![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the symptoms of Depression?
|
-depressed mood
-loss of interest -loss of enjoyment -Guilt -Altered sleep -altered eating -suicidal thoughts |
|
|
What is the etiology of Depression?
What is the Pathophysiology? |
Unknown but may arise spontaneously or be triggered by life events
May involve deficits in Noradrenergic or Serotonergic neurotransmission |
|
|
Define "Bipolar Disorder"
|
periods of depression alternating with periods of mania or hypomania
|
|
|
Bipolar Disorder treatment:
-Acute depression? -Acute Mania? |
Depression = Antidepressants
Mania = Antipsychotics |
|
|
What effect should Anti-depressants have in normal people?
|
should NOT elevated mood
|
|
|
What are the 4 major classes of Antidepressants?
|
1. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
2. Tricyclics (TCA's) 3. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI's) 4. Miscellaneous |
|
|
What is the hypothesized mechanism of Antidepressants?
|
increased synaptic availability of NE &/or Serotonin
|
|
|
What 3 things may the ultimate effect of Antidepressants be due to?
|
1. secondary changes in receptors - e.g. downregulation of Alpha-2 & Beta receptors
2. increase in brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the Hippocampus 3. Cognitive changes |
|
|
What are the 2 MOAI's?
|
Phenel-zine
Tranyl-cyp-romine |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Phenelzine & Tranylcypromine?
|
-increase synaptic availability of Norepinephrine & Serotonin by blocking their catabolism
-irreversible inhibit MAO-A (NE & 5-HT) and MAO-B (DA = Dopamine) |
|
|
What are the side effects of MAOI's?
|
1. Dry mouth
2. Constipation 3. Headache 4. Drowsiness 5. Postural Hypotension 6. Weight gain 7. Sexual dysfunction 8. Sleep disturbances |
|
|
Overdose with MAOI's is unsusual, but what can it cause?
|
1. Seizures
2. Shock 3. Delerium 4. Hyperthermia |
|
|
What can MAOI's potentiate the action of?
|
Other Sedatives such as alcohol
|
|
|
What could happen if MAOI's & Tyramine are taken at the same time?
|
Hypertensive Crisis
**Tyramine is a compound found in many foods, displaces NE from neuronal storage vesicles |
|
|
What drugs in combination with MAOI's may produce "Serotonin Syndrome"? What are the symptoms?
|
Meperidine & SSRI's
Tremor Muscle rigidity Hyperthermia HTN Tachycardia Myoclonus |
|
|
How long does it take for the effects of MAOI's to wear off?
|
2 weeks due to irreversible inactivation of MAO
**So don't give SSRI's or Meperidine until after discontinuing MAOI's for 2 wks |
|
|
List the Tricyclic Antidepressants
|
Imipramine
Amytriptyline Desipramine Nortriptyline Clomipramine **-PRAMINE or TRIPTYLINE |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of the TCA's?
|
inhibit the reuptake of NE &/or Serotonin
*relative proportion of Serotonin/NE activity varies for each drug |
|
|
TCA's are also potent antagonists at various receptors including...
|
Cholinergic
Histaminergic = sedation Alpha-adrenergic = hypotension |
|
|
What are the side effects of the TCA's?
|
1. Sleepiness
2. Sympathomimetic effects = tremor or insomnia 3. Anticholinergic effects 4. Arrhythmias 5. Seizures 6. Weight gain 7. Sexual dysfunction |
|
|
What are the life-threatening side effects of TCA overdose?
|
1. Coma
2. Respiratory depression 3. Delirium 4. Seizures 5. Hyperpyrexia 6. Bowel & Bladder dysfunction 7. Cardiac effects = arrhythmias |
|
|
What class of drugs do TCA's have adverse interactions with?
|
MAOI's
|
|
|
List the Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI's)
|
1. Fluoxetine
2. Sertraline 3. Paroxetine 4. Fluvoxamine 5. Citalopram 6. Escitalopram |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of the SSRI's?
|
Inhibit Serotonin reuptake
*can inhibit reuptake of NE at higher doses |
|
|
List the side effects of the SSRI's
|
1. Acute anxiety
2. Insomnia 3. Sleepiness 4. Fatigue 5. Tremor 6. GI symptoms 7. Rashes 8. Weight loss or gain 9. decreased libido 10. Sexual dysfunction |
|
|
What class of drugs do SSRI's have adverse interactions with?
