![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
113 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are nucleic acids made from?
|
Several nucleotides
|
|
|
What are Ribosomal RNAs?
|
Components of ribosomes, in which are complexes that carry out the synthesis of proteins.
|
|
|
What are Transfer RNAs?
|
Translate the information in mRNA into a specific sequences of amino acids.
|
|
|
What are Messenger RNAs?
|
Carry genetic information from one or a few gene to a ribosome, where it can synthesized.
|
|
|
What are 3 characteristic components of a NUCLEOTIDES?
|
1. Nitrogenous Base
2. Sugar - Pentose 3. Phosphate Group |
|
|
If a nucleotide removes the phosphate group, what is it consider then?
|
Nucleoside
|
|
|
What are two types of NITROGENOUS BASES?
|
1. Pyimidine
2. Purine |
|
|
Identify the 2 Purines in RNA?
|
Adenine
Guanine |
|
|
Identify the 2 Purines in DNA?
|
Adenine
Guanine |
|
|
Identify the 2 Pyrimidines in RNA?
|
Cytosine
Uracil |
|
|
Define PHOSPHODIESTER LINKAGE ?
|
Phosphodiester linkage can be illustrated as having the 5’ phosphate group of one nucleotide unit join to the 3’ hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide
|
|
|
True or False and why: The backbone of both DNA and RNA are HYDROPHILIC?
|
True because the hydroxyl groups of the sugar residues form hydrogen bonds with water while the phosphate group is completely ionized.
|
|
|
True or False: Both DNA and RNA has a linear nucleic acid strands, however ONLY DNA are characterized as having a distinct 5’ to 3’?
|
False; Both DNA and RNA have a distinct 5’ to 3’ strand
|
|
|
Structurally, what allows RNA to hydrolyzed more rapidly then DNA?
|
Because RNA containa 2’ hydroxyl group where as DNA is absent of one.
|
|
|
What are the differences between OLIGONUCLEOTIDE and POLYNUCLEOTIDE?
|
OLIGO: A short nucleic acid (50 or fewer)
POLY: A longer nucleic acids |
|
|
Define PHOSPHODIESTER LINKAGE ?
|
Phosphodiester linkage can be illustrated as having the 5’ phosphate group of one nucleotide unit join to the 3’ hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide
|
|
|
True or False and why: The backbone of both DNA and RNA are HYDROPHILIC?
|
True because the hydroxyl groups of the sugar residues form hydrogen bonds with water while the phosphate group is completely ionized.
|
|
|
True or False: Both DNA and RNA has a linear nucleic acid strands, however ONLY DNA are characterized as having a distinct 5’ to 3’?
|
False; Both DNA and RNA have a distinct 5’ to 3’ strand
|
|
|
Structurally, what allows RNA to hydrolyzed more rapidly then DNA?
|
Because RNA containa 2’ hydroxyl group where as DNA is absent of one.
|
|
|
What are the differences between OLIGONUCLEOTIDE and POLYNUCLEOTIDE?
|
OLIGO: A short nucleic acid (50 or fewer)
POLY: A longer nucleic acids |
|
|
True or False: Are pyrimidines and purines weak compounds?
|
True, that’s why they are bases.
|
|
|
True or False: Both purines and pyrimidine bases are HYDROPHILIC?
|
True
|
|
|
Why is base stacking so important as a structural component of RNA or DNA?
|
Minimize contact of the bases with water
Stabilizes the 3D structure of nuclei acid |
|
|
True or False: Are pyrimidines and purines weak compounds?
|
True, that’s why they are bases.
|
|
|
What kind of bonds are found between the interaction of one purine to pyrimidines?
|
Hydrogen bonding
|
|
|
True or False: Both purines and pyrimidine bases are HYDROPHILIC?
|
True
|
|
|
Between A, G, C, T (or U) bases, which ones are based pair?
|
A T (U)
C G |
|
|
Why is base stacking so important as a structural component of RNA or DNA?
|
Minimize contact of the bases with water
Stabilizes the 3D structure of nuclei acid |
|
|
What are 2 types of NUCLEIC ACIDS?
|
RNA
DNA |
|
|
What kind of bonds are found between the interaction of one purine to pyrimidines?
|
Hydrogen bonding
|
|
|
Base on the structure of RNA and DNA, which constituients are located inside the double helix and which ones are located outside?
|
Deoxyribose and phosphate are located outside of the double helix, facing the water.
