![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When does Ovarian function begin?
|
When the ovaries respond to Pituitary Gonadotropins (FSH & LH) at puberty (menarche or gonadarche)
|
|
|
Why does Menopause occur?
|
Ovaries fail to respond to FSH & LH
|
|
|
Explain the regulation of Menstruation
|
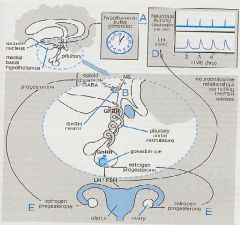
1. Menstrual cycles are automatically reactivated every 28-30 days by a neuronal 'clock' (hypothalamic arcuate nucleus) serving as a pulse generator that fires at regular intervals
2. releases GnRH periodically into the Hypothalamic-pituitary portal vasculature 3. GnRH acts on Anterior Pituitary to release LH & FSH 4. LH & FSH stimulate ovaries to secrete Estrogen and Progesterone |
|
|
Explain the Negative Feedback regulation of Menstruation
|
1. Estrogen acts on the Pituitary to decrease FSH & LH
2. Progesterone acts on Hypothalamus to decrease GnRH |
|
|
Menstrual cycles:
-As each cycle starts, __1__ become larger ➡ after 5-6 days a dominant follicle develops more rapidly ➡ __2__ cells multiply to release __3__ ➡ Estrogen secretion peaks just before __4__ ➡ brief surge in __5__ release ➡ __6__ -After Ovulation, the follicular cavity fills with __7__ ➡ __8__ cells proliferate to form __9__ which then produces Estrogen and Progesterone for the rest of the cycle |
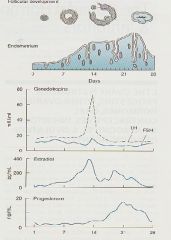
1. Vesicular follicles
2. theca & granulosa 3. Estrogen 4. Midcycle 5. LH & FSH 6. Ovulation 7. blood 8. Luteinized theca & Granulosa 9. Corpus luteum |
|
|
What would constant infusions of GnRH do to the Menstrual cycle?
|
stop LH and FHS release ➡ decrease Estrogen & Progesterone ➡ Amenorrhea
|
|
|
What are the 3 major estrogens normally secreted?
|
1. Estrone (E1)
2. Estradiol (Estradiol-17b; E2) 3. Estriol (E3) |
|
|
What is the major Estrogen?
When does it peak the highest? |
Estradiol
during Ovulation = produced by Ovary |
|
|
2 Estrogens that are produced in the Liver
|
1. Estrone
2. Estriol **some Estrone is produced in the ovaries |
|
|
What is Estradiol bound to in circulation? What happens to it in the Liver?
|
Sex Hormone-binding Globin & Albumin
converted to Hydroxylated derivatives and conjugated metabolites which are excreted in bile |
|
|
What are the most prolific natural sources of Estrogens?
|
Stallions = male horse
|
|
|
What type of receptors are Estrogen Receptors?
Where are they mainly found? |
Nuclear receptors
Uterus, Vagina, Ovary |
|
|
Explain the mechanism of action of Estrogen when binding to its receptor
|
1. Estrogen binds to 2 receptors ER-alpha & ER-beta on Heat Shock Proteins in the nucleus
2. Releases hormone-receptor complex to form homodimers that bind to Estrogen Response Elements (EREs) 3. ERE's regulate gene tsc 4. mRNA edited to form protein -> estrogen effects |
|
|
List the effects of Estrogen on Female Maturation
|
1. stimulate development of vagina, uterus, & fallopian tubes as well as Secondary Sex characteristics
2. Stimulate Stromal and Ductal growth causing Breast enlargement 3. responsible for accelerated growth & closing epiphyses of Long bones at puberty 4. growth of axillary & pubic hair 5. alter body fat distribution to produce female body contour 6. develop skin pigmentation of nipples, areolae, and genitals |
|
|
List Estrogen's effects on the Endometrium
|
1. stimulate growth of Uterine muscle and development of Endometrial lining
2. Regular periodic bleeding and shedding of the Endometrial lining during menstrual cycles |
|
|
What happens to the Endometrium is there is continuous Estrogen exposure for prolonged periods?
