![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are two main TYPES of cholinergic receptors?
|
NICOTINIC
MUSCARINIC |
|
|
Muscarinic receptor subtype primarily associated with the heart:
|
M2
|
|
|
Acetylcholine is rapidly inactivated by synaptic
_____. |
Acetylcholine is rapidly inactivated by synaptic
acetyl-cholinesterase (AChE). |
|
|
Cholinergic drugs mimic or
block the action of _____. |
Cholinergic drugs mimic or
block the action of Acetylcholine. |
|
|
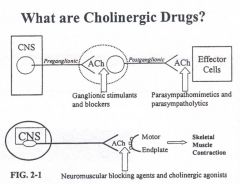
Effector organs of acetylcholine ?
|
Effector organs:
Smooth muscle Skeletal muscle CNS |
|
|
Which type of cholinergic receptor is:
Postsynaptic to preganglionic neurons in all autonomic ganglia including: Chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla i.e. the perikarya of post ganglionic neurons. |
Nicotinic receptor (Nn)
|
|
|
Cholinergic receptor type primarily localized at skeletal muscle neuromuscular junctions:
|
nicotinic (more specifically Nm)
|
|
|
Subtypes of nicotinic receptors?
|
1. N^M Nicotinic muscular receptors – in neuromuscular junction. activation opens cation ch. resulting in end plate depol. and sk. muscle contractions
2. N^N postsynaptic neurons: autonomic ganglia, adrenal medulla (chromaffin cells), >coupled to activ. of cation ch. 3. CNS 4. presynaptic nerve terminals |
|
|
Name 3 Subtypes of muscarinic receptors?
Where is body are each of these found? |
M1 - autonomic ganglia, CNS
M2 - Heart (SA node, AV node, atrial) M3 - smooth muscle, secretory glands |
|
|
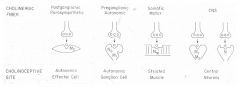
Location of different Muscarinic Receptors?
|
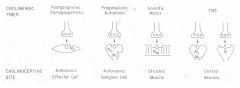
1. On post-synaptic membrane of neuro-effector junction innervated by postganglionic parasympathetic neurons
2. On post-synaptic membrane of neuro-effector junction innervated by some postganglionic sympathetic neurons 3. On vascular endothelium - these receptors are pharmacologically important since they are not innervated, their physiological importance is unclear. 4. In autonomic ganglion 5. On pre-synaptic nerve terminal 6. In CNS |
|
|
What receptor is responsible for signal transd. pathway associated with:
stimulation of enzyme phospholypase C and increased cytosolic Ca2+ |
Activation of M1 and M3 receptors -->
stimulation of enzyme phospholipase C and increased cytosolic Ca2+ note: increased uptake of Ca+2 --> depolarization? |
|
|
What receptor is responsible for signal transd. pathway associated with:
associated with activation of K+ channel and inhibition of enzyme adenylyl cyclase. |
M2 receptor
|
|
|
Name 4 directly-acting Cholinergic Agonists (drugs not naturally occurring)
|
Methacholine, Carbachol, and bethanechol, Synthetic Choline esters
|
|
|
Methacholine agents show selectivity to what organs?
|
cardiovascular system
|
|
|
Carbachol and Bethanechol agents show selectivity to what organs?
|
smooth muscles of the GI tract and urinary bladder
is this associated with M3? |
|
|
* Mild nicotinic, strong MUSCARINIC agonist.
* Has longer duration of action than ACh, since it is hydrolyzed at a slower rate by AChE, moreover it is almost totally resistant to hydrolysis by other cholinesterases. |
Methacholine
|
|
|
* Very potent nicotinic and muscarinic agonist.
* Totally resistant to hydrolysis by AChE and other cholinesterases, therefore long duration of action. * can stimulate autonomic ganglion and some of its effects can be due to ACh release from terminals of cholinergic fibers. |
Carbachol (carbamylcholine)
|
|
|
* Pure muscarinic agonist
* Used at times in treatment of GI tract atony, and detrusor atony in dog and cats. |
Bethanechol (Carbamyl-β-methylcholine)
|
|
|
Localization of muscarinic cholinergic receptors:?