The bases are stack inside the double helix |
|
|
Bases G and C are form with how many hydrogen bonds?
|
Triple
|
|
|
Between A, G, C, T (or U) bases, which ones are based pair?
|
A T (U)
C G |
|
|
Bases A and T are form with how many hydrogen bonds?
|
Double
|
|
|
What are 2 types of NUCLEIC ACIDS?
|
RNA
DNA |
|
|
Does DNA run parallel or antiparallel?
|
Antiparallel
|
|
|
Base on the structure of RNA and DNA, which constituients are located inside the double helix and which ones are located outside?
|
Deoxyribose and phosphate are located outside of the double helix, facing the water.
The bases are stack inside the double helix |
|
|
Bases G and C are form with how many hydrogen bonds?
|
Triple
|
|
|
Bases A and T are form with how many hydrogen bonds?
|
Double
|
|
|
Does DNA run parallel or antiparallel?
|
Antiparallel
|
|
|
Between B, A, and Z form of DNA, which one is a more stable structure?
|
B form
|
|
|
Define Gene?
|
Gene is all the DNA that encodes the primary sequence of some final gene product
|
|
|
What roles does regulatory sequences play?
|
Provide signals that may denote the beginning or the end of genes
Influences the transcription of genes Function as initiation point for replication or recombination |
|
|
Each amino acid of a polypeptide chain is coded for by a sequence of ________consecutive nucleotides in a single strand of DNA?
|
Three
|
|
|
What is the term for a distinct alternative form of a characteristic?
|
Trait
|
|
|
Define ALLELE?
|
The variant (wild type) forms of a gene at a particular location on a chromosome
|
|
|
Define the terms DOMINANT and RECESSIVE?
|
Dominant is any gene form which expresses itself in the presence of its allele in the heterozygote.
Recessive is an allele whose phenotype effect is not expressed in a heterozygote |
|
|
Define GENOTYPE?
Define PHENOTYPE? |
Genotype is the genetic constitution of a cell or of an individual
Phenotype is any detectable feature of living organism |
|
|
Define AUTOSOME?
|
Autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome
|
|
|
What is the difference between AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT and AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE?
|
Autosomal dominant means you only need to get the abnormal gene from one parent in order for you to inherit the disease
Autosomal recessive means two copies of an abnormal gene must be present in order for the disease or trait to develop |
|
|
What is the difference between SEX LINKED DOMINANT and SEX LINKED RECESSIVE?
|
Sex linked dominant occurs when an abnormal gene from one parent is able to cause disease even though the matching gene from the other parent is normal.
Sex linked recessive occurs when both matching genes must be abnormal to produce disease |
|
|
Define Genetics?
|
The branch of biology that studies heredity and variation in organisms
|
|
|
If the chromosome arm is designated as p, what does that mean?
|
Short Arm
|
|
|
If the chromosome arm is designated as q, what does that mean?
|
Long Arm
|
|
|
What is the purpose of International System for Cytogenetic Nomenclature?
|
A set of conventions that is used to number chromosomes
|
|
|
By convention, which arm of the chromosome is always shown at the top in a karyotype?
|
P arm
|
|
|
If given an example like 17q21.1, what does the 17 means? q means? and 21.1 means?
|
17: refers to the chromosome
q: long arm 21.1: position on the chromosomes |
|
|
Define GENE?
|
A gene is a basic unit of the heredity passed from parent to offspring. Most gene contain the information for making a specific protein or coding for a non translated RNA
|
|
|
Give some example of AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE?
|
Phenylketonura
Cystic fibrosis Sickle cell anemia Oculocutaneous albinism |
|
|
Give an example of AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT?
|
Huntington's disease
|
|
|
What does pedigree analysis allow?