|
Endometrial hyperplasia ➡ abnormal bleeding patterns
|
|
|
Estrogen is partly responsible for the normal structure of these 2 things in women
|
Skin
Blood vessels |
|
|
How does Estrogen decrease bone resorption
|
promote Osteoclast apoptosis and antagonize bone effects of PTH
|
|
|
What does Estrogen stimulate adipose tissue to produce?
|
Leptin
|
|
|
Explain Estrogens effects on plasma lipoprotein profiles
|
1. slightly reduce serum cholesterol
2. increases HDL 3. decreases LDL & Lp(a) 4. elevates serum Triglycerides (bad effect) |
|
|
What effect does Estrogen have on Blood coagulation?
|
enhanced by increasing coagulation factors (2, 7, 9, 10) and by decreasing Antithrombin III and platelet adhesiveness
= increased risk of Thromboembolism |
|
|
List the 3 Steroidal, Synthetic Estrogens that are most commonly used as Oral Contraceptives
|
1. Ethinyl Estradiol
2. Mestranol 3. Quinestrol |
|
|
List 3 Synthetic Nonsteroidal compounds with Estrogen activity
|
1. Diethyl-still-bestrol
2. Chloro-trian-isene 3. Methallen-estril |
|
|
Why is there a high ratio of hepatic to peripheral effects when Estrogens are given orally?
How can this be minimized? |
b/c significant amounts are excreted in Bile and reabsorbed in the Intestine
Minimized by vaginal, transdermal, or parenteral administration |
|
|
What are the 2 main clinical uses of Estrogens?
|
1. Primary Hypogonadism
2. Postmenopausal Hormonal therapy |
|
|
Why would Estrogen be used to treat Primary Hypogonadism?
What does the treatment attempt to mimic? |
for replacement therapy in Estrogen-deficiencies due to underdeveloped Ovaries, premature menopause, castration, or menopause
Physiology of puberty |
|
|
When does Estrogen treatment usually start in Primary Hypogonadism? What are the 3 benefits of the therapy?
|
11-13 years of age
1. stimulate development of Secondary Sex characteristics and Menses 2. prevent Osteoporosis 3. avoid psychologic effects of delayed puberty and Estrogen deficiency |
|
|
What are the main therapeutic indications for Postmenopausal Hormonal Therapy?
|
Hot flashes
Osteoporosis |
|
|
Why should only the lowest possible doses of Estrogens be used in Postmenopausal Hormonal Therapy?
|
due to increased risks for Breast & Endometrial cancer
|
|
|
What are 2 uses of combined Estrogen & Progestins
|
1. suppress ovulation in intractable Dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation)
2. suppress ovarian fxn for treatment of Hirsutism and Amenorrhea caused by excessive Ovarian secretion of Androgens |
|
|
What are the 2 major adverse Estrogen effects?
|
1. Postmenopausal Uterine bleeding
2. increased risks for Breast & Endometrial cancer **others = Nausea, breast tenderness, hyperpigmentation, migraine, cholestasis, gall bladder disease, HTN |
|
|
How would you avoid confusing Postmenopausal Uterine Bleeding and Vaginal bleeding caused by Endometrial Cancer when using Estrogen therapy?
|
use the smallest amounts of Estrogen cyclically
|
|
|
What 5 conditions are Estrogens contraindicated?
|
1. Breast or Endometrial cancer
2. Undiagnosed genital bleeding 3. Liver disease 4. Thromboembolic disorders 5. Heavy smokers |
|
|
What is the natural and most important progestin?
|
Progesterone
|
|
|
Aside from important hormonal effects, what else does Progesterone serve as?
|
Estrogens, Adrogens, & Adrenocortical steroids
|
|
|
Where is Progesterone primarily produced?
