![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are antinodes? |
The point on a stationary wave where the displacement of particles varies by the maximum amount |
|
|
What is the fundamental mode of vibration? |
In the fundamental mode of vibration the length of the string is half the wavelength. This produces the lowest possible frequency called the first harmonic |
|
|
The number of harmonic equals the number of what? |
Antinodes Second harmonic has two antinodes |
|
|
What are transverse waves |
Transverse waves oscillates perpendicular to the propagation |
|
|
What are longlitudinal waves? |
Longlitudinal waves oscillates parallel to the propogation |
|
|
What type of wave can be polarised? |
Transverse waves |
|
|
Define polarisation |
The transmition of vibration or waves in one plane (direction) |
|
|
What's a polarisation filter? |
An apparatus that allows waves to occur in one plane only. Made of crystalline material that absorb light. |
|
|
What's the difference between a progressive wave and stationary wave? |
A Stationary wave stores energy A progressive wave transfers energy |
|
|
Define displacement |
The distance any part of the wave has moved from its mean or rest position |
|
|
Define period |
The time taken for one complete pattern of oscillation to take place at any point |
|
|
How are stationary waves produced |
Stationary waves are produced by interference in accordance with principle of superposition |
|
|
What's the principle of superposition |
States that the resultant displacment of two or more waves is equal to the vector sum of the waves displacement at that point |
|
|
In order for a stationary wave to be produced what must there be? |
-two waves that overlap must be travelling in the opposite direction - Have the same frequency - Have approximately equal amplitude |
|
|
Define path difference |
Which we refer to in relation to the wavelength is the differences between the distance travelled by two waves arriving at the same point |
|
|
What equation do we use to find out frequency? |

|
|
|
What equation do we use to find out the velocity of a wave? |
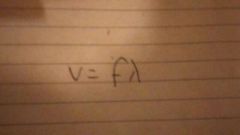
|
|
|
What are nodes? |
Nodes are the point on a stationary wave at which there is no displacement |
|
|
Define phase difference |
The relationship between the pattern of vibration at two points. Two points that have exactly the same pattern of oscillation are said to be in phase |
|
|
What is the equation for the refractive index? |

|
|
|
Define diffraction |
Its the spreading out of a wave after passing around an obstacle or gap |
|
|
Define interference |
The addition of two or more waves (superposition) that results in a new wave pattern |
|
|
Define refraction |
Refraction occurs when light enters a different optical density, this causes a change in speed, this may cause a change in direction |
|
|
What's young doubles equation? |

|
|
|
Define monochromatic light? |
Light wave with a single frequency or wavelength |
|
|
Define coherence |
Two waves with a constant phase relationship |