|
Enables the determination of mode of inheritance.
|
|
|
If a disease is consider MONOGENIC, can other gene affect the severity of the disease to varying extents? Yes or No
|
Yes, the gene that affect the severity of the disease to varying extent is called modifier genes
|
|
|
True or False: Genes act in isolation?
|
False: genes do not act in isolation
|
|
|
Even though cystic fibrosis is considered to be monogenic, other genes can affect the severity of the disease to varying extents, what is the term?
|
Modifier genes
|
|
|
What is the difference PENETRANCE and VARIABLE EXPRESSIVITY?
|
Penetrance is the probability that a person carry a disease associated genotype will develop the disease within a given time period.
Variable expressivity: two individuals may have the same mutation but two different results |
|
|
Which organism does not have histones, but does have NUCLEOID that will compack its DNA?
|
E.coli
|
|
|
Define PROKARYOTES?
|
Prokaryotes are organism of the Kingdom Monera comprises the bacteria and cyanobacteria.
|
|
|
What is one characteristic of prokaryotes that differentiate it from eukaryotes?
|
Characterized by the absence of a distinct, membrane bound nucleus or membrane bound organelles and the circular DNA is not organized into chromosomes.
|
|
|
Size of atoms?
|
10^-10 meters
|
|
|
Size of small molecules?
|
10^-10 meters - 10^-9 meters
|
|
|
Size of proteins?
|
10^-9 meters to 10^-8 meters
|
|
|
Size of Viruses?
|
10^-8 meters to 10^-6 meters
|
|
|
Size of Prokaryotes?
|
10^-7 meters to 10^-4 meters
|
|
|
Size of Eukaryotes?
|
10^-5 meters to 10^-3 meters
|
|
|
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genes in relation to introns and operons?
|
Prokaryotic genes lack introns
Eukaryotic gene HAVE introns Some prokaryotics genes are clustered tightly together into an operon, where as most eukaryotic gene are not |
|
|
Define INTRONS?
|
A segment of a gene situated between exons that does not function in coding for protein synthesis.
|
|
|
What does ALTERNATIVE SPLICING ALLOWS?
|
Different protein to form one gene
|
|
|
True or False: Individual who are aging, smoke cigarettes, or have bladder cancer tend to have SHORTEN TELOMERES?
|
True, a study conducted by McGrath et al at the school of harvard public health
|
|
|
True or False: Mitochrondria are only found in muscle cells?
|
False, mitochrondria are found in all nucleated cells.
|
|
|
The generator of cellular ATP is?
|
Mitochonria
|
|
|
Mitochondria are the only location of ____ ___________ _____ within the cell?
|
Extra chromosomal DNA
|
|
|
What were the goals of the Human Genome Project?
|
Identify all the gene in human DNA and its sequences
|
|
|
What is the difference between PHARMACOGENETICS and PHARMACOGENOMICS?
|
Pharmacogenetics evaluates how an individual's genetic makeup corresponds to their response to a particular medication.
Pharmacogenomics combines pharmacogenetics with genomic studies. Use large group of patients to evaluate how candidate drug interacts with a range of genes and their protein products |
|
|
What does PHARMACOGENOMICS have the capability to do?
|
Potential to optimize drug therapy by minimizing toxicity and maximize drug effficacy
Personalized medicine using novel technologies Optimize drug development |
|
|
What is the difference between PHARMACOKINETICS and PHARMACODYNAMICS?
|
Pharmacokinetics is the process by which a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and eliminated by the body.