When are plasma levels at a peak? |
Corpus luteum in the Ovary
3rd Trimester of pregnancy |
|
|
Why are oral preparations of Progesterone ineffective?
|
b/c it is completely metabolized after one passage through the liver where it forms PREGNANEDIOL, is conjugated with GLUCURONIC ACID, and then excreted in urine as PREGNANEDIOL GLUCURONIDE
|
|
|
What is used as an index of Progesterone secretion?
|
Urinary Pregnanediol
|
|
|
Half-life of Progesterone
|
5 minutes and small amounts are stored in body fat
|
|
|
What Synthetic Progestins are active when given orally?
|
1. Meg-estrol
2. Di-methi-sterone 3. Medroxy-progesterone **all have 'ME' |
|
|
3rd-generation Progestins that are used primarily in Oral Contraceptives are derivatives of what?
List 4 of them |
19-nortestosterone
Desog-estrel Nor-ethyno-drel Nor-ethin-drone Nor-gestimate |
|
|
What are the 4 effects of Progesterone?
|
1. stimulate Lipoprotein Lipase to favor fat deposition
2. INCREASES INSULIN AND INSULIN RESPONSE TO GLUCOSE; PROMOTES GLYCOGEN STORAGE 3. competes with Aldosterone for mineralocorticoid receptors in renal collecting tubules to decreases Na+ reabsorption which in turn increases Adrenal secretion of Aldosterone 4. increases body temperature, respiratory responses to CO2, development of breast secretory mechanisms, endometrial maturation |
|
|
What are the 4 clinical uses of Progestins?
|
1. Hormone Replacement therapy
2. Oral Contraception 3. Long-term ovarian suppression 4. treatment of Dysmenorrhea, Endometriosis, & bleeding disorders for which Estrogen is contraindicated |
|
|
Progesterone that is injected in large doses Intramuscularly and results in Anovulation and Amenorrhea
|
Medroxy-progesterone
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic use of Progestins? How does it work?
|
To test for Estrogen secretion
After treatment with Progesterone or Medro-progesterone in Amenorrheic women, withdrawal bleeding occurs only when there has been Endometrial stimulation by Estrogen |
|
|
What are the 2 types of preparations used for Oral Contraceptives?
|
1. Combinations of Estrogens and Progestins
2. continuous Progestin w/out concomitant estrogen |
|
|
What is the effectiveness when OC's are taken properly?
When do contraceptive failures occur? |
97-98%
when 1 or more doses are missed |
|
|
What are the 2 most commonly used estrogens as Oral Contraceptives?
|
Ethinyl Estradiol
M-estranol |
|
|
What is the advantage and disadvantage of Progestin-only contraceptives?
|
Advantage = avoid adverse effects due to Estrogen
Disadvantage = slightly less effective = 96-97% effective |
|
|
List 3 examples of Progestin-only contraceptives
|
1. Oral Nor-ethin-drone or Norg-estrel
2. SubQ Norg-estrel implants 3. Medroxy-progesterone for IM injection |
|
|
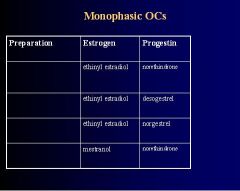
Explain the Monophasic Oral Contraceptives
|
1. fixed amount of Estrogen & Progestin
2. taken daily for 21 days 3. followed by 7-day "pill-free" period 4. 28 day packs with last 7 pills inert |
|
-
|

-
|
|
|
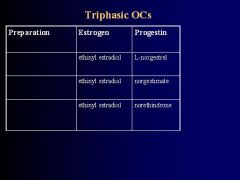
Describe the properties of Triphasic Oral Contraceptives
|
1. Three different pills each taken daily for 7 days
2. reduces steroid amounts 3. approximates Menstrual estrogen-progestin-ratio more closely |
|
-
|

-
|
|
|
What is the main action of Oral Contraceptives?