A. postganglionic parasympathetic effector sites B. autonomic ganglia cells C. adrenal medulla D. A & C E. A, B & C |
E. muscarinic cholinergic receptors at all these
|
|
|
Highest nicotinic receptor activity among choline esters:
A. acetylcholine B. atropine C. methacholine D. carbachol |
D. carbachol
Carbachol = very potent nicotinic and muscarinic agonist. |
|
|
Choline ester most susceptible to hydrolysis by acetylcholinesterase:
|
acetylcholine
|
|
|
Atony
|
- loss of muscle tone
|
|
|
Which directly-acting Cholinergic Agonists are similar in their selectivity?
|
Bethanechol & carbachol
* both somewhat selective for smooth muscles of GI tract and urinary bladder |
|
|
Resistant to hydrolysis by acetylcholinesterase?
|
carbachol
Bethanechol |
|
|
What do these compounds have in common?
Muscarine Arecoline Pilocarpine |
All naturally occurring, direct-acting cholinergic AGONISTS
MAP "Directs u to nature's cholon" -ine |
|
|
Name naturally occurring alkaloid which is a directly-acting cholinergic agonists
* producing all parasympathomimetic effects * used topically to reduce intraocular pressure in canine glaucoma therapy. |
pilocarpine!!!
- topically to reduce intraocular pressure in canine glaucoma therapy. - primarily a muscarinic agonist derived from Pilocarpus plant |
|
|
Diisopropyl-phospho-fluorodate is the prototype for ?
|
Indirect, Irreversible, Cholinergic Agonists
|
|
|
Indirect Cholinergic agonists are divided into what 2 groups?
What is their main mode of action? |
All are cholinesterase inhibitors:
* Anticholinesterases Divided into two groups * Reversible inhibitors * Irreversible inhibitors |
|
|
Indirect, Irreversible, Cholinergic Agonists are used for:
|
* Insecticides
* Dichlorvos (highly volatile organophosphate, widely used as a insecticide) - flea collars, antihelmintic * Nerve Gas |
|
|
Main side effects are: intense contraction of GI tract accompanied by salivation, nausea and vomiting therefore it should be used with caution. .
|
Bethanechol <-- GI side effects
|
|
|
parasympathomimetics example?
|
Muscarinic agonists
a drug or poison that acts by stimulating or mimicking the P.S. nervous system |
|
|
parasympatholytics example?
|
Muscarinic antagonists
Atropine and scopolamine |
|
|
Describe 3 groups of Cholinergic Antagonists (what do they inhibit?)
|
Drugs that interfere with actions of ACh by blocking cholinergic receptors.
Grouped in categories: 1. Anti-muscarinics: for receptors present on PS neuroeffectors and vascular endoth. 2. Ganglionic blockers: for receptor on post-ganglionic neurons 3. Neuro-muscular blockers: for receptors present on motor end plate of skeletal muscles |
|
|
Associated with parasympathetic activation (direct effects):
A. increase heart rate B. decreased GI motility C. decrease cardiac contractility D. urinary retention |
C. decrease cardiac contractility
parasympathetic effects decrease both heart rate and contractility, mainly atrial contractility |
|
|
Name 2 synthetic anti-muscarinic drugs (atropine-like agents)
|
Pirenzepine
Telenzepine |
|
|
Name this Synthetic anti-muscarinic drug:
Exibits selective for M1 receptors on post-ganglionic neurons of autonomic ganglia. It reduces gastric acid secretion. (Ulcer treatment in other country other than the US). |
Pirenzepine (anti-muscarinic)
It reduces gastric acid secretion. (Ulcer treatment in other country other than the US). |
|
|
An analogue of pirenzepine (a more selective inhibitor of gastric secretion)
|
Telenzepine
|
|
|
What effect does Pirenzepine have gastric acid secretion?