Pharmacodynamics: is the study of the action or effects of drugs on living organisms |
|
|
What is a POLYMORPHISM?
|
A polymorphism is defined as a variation in DNA sequence.
|
|
|
If the DNA variation is less than 1% of the population, this is know has what?
|
Mutation
|
|
|
If the DNA variation is more than 1% of the population, this is know has what?
|
Genetic polymorphism
|
|
|
How many types of POLYMORPHISM are there? Describe?
|
1. Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP/snip): a single base substitution within the genome
2. Includes more than one nucleotide change or an entire gene insertion or deletions, or extra copies of a gene |
|
|
If given the SNP nomenclature of VKORC1 1173 C > T, what does each letters or numbers indicate?
|
VKORC1 : gene
1173: nucleotide location on gene C : cytosine, the original nucleotide T : the nucleotide that has change to thymine |
|
|
If given the ALLELE "STARE" NOMENCLATURE of CYP2C19 *1(CYP2C19 681 G>A), what does each letter or number indicate?
|
CYP2C19: gene
*1: designate allele type ( ): describes the same allele type |
|
|
What purpose does the ALLELE "STAR" NOMENCLATURE served?
|
Determine the allele type, one can determine its function
|
|
|
True or False: The key point to the allele "star" nomenclature can look exactly the same but have different functional effect based on the specific protein?
|
True
|
|
|
Another way to name is called the "rs" naming system, what is it?
|
SNP database for all genetic variation information
|
|
|
Another way to describe SNP is by _____ _____.
|
Genotype Nomenclature
|
|
|
For an individual with CYP2CIP*1/*1, what kind of enzyme activity would be expected for Genotype nomenclature?
|
Normal
|
|
|
For an individual with CYP2CIP*1/*3, what kind of enzyme activity would be expected for Genotype nomenclature
|
Reduced enzymes
|
|
|
For an individual with CYP2CIP*2/*2, what kind of enzyme activity would be expected for Genotype nomenclature
|
No enzymes
|
|
|
What is HAPLOTYPE?
|
Haplotype is a set of alleles at multiple loci or areas of a gene that co-exist on the same chromosomes
|
|
|
What are 3 types of polymorphisms?
|
Synonymous SNP
Non synonymous SNP Premature stop codon SNP |
|
|
Describe Synonymous coding SNP?
|
A nucleotide change can occur (c-->t) but the resulting amino acids remain the unchanged (lle)
|
|
|
Describe NON SYNONYMOUS SNP?
|
A nucleotide change occur resulting in an amino acid change.
|
|
|
Describe PREMATURE STOP CODON?
|
A nucleotide change occur, in which the reference amino acid is no longer coded and the results in termination of protein synthesis
|
|
|
Draw the structure of PURINE?
|
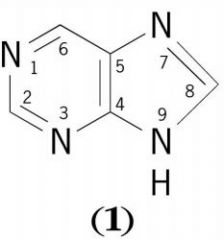
|
|
|
Draw the structure of PYRIMIDINE?
|
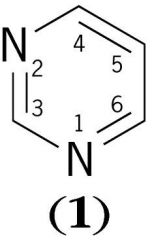
|
|
|
Draw the structure of a NUCLEOTIDE?
|
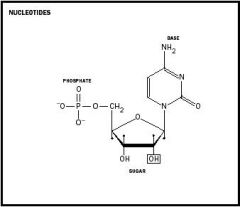
|
|
|
Draw a phosphodiester linkage?
|
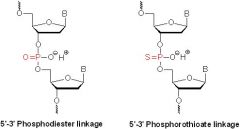
|
|
|
Draw the structure of DNA and RNA that allows RNA to hydrolyzed rapidly under alkaline conditions?
|
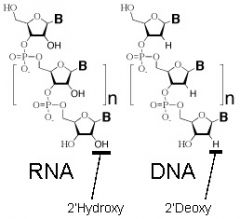
RNA is able to hydrolyzed rapidly under alkaline conditions is because the 2' hydroxyl group is directly involved in the process, whereas DNA lacks a 2' hydroxyl group
|
|
|
What purpose does REGULATORY SEQUENCES served?
|
Provide signals that may denote the beginning or the end of genes
Influences the transcription of genes Function as initiation points for replication or recombination |
|
|
What kind of structural DNA does E.coli have?
|
Circular DNA
|
|
|
Estimate how may base pairs does E.coli have?
|
4,700,000 BASE PAIRS for about 4,300 GENES
|
|
|
What are PLASMIDS?
|
Extrachromosmal elements (small circular DNA molecules that are free in the cytosol)
|
|
|
What is the sole function of PLASMIDS?
|
Self propagation
|

