![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is consciousness? |
“State of full awareness of the self and oneʼs |
|
|
Describe the two different anatomical regions of consciousness. |

|
|
|
What parts of the brain are responsible for arousal? |
• Reticular activating system |
|
|
Describe the relationship between arousal and awareness in differing states of consciousness. |

|
|
|
What is the vegetative state? |
• Complex neurological condition in which |
|
|
What is the minimal consciousness state? |
• Wakefulness accompanied by inconsistent |
|
|
What are the causes of vegetative state? |
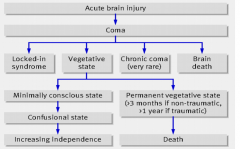
n.b. common stem of acute brain injury |
|
|
How is PVS diagnosed? |
• Detailed clinical history |
|
|
What are diagnostic criteria of PVS? |
• Cycles of eye opening and closing giving |
|
|
What electrophysiology can be used to diagnose PVS? |
• Somato-sensory evoked potentials; absent |
|
|
What anatomical correlates are seen in PVS? |
• Widespread subcortical |
|
|
Describe the cerebral metabolism in varying states of consciousness. |

|
|
|
On an fMRI, what can be used to measure neural activity? |
Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent (BOLD) signal - Indirect measure of neural activity
neural activity -> ↑ blood oxygen -> ↑ fMRI signal |
|
|
What factors affect recovery from PVS? |
• Time spent in Vegetative state |
|
|
What are the factors of chances of recovery? |
Time inversely proportional to chance of recovery
Age - younger patient better recovery Traumatic brain injury better than anoxic |

