ray tube emitting beams which are then detected by a detector on the opposite side |
|
|
How does X-ray treat cancer? |
It focuses on a certain point and certain dosage to kill the cancer cells without harming too many normal cells |
|
|
How do people take precautions to minimise radiation dose? |
Wearing lead aprons, standing behind lead screen and leaving the room when scans are being done |
|
|
What is ultrasound? |
It is a sound in a high frequency that we can't hear |
|
|
How thick is the layer of fat if the ultrasound was travelling 1000m/s and the time between the two reflected pulse of ultrasound is 0.00004 seconds? |
1000m/s x 0.00004 =0.04m 0.04m ÷ 2 = 0.02m |
|
|
Why is ultrasound used for scanning a fetus rather than an X-ray? |
X-rays may cause cancer as they are ionising, which mean they are unsafe |
|
|
How may ultrasound be used to break down kidney stones? |
An ultrasound beam can be used to concentrate high-energy waves at the kidney stone and turn it into sand-like particles and then pass out in urine |
|
|
What is refraction? |
It is when waves change direction as it enters a different medium |
|
|
How to find out the refractive index? |
sin (angle of incident) ÷ sin (angle of refraction) |
|
|
Show a diagram of a converting lens. |
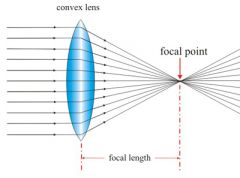
It is convex, which causes the parallel ray of light to move together at the principal focus. |
|
|
Show a diagram of a diverging lens. |
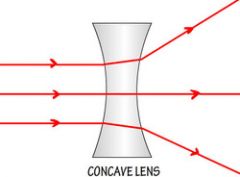
It is concave, which causes the parallel ray of light to spread out. |
|
|
What is the principal focus of a lens? |
It is where the parallel rays come together at a point
|
|
|
Draw a ray diagram for light from a distant object being focused by a convex lens. |
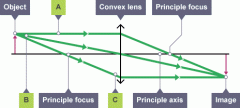
Is it a virtual/real image? |
|
|
What is the formula of finding the Magnification? |
image height ÷ object height |
|
|
How to find the power of a lens? |
1 ÷ focal length (m) |
|
|
Draw a diagram of the eye. |
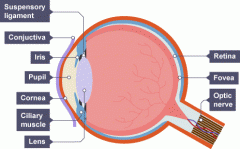
|
|
|
What type of lens is most suitable for short sighted people? |
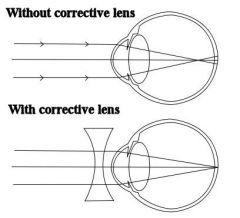
|
|
|
What type of lens is most suitable for long sighted people? |
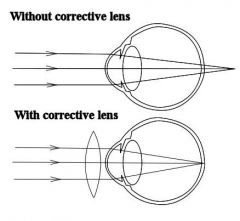
|
|
|
How are lasers used to correct eye problems? |
The lasers are used to vaporise some of the cornea to change its shape, which in-turn changes the focusing ability |
|
|
What is Total internal reflection? |
It happens when a wave travels through a dense substance like glass or water towards a less dense substance like air |
|
|
What happens if the angle of incidence is less than the critical angle? |
Most of the light passes out but a little bit of it is internally reflected |
|
|
What happen if the angle of incidence is more than the critical angle? |
No light comes out, as it is all internally reflected |
|
|
What is an endoscope? |
It is a small tube optical fibres that let surgeons examine inside the body, due to this it had enable a technique called keyhole surgery to be possible |
|
|
PAGE 92 |
PAGE 92 |