How does it pull this off? |
* reduces gastric acid secretion by blocking M1 receptors in intramural ganglia of stomach and on gastric entero-chromaffin-like cells
|
|
|
Mydriasis?
|
dilation of the pupil
|
|
|
Found in bethel nut has some nicotinic activity but is primarily muscarinic and has some CNS effects (stimulation and euphoria).
|
Arecoline (naturally occurring, direct-acting cholinergic AGONISTS)
|
|
|
Indirect Cholinergic agonists are reversible inhibitors of _____?
|
Indirect Cholinergic agonists are reversible inhibitors of cholinesterases
|
|
|
Name 4 Indirect Cholinergic agonists (REVERSIBLE inhibitors of ChE)
note: ChE = cholinesterase which break down ACh |
Reversible inhibitors of ChE: physostigmine
pyridostigmine endrophonium neostigmine fyi: 3 end w/-stigmine |
|
|
What clinical application do these reversible cholinesterase inhibitors share?
What distinguishes them? |
Used in the treatment of myasthenia gravis.
similar pharmacologic action but duration of action different |
|
|
Which indirect cholinergic agonists used for glaucoma, for antimuscarinic poisoning
- atropine toxicity, and is drug of choice for myasthenia gravis b/c has longer duration of action? (but discontinued in some circles b/c can cause additional poisoning) |
Physostigmine: longest duration
|
|
|
Name only reversible inhibitors of ChE that does NOT end w/-stigmine??
|
endrophonium
|
|
|
Used to reverse neuromuscular
blockade induced by certain neuromuscular blocking agents. |
Neostigmine
|
|
|
Rank 4 indirect ACh agonists based on duration of action (longest to shortest)
|
1. Physostigmine: longest duration
2. Pyridostigmine 3. Neostigmine 4. Endrophonium : shortest duration |
|
|
T/F Both Neostigmine & Physostigmine effective given orally, but Neostigmine easily penetrates BBB (causes CNS effects).
|
False;
Both Neostigmine & Physostigmine effective given orally, but Physostigmine PHYSOSTIGMINE easily penetrates BBB (causes CNS effects). |
|
|
These are example of ?
atracurium vecuronium mivacurium pancuronium |
Noncompetitive NM blockers are used in vet med:
- skeletal muscle relaxant - used adjunct. in anesthesia to facil. endotracheal intubation and sk. muscle relaxation during surgery, etc - inhibit neuron transmission to muscle by blocking NAR? (nicotinic AcH receptor) |
|
|
What receptor(s) have these effects?
* Phospholipae C stimulation >> increased cytostolic Ca++ * Smooth muscle contraction (M3) * Secretion of exocrine gland (Cellular responses) |
Effects Mediated by M1 and M3 receptor
* Phospholipae C stimulation >> increased cytostolic Ca++ |
|
|
Effects Mediated by M2 receptor?
|
M2: Decrease adenylyl cyclase
* Increased K+ channel * Causes decreased conduction rate >> decreased heart rate |
|
|
selective anti-muscarinic (muscarinic antagonist).
* slow onset of action, does not cross BBB * less arrhythmogenic * don't use in horses |
glycopyrrolate
|
|
|
Bronchoconstriction in an asthmatic is treated with?
A. Atropine B. ACh agonist |
Atropine
Anticholinergic agents (antimuscarinic) are used in treating asthma, because block bronchioconstriction of PS. (decr. in PS activity may may decrease brochiolar smooth muscle tone) |
|
|
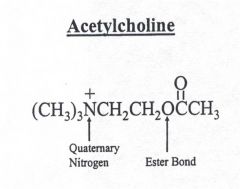
What compound is a prototype of all directly acting cholinergic agonists?
|
Acetylcholine
|
|
|
What compound rapidly inactivates acetylcholine after it is released?
|
synaptic Acetyl-cholinesterase
|
|
|
What compounds inactivate non-synaptic acetylcholine?
|
Liver and plasma cholinesterase
|
|
|
What enzyme catalyzes the synthesis of acetylcholine from choline and acetate?
|
Choline acetyl transferase
|
|
|
What are some subtypes of nicotinic receptors?
|
Nm - Neuromuscular junction
Nn - Autonomic ganglia, adrenal medulla, CNS |