|
Selective inhibition of pituitary function to depress ovarian function and prevent ovulation
-minimal follicular development -Corporea lutea, larger follicles, stromal edema, & other features of ovulation are ABSENT -ovaries usually become smaller |
|
|
What are the secondary actions of Oral Contraceptives?
|
decrease likelihood of implantation & conception by:
-changing cervical mucus -changinb endometrium -altering tubal motility and secretion |
|
|
What are the uterine effects after prolonged OC use?
|
Cervical hypertrophy
Polyp formation |
|
|
What are the 3 pharmacologic effects of the Oral Contraceptives
|
1. Ovarian depression
-minimal follicular development -loss of Corpora lutea -large follicles -stromal edema -smaller ovaries 2. Uterine effects (after prolonged use) -cervical hypertrophy & polyp formation -cervical mucus thicker & less copius 3. Breast stimulation -breast enlargement with suppressed lactation |
|
|
Other Oral Contraceptive effects (after prolonged use)
1. CNS effects 2. Endocrine effects 3. Thromboembolism 4. Hepatic effects 5. Lipid metabolism 6. Carbohydrate metabolism 7. Cardiovascular effects 8. Skin effects |
1. Mood & behavior
2. may alter adrenal steroids, RAS, aldosterone, thyroxine, and androgens 3. changes in clotting factors & blood coagulation 4. may alter drug excretion & metabolism 5. increases serum Triglycerides, phospholipids, cholesterol 6. reduced GI sugar absorption, increase in basal insulin 7. increases in BP, HR, & cardiac output 8. increase in pigmentation & decreased sebum formation, acne, & terminal hair growth |
|
|
What are the mild adverse effects of Oral Contraceptives
List the Moderate adverse effects of OC's |
Nausea
Edema transient headaches & worsened migraine -Breakthrough bleeding -Weight gain, skin pigmentation, ureteral dilation, vaginal fungal infections, galactorrhea, & amenorrhea -Acne & Hirsutism may be aggravated by Androgenic activity of 19-nortestosterone derivatives (Desogestrel, Norethynodrel, Norethindrone, Norgestrel) |
|
|
Oral Contraceptives that may cause Acne and Hirsutism
|
19-nortestosterone derivatives
- Deso-gestrel - Nor-ethyn-odrel - Nor-ethin-drone - Nor-gestrel |
|
|
List the Severe adverse effects of Oral Contraceptives (6)
|
1. Thromboembolism = 3X higher risk related to Estrogen
2. Myocardial Infarction = especially in obese, Hypertensive, Diabetic, or Hyperlipidemic women 3. Increased risk for Strokes = especially over age 35 4. GI disorders = Cholestatic jaundice, gall bladder disease, hepatic adenomas 5. Depression 6. Cancer |
|
|
What markedly increases the risk of Myocardial Infarction in women taking Oral Contraceptives?
|
Smoking
|
|
|
What 3 things do OC's lower the RISKS of when used in REDUCED doses?
|
1. Ovarian cysts
2. Ovarian & Endometrial Cancer 3. Benign Breast disease |
|
|
What 3 things do OC's lower the INCIDENCE of when used in REDUCED doses?
|
1. Ectopic pregnancy
2. Iron deficiency 3. Rheumatoid arthritis |
|
|
What 5 things do OC's relieve or amerliorate when used in reduced doses?
|
1. Premenstrual symptoms
2. Dysmenorrhea 3. Endometriosis 4. Acne 5. Hirsutism |
|
|
What estrogen and progestin are used in the Vaginal Ring (NuvaRing)?
|
Ethinyl Estradiol
Etonogestrel |
|
|
How is the Vaginal Ring used?
|
inserted for 21 days & removed for one week
**mechanism of action, risks, & failure rate similar to OC's |
|
|
What are the 2 types of Intrauterine Devices currently used in the US?
|
1. Copper IUD
2. Hormone-containing IUD |
|
|
List the mechanisms of action of the Copper IUD
|
1. T-shaped device that is mostly spermicidal due to the sterile inflammatory rxn created to a foreign body in the uterus
2. Copper salts are released to alter the Endometrium & Cervical mucus 3. WBC's are attracted to kill spermatozoa by phagocytosis and sperm transport is significantly impaired |
|
|
What is the name of the Progesterone-releasing IUD?