|
MAOI's
Serotonin Syndrome -Hyperthermia -Muscle rigidity -CV collapse |
|
|
T or F: SSRI's have a high risk of fatal overdose
|
False
|
|
|
Explain the SSRI Discontinuation Syndrome
|
Flu-like &/or GI symptoms occurring within a week after stopping the drug
Most associated with drugs with short half-lives |
|
|
Misc. Antidepressant that inhibits the reuptake of Serotonin & NE (5-HT > NE)
|
Duloxetine
|
|
|
Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) with similar side effects as TCA's
|
Maprotiline
|
|
|
Misc. antidepressant that increases 5-HT & NE release by blocking Alpha-2 receptors on nerve terminals
|
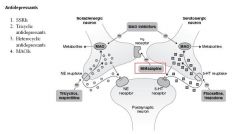
Mirtazepine
|
|
|
Misc. antidepressant that has anti-dopaminergic activity & is used in Psychotic depression; causes EPS & Tardive Dyskinesia
|
Amoxapine
"A Morning Pine Ox" inhibits Dopamine & does not have Psychotic Depression anymore; gets EPS & Tardive Dyskinesia |
|
|
Misc. antidepressant that inhibits Serotonin reuptake; is very sedating & is used as a hypnotic & pre-anesthetic; can cause priapism
|
Trazodone
"alca-TRAZodone inhibits Serotonin reuptake, makes you sleepy, and gives you Priapism |
|
|
Misc. antidepressant that blocks Dopamine reuptake
Side effects: dizziness, sweating, aggravation of psychosis, seizures |
Bupropion
|
|
|
Misc. antidepressant that has a similar mechanism to TCA's (inhibits Serotonin, NE, & Dopamine reuptake) but with improved Side Effect profile
Can cause SSRI discontinuation syndrome |
Venlafaxine
|
|
|
Most antidepressants have long half-lives, which 3 do not?
|
Trazodone
Venlafaxine Bupropion **unless in time-release formulations **TVB have short half-lives |
|
|
What is the route of administration for the Antidepressants?
|
Oral
|
|
|
Which 2 antidepressants are CYP2D6 inhibitors?
|
Fluoxetine & Paroxetine
F is 6th letter in alphabet, Paroxetine has same ending |
|
|
Antidepressants used for Panic Disorders?
|
TCA's
MAOI's SSRI's |
|
|
Antidepressants used for Obsessive-Compulsive disorder
|
SSRI's
|
|
|
Antidepressants used for Enuresis (bedwetting)
|
TCA's = esp. Imipramine
|
|
|
Antidepressants used for Chronic pain, esp. neuropathic
|
TCA's
|
|
|
Antidepressants used for Eating disorders
|
SSRI's
|
|
|
Antidepressant used for Smoking Cessation
|
Bupropion
|
|
|
Antidepressant used as a Sedative
|
Trazodone
|
|
|
Antidepressant used for ADHD
|
Bupropion
|
|
|
List the 4 Mood Stabilizing agents
|
1. Lithium
2. Carbamazepine 3. Valproic Acid 4. Lamotrigine |
|
|
What is Lithium's mechanism of action?
|
may affect Ion transport, the serotonin system, or the PI cascade
|
|
|
Describe the pharmacokinetics of Lithium
|
1. Absorbed rapidly but accumulates slowly in the brain
2. Therapeutic levels reached in 6-10 days 3. >95% excreted in the urine |
|
|
List the side effects of Lithium (8)
|
1. Tremor = most common
2. Thyroid enlargement -> hypothyroidism 3. Polydipsia & Polyuria = ADH antagonist 4. EEG alterations 5. Leukocytosis 6. Edema 7. Acne 8. Teratogenesis "Nathan Bell was bipolar so he took Lithium. As a result he got Tremors, Thyroid Enlargement, & Pee'd alot. He also had alot of Acne, Leukocytosis, Edema, & EEG abnormalities" |
|
|
If a patient gets tremors while taking Lithium, what do you give to treat?
|
Propranolol
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Lithium overdose?
|
1. Tremor
2. NVD 3. Sedation |
|
|
What are the symptoms of overdose of Lithium in severe cases?
|
1. Ataxia
2. Confusion 3. Coma 4. Arrhythmias 5. Hypotension 6. Albuminemia 7. Death |
|
|
When is Lithium contraindicated?
|
1. Renal or Cardiovascular disease
2. Pregnancy = Teratogenic |