What is the mechanism of action? |
1. Progest-asert
2. Progesterone is released at a rate of 65 mg/day (approved for 1 year) to diffuse into the endometrial cavity & cause decidualization & atrophy of the endometrium |
|
|
What is the name of the Levonorgestrel-releasing IUD?
How long is it active for? |
Mirena
5 years = releases 20 ug/day of Levonorgestrel |
|
|
When should the IUD's be placed in the Uterus?
When does protection begin? List the failure rates from best to worst |
within 7 days after onset of menstrual cycle
immediately after insertion Mirena (0.1-0.2%) > Copper (0.5-0.8%) > Progestasert (1.3-1.6%) |
|
|
Describe the Combination Method of Emergency Contraception
|
2 doses of 2 tablets 12 hours apart = Ovral = Ethinyl Estradiol + Norgestrel
** = high doses |
|
|
Describe the Progestin-only method in Emergency Contraception
|
2 doses of TEN pills at 12 hours apart = Ovrette
|
|
|
The maximum efficacy of Emergency Contraception is achieved if the first dose is taken within how long after intercourse?
|
72 hours and then repeated in 12 hours
|
|
|
What is the failure rate of Combination Emergency Contraception? Progestin-only?
|
Combination = 2-3% failure
Progestin-only = 1% failure |
|
|
Define "Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators" (SERMs)
|
compounds with tissue-selective estrogenic activities acting ONLY in tissues where their actions would be beneficial (bone, brain, liver during postmenopausal hormone replacement) BUT not in tissues where estrogenic actions would be harmful (breast or endometrium)
|
|
|
What are SERMs used for in Postmenopausal women?
|
palliative treatment (reduce symptoms/severity) of advanced Breast Cancer
|
|
|
2 SERM partial agonist inhibitors of Estradiol that are used for the treatment of breast cancer in postmenopausal women
|
Tamox-ifen & Torem-ifen
|
|
|
SERMs that inhibit Breast Cancer cells and tumor size, but stimulate Endometrial proliferation and thickening, and may increase the risk of Endometrial cancer
|
Tamox-ifen
Torem-ifene |
|
|
Aside from treating Breast CA, what are 2 other beneficial effects of Tamoxifen & Torem-ifene?
|
1. prevent loss of bone density
2. reduce risk of Atherosclerosis |
|
|
SERM that is a partial estrogen agonist-antagonist at some but not all target tissues
-has beneficial effects on bone but without affecting the Endometrium or breast |
Ralox-ifene
|
|
|
SERM used to prevent Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
|
Ralox-ifene
|
|
|
Partial estrogen agonist that acts by blocking Estrogen receptors in the Anterior Pituitary
|
Clomi-phene
|
|
|
What is the outcome of Clomiphene's action?
|
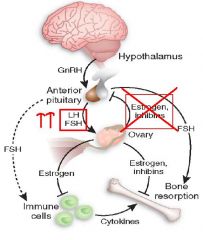
blocks Estrogen receptors ➡ b/c estrogen normally inhibits the pituitary it reduces the negative feedback by Estradiol on Pituitary➡ INCREASE FSH & LH secretion
**effects are mostly due to FSH secretion |
|
|
What is the clinical use of Clomiphene?
|
used for stimulating ovulation in Amenorrheic women who want to become pregnant
|
|
|
What does Ovarian stimulation result in when using Clomiphene?
|
Enlarged Ovaries
|
|
|
What is the most common adverse effect of Clomiphene?
What are occasional symptoms? (5) |
Hot Flashes
Eye symptoms, headaches, constipation, skin allergies, & reversible hair loss |

